Abstract
Objectives
Although evidence links increased adiposity status with bullying involvement, it is unknown whether this leads to behaviors such as weapon carrying. The purpose of this study was to: (1) analyze relationships between adiposity status and risks for weapon carrying among Canadian school children, and (2) whether this relationship was mediated by reports of bullying.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of the health experiences of 7,877 Canadian children. Relationships between adiposity status and weapon carrying were evaluated. Evidence of mediation by bullying involvement was assessed.
Results
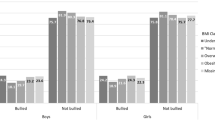
Overweight (OR: 1.45, 95% CI 1.04–2.02) and obese (OR: 2.19, 95% CI 1.43–3.35) males reported higher odds of weapon carrying relative to normal weight males. There was partial mediation of this relationship by physical and relational bullying, both as a perpetrator or a victim. No evidence of a relationship was identified for female students.
Conclusions
Overweight and obese male students appear to be more likely to carry weapons for defensive and offensive purposes, a behavior mediated partially by bullying involvement. However, other factors may play a role as mediators in these etiological relationships.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron RM, Kenny DA (1986) The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol 51:1173–1182
Bauer NS, Lozano P, Rivara FP (2007) The effectiveness of the Olweus Bullying Prevention Program in public middle schools: a controlled trial. J Adolesc Health 40:266–274
Bellizzi MC, Dietz WH (1999) Workshop on childhood obesity: summary of the discussion. Am J Clin Nutr 70:173S–175S
Boyce W (2008) Healthy settings for young people in Canada. Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, pp 93–95
Brener ND, Kann L, McManus T, Kinchen SA, Sundberg EC, Ross JG (2002) Reliability of the 1999 youth risk behaviour survey questionnaire. J Adolesc Health 31:336–342
Brener ND, McManus T, Galuska DA, Lowry R, Wechsler H (2003) Reliability and validity of self-reported height and weight among high school students. J Adolesc Health 32:281–287
Carr D, Friedman MA (2005) Is obesity stigmatizing? Body weight, perceived discrimination, and psychological well-being in the United States. J Health Soc Behav 46:244–259
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000) Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320:1240–1243
Currie C, Molcho M, Boyce W, Holstein B, Torsheim T, Richter M (2008) Researching health inequalities in adolescents: the development of the health behaviour in school-aged children (HBSC) family affluence scale. Soc Sci Med 66:1429–1436
Emond A, Ormel J, Veenstra R, Oldehinkel AJ (2007) Preschool behavioral and social-cognitive problems as predictors of (pre)adolescent disruptive behaviour. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 38:221–236
Fekkes M, Pijpers FIM, Verloove-Vanhorick S (2005) Bullying: who does what, when and where? Involvement of children, teachers and parents in bullying behaviour. Health Educ Res 20:81
Flegal KM, Troiano RP (2000) Changes in the distribution of body mass index of adults and children in the US population. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24:807–818
Forrest KY, Zychowski AK, Stuhldreher WL, Ryan WJ (2000) Weapon-carrying in school: prevalence and association with other violent behaviors. Am J Health Stud 16:133
Frisén A, Holmqvist K, Oscarsson D (2008) 13-year-olds’ perception of bullying: definitions, reasons for victimisation and experience of adults’ response. Educ Stud 34:105–117
Griffiths LJ, Wolke D, Page AS, Horwood JP, ALSPAC Study Team (2006) Obesity and bullying: different effects for boys and girls. Arch Dis Child 91:121–125
Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children: A World Health Organization Study (2007) Research Protocol for the 2006/07 Surveys. University of Edinburgh, Scotland
Himes JH, Hannan P, Wall M, Neumark-Sztainer D (2005) Factors associated with errors in self-reports of stature, weight, and body mass index in Minnesota adolescents. Ann Epidemiol 15:272–278
Janssen I, Craig WM, Boyce WF, Pickett W (2004) Associations between overweight and obesity with bullying behaviors in school-aged children. Pediatrics 113:1187–1194
Khoury-Kassabri M, Astor RA, Benbenishty R (2007) Weapon carrying in Israeli schools: the contribution of individual and school factors. Health Educ Behav 34:453–470
Kyriakides L, Kaloyirou C, Lindsay G (2006) An analysis of the Revised Olweus Bully/Victim Questionnaire using the Rasch measurement model. Br J Educ Psychol 76:781–801
Lowry R, Powell KE, Kann L, Collins JL, Kolbe LJ (1998) Weapon-carrying, physical fighting, and fight-related injury among U.S. adolescents. Am J Prev Med 14:122–129
Merrell KW, Gueldner BA, Ross SW, Isava DM (2008) How effective are school bullying intervention programs? A meta-analysis of intervention research. Sch Psychol Q 23:26–42
Ministry of Education. Ontario Education Act (1990) 7:310. http://www.e-laws.gov.on.ca/html/statutes/english/elaws_statutes_90e02_e.htm#BK548. Accessed 21 May 2009
Muula AS, Rudatsikira E, Siziya S (2008) Correlates of weapon carrying among high school students in the United States. Ann Gen Psychiatry 7:8
Nansel TR, Overpeck MD, Haynie DL, Ruan WJ, Scheidt PC (2003) Relationships between bullying and violence among US youth. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 157:348–353
Papas MA, Alberg AJ, Ewing R, Helzlsouer KJ, Gary TL, Klassen AC (2007) The built environment and obesity. Epidemiol Rev 29:129–143
Pearce MJ, Boergers J, Prinstein MJ (2002) Adolescent obesity, overt and relational peer victimization, and romantic relationships. Obes Res 10:386–393
Pickett W, Craig W, Harel Y, Cunningham J, Simpson K, Molcho M, Mazur J, Dostaler S, Overpeck MD, HBSC Currie CE Injuries Violence Writing Group (2005) Cross-national study of fighting and weapon carrying as determinants of adolescent injury. Pediatrics 116:e855–e863
Puhl RM, Brownell KD (2006) Confronting and coping with weight stigma: an investigation of overweight and obese adults. Obesity 14:1802–1815
Reilly JJ, Armstrong J, Dorosty AR, Emmett PM, Ness A, Rogers I, Steer C, Sherriff A, Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents, Children Study Team (2005) Early life risk factors for obesity in childhood: cohort study. BMJ 330:1357
Robinson S (2006) Victimization of obese adolescents. J Sch Nurs 22:201–206
Samdal O, Nutbeam D, Wold B, Kannas L (1998) Achieving health and educational goals through schools—a study of the importance of the school climate and the students’ satisfaction with school. Health Educ Res 13:383–397
Schmitz KH, Harnack L, Fulton JE, Jacobs DR Jr, Gao S, Lytle LA, Van Coevering P (2004) Reliability and validity of a brief questionnaire to assess television viewing and computer use by middle school children. J Sch Health 74:370–377
Sobel ME (1982) Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects in structural equation models. Sociol Methodol 13:290–312
Solberg ME, Olweus D (2003) Prevalence estimation of school bullying with the Olweus Bully/Victim Questionnaire. Aggress Behav 29:239–268
Statistics Canada (2007) Standard Geographical Classification (SGC), vol I. The Classification 12-571-XI
Strauss RS (2000) Childhood obesity and self-esteem. Pediatrics 105:e15
Tremblay MS, Katzmarzyk PT, Willms JD (2002) Temporal trends in overweight and obesity in Canada, 1981–1996. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26:538–543
Welk GJ, Corbin CB, Dale D (2000) Measurement issues in the assessment of physical activity in children. Res Q Exerc Sport 71:S59–S73
Ybarra ML, Diener-West M, Leaf PJ (2007) Examining the overlap in internet harassment and school bullying: implications for school intervention. J Adolesc Health 41:S42–S50
Acknowledgments
Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children is a World Health Organization/European Region collaborative study. International Coordinator of the 2005–2006 study: Candace Currie, University of Edinburgh, Scotland; Data Bank Manager: Oddrun Samdal, University of Bergen, Norway. The Canadian data bank manager is Matthew King, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. This publication reports data solely from Canada (2006 Principal Investigator: Dr. William Boyce). The study was supported by research agreements with the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (operating grant: 2004MOP-CHI-128223-C) and the Public Health Agency of Canada (contract: HT089-05205/001/SS) which funds the Canadian version of the Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children survey.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukaswadia, A., Craig, W., Janssen, I. et al. Bullying as a mediator of relationships between adiposity status and weapon carrying. Int J Public Health 57, 505–512 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-011-0329-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-011-0329-6