Abstract
Objective
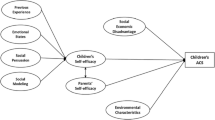
To examine school-level opportunity structures of the built environment and student characteristics associated with being overweight.
Methods
Multi-level logistic regression analysis were used to examine the school- and student-level characteristics associated with the odds of a student being overweight among grade 5–8 students attending 30 elementary schools in Ontario, Canada, as part of the Play-Ontario (PLAY-ON) study.
Results
Significant between school random variation in overweight was identified [σ 2μ0 = 0.187 (0.084), P < 0.001]; school-level differences accounted for 5.4% of the variability in the odds of a student being overweight. The more fast-food retailers there were surrounding a school, the more likely a student was to be overweight; students in grade 5 were at increased risk relative to students in grades 6–8. The more grocery stores there were surrounding a school, the more likely a student was to be overweight; students in grade 5 were at increased risk relative to students in grades 6–8.
Conclusions
Developing a better understanding of the school- and student-level characteristics associated with overweight among youth is critical for informing intervention programs and policies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Dietetic Association (2006) Position of the American Dietetic Association: individual-, family-, school-, and community-based interventions for pediatric overweight. J Am Diet Assoc 106:925–945
Anderson PM, Butcher KE (2006) Childhood obesity: trends and potential causes. Future Child 16:19–45
Arbour-Nicitopoulous KP, Faulkner GE, Leatherdale ST (2010) Learning from missing data: interpreting missing Body Mass Index (BMI) values in young children. In: 3rd International congress on physical activity and public health, Toronto, ON, Canada, 06 May 2010
Borradaile KE, Sherman S, Vander Veur SS, McCoy T, Sandoval B, Nachmani J et al (2009) Snacking in children: the role of urban corner stores. Pediatrics 124:1293–1298
Cecil-Karb R, Grogan-Kaylor A (2009) Childhood body mass index in community context: neighborhood safety, television viewing, and growth trajectories of BMI. Health Soc Work 34:169–177
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2006) BMI—Body Mass Index: about BMI for children and teens. BMI growth charts for male and female youth. www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dnpa/BMI/childrens_bmi/about_childrens_bmi.htm
Colditz G, DeJong W, Hunter D, Trichopoulos D, Willett W (1996) Harvard report on cancer prevention. Volume 1. Causes of human cancer. Cancer Causes Control 7:S3–S58
Davis B, Carpenter C (2009) Proximity of fast-food restaurants to schools and adolescent obesity. Am J Pub Health 99:505–510
ESRI (2002) ArcView GIS 3.3. Redlands, CA
Evenson KR, Scott MM, Cohen DA, Voorhees CC (2007) Girls’ perception of neighborhood factors on physical activity, sedentary behavior, and BMI. Obesity 15:430–445
Ewing R, Borwnson RC, Berrigan D (2006) Relationship between urban sprawl and weight of United States youth. Am J Prev Med 31:464–474
Galvez MP, Hong L, Choi E, Liao L, Godbold J, Brenner B (2009) Childhood obesity and neighborhood food-store availability in an inner-city community. Acad Pediatr 9:339–343
Grafova IB (2008) Overweight children: assessing the contribution of the built environment. Prev Med 47:304–308
Herman KM, Craig CL, Gauvin L, Katzmarzyk PT (2009) Tracking of obesity and physical activity from childhood to adulthood: the Physical Activity Longitudinal Study. Int J Pediatr Obes 4:281–288
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Boyce WF, Vereecken C, Mulvihill C, Roberts C et al (2005) Comparison of overweight and obesity prevalence in school-aged youth from 34 countries and their relationships with physical activity and dietary patterns. Obes Rev 6:123–132
Kurc A, Leatherdale ST (2009) The effect of social support and school- and community-based sports on youth physical activity. Can J Pub Health 100:60–64
Leatherdale ST, Papadakis S (2009) A multi-level examination of the association between older social models in the school environment and overweight and obesity among younger students. J Youth Adolesc Dec 16 [Epub ahead of print]
Leatherdale ST, Wong SL (2008) Modifiable characteristics associated with sedentary behaviours among youth. Int J Pediatr Obes 3:93–101
Leatherdale ST, Manske S, Wong S, Cameron R (2009) Integrating research, policy and practice in school-based physical activity prevention programming: the School Health Action, Planning and Evaluation System (SHAPES) Physical Activity Module. Health Promot Pract 10:254–261
Leatherdale ST, Manske S, Faulkner G, Arbour-Nicitopoulos K, Bredin C (2010) A multi-level examination of school programs, policies and resources associated with physical activity among elementary school youth in the PLAY-ON study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 7:6. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-7-6
McMurray RG, Ring KB, Treuth MS, Welk GJ, Pate RR, Schmitz KH et al (2004) Comparison of two approaches to structured physical activity surveys for adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:2135–2143
Murnaghan DA, Sihvonen M, Leatherdale ST, Kekki P (2007) The relationship between school-based smoking policies and prevention programs on smoking behavior among grade 12 students in Prince Edward Island: a multilevel analysis. Prev Med 44:317–322
O’Malley PM, Johnston LD, Delva J, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2007) Variation in obesity among American secondary school students by school and school characteristics. Am J Prev Med 33:S187–S194
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM (2006) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295:1549–1555
Pouliou T, Elliott SJ (2010) Individual and socio-environmental determinants of overweight and obesity in urban Canada. Health Place 16:389–398
Powell LM, Auld MC, Chaloupka FJ, O’Malley PM, Johnston LD (2007) Associations between access to food stores and adolescent body mass index. Am J Prev Med 33:S301–S307
Rasbash J, Browne W, Healy M, Cameron B, Chalton C (2005) MLwiN version 2.02. Institute of Education, Multilevel Models Project
Seliske LM, Pickett W, Boyce WF, Janssen I (2009) Association between the food retail environment surrounding schools and overweight in Canadian youth. Public Health Nutr 12:1384–1391
Shields M (2006) Overweight and obesity among children and youth. Health Rep 17:27–42
Singh AS, Paw MJMCA, Brug J, van Mechelen W (2007) Short-term effects of school-based weight gain prevention among adolescents. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 161:565–571
Singh GK, Siahpush M, Kogan MD (2010) Rising social inequalities in US childhood obesity, 2003–2007. Ann Epidemiol 20:40–52
Storey ML, Forshee RA, Weaver AR, Sansalone WR (2003) Demographic and lifestyle factors associated with body mass index among children and adolescents. Int J Food Sci Nutr 54:491–503
Story M, Nanney MS, Schwartz MB (2009) Schools and obesity prevention: creating school environments and policies to promote healthy eating and physical activity. Millbank Q 87:71–100
Tiggemann M (2006) Nonreporting of body mass index: a research note on the interpretation of missing data. Int J Eat Disord 39:346–349
Trost SG, Kerr LM, Ward DS, Pate RR (2001) Physical activity and determinants of physical activity in obese and non-obese children. Int J Obes 25:822–829
Veugelers P, Sithole F, Zhang S, Muhajarine N (2008) Neighbourhood characteristics in relation to diet, physical activity and overweight of Canadian children. Int J Ped Obes 3:152–159
Veuglers PJ, Fitzgerald AL (2005) Effectiveness of school programs in preventing childhood obesity: a multilevel comparison. Am J Pub Health 95:432–435
Wong SL, Leatherdale ST, Manske S (2006) Reliability and validity of a school-based physical activity questionnaire. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:1593–1600
Acknowledgments
The project was conducted by the Population Health Research Group at the University of Waterloo under the management of Chad Bredin. Funding for the student-level data collection was provided by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Ontario (grant awarded to S. Leatherdale). Funding for the data linkage to the built environment data was provided by Cancer Care Ontario and the Canadian Heart Health Surveys Longitudinal Follow-up Study Ancillary and Pilot Project (Awarded to E. Hobin and S. Leatherdale). Dr. Leatherdale is a Cancer Care Ontario Research Chair in Population Studies. The Canadian Cancer Society provided funding to develop SHAPES, the system used to collect the PLAY-ON data. Erin Hobin is funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada and the CIHR/Training Grant in Population Intervention for Chronic Disease Prevention: A Pan-Canadian Program (Grant #: 53893) as well as a CIHR Doctoral Award in Public Health.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leatherdale, S.T., Pouliou, T., Church, D. et al. The association between overweight and opportunity structures in the built environment: a multi-level analysis among elementary school youth in the PLAY-ON study. Int J Public Health 56, 237–246 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-010-0206-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00038-010-0206-8