Abstract
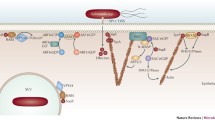
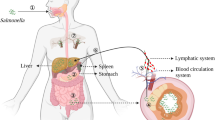
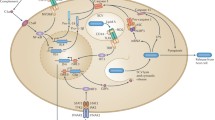
Acute gastroenteritis caused by Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium is a significant public health problem. This pathogen has very sophisticated molecular machinery encoded by the two pathogenicity islands, namely Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 and 2 (SPI-1 and SPI-2). Remarkably, both SPI-1 and SPI-2 are very tightly regulated in terms of timing of expression and spatial localization of the encoded effectors during the infection process within the host cell. This regulation is governed at several levels, including transcription and translation, and by post-translational modifications. In the context of a finely tuned regulatory system, we will highlight how these effector proteins co-opt host signaling pathways that control the ability of the organism to infect and survive within the host, as well as elicit host pro-inflammatory responses.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alto NM, Shao F, Lazar CS, Brost RL, Chua G, Mattoo S, McMahon SA, Ghosh P, Hughes TR, Boone C, Dixon JE (2006) Identification of a bacterial type III effector family with G protein mimicry functions. Cell 124(1):133–145
Arnold R, Brandmaier S, Kleine F, Tischler P, Heinz E, Behrens S, Niinikoski A, Mewes HW, Horn M, Rattei T (2009) Sequence-based prediction of type III secreted proteins. PLoS Pathog 5(4):e1000376 Epub 2009 Apr 24. Erratum in: PLoS Pathog. 2009 Apr; 5(4)
Bajaj V, Lucas RL, Hwang C, Lee CA (1996) Co-ordinate regulation of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes by environmental and regulatory factors is mediated by control of hilA expression. Mol Microbiol 22(4):703–714
Bakowski MA, Cirulis JT, Brown NF, Finlay BB, Brumell JH (2007) SopD acts cooperatively with SopB during Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium invasion. Cell Microbiol 9(12):2839–2855 Epub 2007 Aug 13
Bakowski MA, Braun V, Brumell JH (2008) Salmonella-containing vacuoles: directing traffic and nesting to grow. Traffic 9(12):2022–2031 Epub 2008 Oct 8. Review
Bernal-Bayard J, Ramos-Morales F (2009) Salmonella type III secretion effector SlrP is an E3 ubiquitin ligase for mammalian thioredoxin. J Biol Chem 284(40):27587–27595 Epub 2009 Aug 18
Boucrot E, Henry T, Borg JP, Gorvel JP, Méresse S (2005) The intracellular fate of Salmonella depends on the recruitment of kinesin. Science 308(5725):1174–1178
Brawn LC, Hayward RD, Koronakis V (2007) Salmonella SPI1 effector SipA persists after entry and cooperates with a SPI2 effector to regulate phagosome maturation and intracellular replication. Cell Host Microbe 1(1):63–75
Browne SH, Lesnick ML, Guiney DG (2002) Genetic requirements for Salmonella-induced cytopathology in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect Immun 70(12):7126–7135
Brumell JH, Goosney DL, Finlay BB (2002) SifA, a type III secreted effector of Salmonella typhimurium, directs Salmonella-induced filament (Sif) formation along microtubules. Traffic 3(6):407–415
Bujny MV, Ewels PA, Humphrey S, Attar N, Jepson MA, Cullen PJ (2008) Sorting nexin-1 defines an early phase of Salmonella-containing vacuole-remodeling during Salmonella infection. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 12):2027–2036 Epub 2008 May 27
Bustamante VH, Martínez LC, Santana FJ, Knodler LA, Steele-Mortimer O, Puente JL (2008) HilD-mediated transcriptional cross-talk between SPI-1 and SPI-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(38):14591–14596
Chang J, Chen J, Zhou D (2005) Delineation and characterization of the actin nucleation and effector translocation activities of Salmonella SipC. Mol Microbiol 55(5):1379–1389
Chubiz JE, Golubeva YA, Lin D, Miller LD, Slauch JM (2010) FliZ regulates expression of the Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 invasion locus by controlling HilD protein activity in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium. J Bacteriol 192(23):6261–6270 Epub 2010 Oct 1
Collazo CM, Galán JE (1997) The invasion-associated type III system of Salmonella typhimurium directs the translocation of Sip proteins into the host cell. Mol Microbiol 24(4):747–756
Collier-Hyams LS, Zeng H, Sun J, Tomlinson AD, Bao ZQ, Chen H, Madara JL, Orth K, Neish AS (2002) Cutting edge: Salmonella AvrA effector inhibits the key proinflammatory, anti-apoptotic NF-kappa B pathway. J Immunol 169(6):2846–2850
Couillault HT, Rockenfeller P, Boucrot E, Dumont A, Schroeder N, Hermant A, Knoedler LA, Steele-Mortimer O, Borg JP, Gorvel JP, Meresse S (2006) The Salmonella effector protein PipB2 is a linker for kinesin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(36):13497–13502 Epub 2006 Aug 25
Deiwick J, Nikolaus Thomas, Erdogan Sezgin, Hensel Michael (1999) Environmental regulation of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 gene expression. Mol Microbiol 31:1759–1773
Deiwick J, Salcedo SP, Boucrot E, Gilliland SM, Henry T, Petermann N, Waterman SR, Gorvel JP, Holden DW, Méresse S (2006) The translocated Salmonella effector proteins SseF and SseG interact and are required to establish an intracellular replication niche. Infect Immun 74(12):6965–6972 Epub 2006 Oct 2
Drecktrah D, Knodler LA, Galbraith K, Steele-Mortimer O (2005) The Salmonella SPI1 effector SopB stimulates nitric oxide production long after invasion. Cell Microbiol 7(1):105–113
Drecktrah D, Levine-Wilkinson S, Dam T, Winfree S, Knodler LA, Schroer TA, Steele-Mortimer O (2008) Dynamic behavior of Salmonella-induced membrane tubules in epithelial cells. Traffic. 9(12):2117–2129 Epub 2008 Oct 18
Ellermeier CD, Ellermeier JR, Slauch JM (2005) HilD, HilC and RtsA constitute a feed forward loop that controls expression of the SPI1 type three secretion system regulator hilA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Mol Microbiol 57(3):691–705
Everest P, Roberts M, Dougan G (1998) Susceptibility to Salmonella typhimurium infection and effectiveness of vaccination in mice deficient in the tumor necrosis factor α p55 receptor. Infect Immun 66:3355–3364
Fass E, Groisman E (2009) Control of Salmonella pathogenicity island-2 gene expression. Curr opin Microbiol 12:199–204
Forest CG, Ferraro E, Sabbagh SC, Daigle F (2010) Intracellular survival of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi in human macrophages is SPI-2 independent. Microbiology 156(Pt 12):3689–3698
Fu Y, Galán JE (1999) A salmonella protein antagonizes Rac-1 and Cdc42 to mediate host-cell recovery after bacterial invasion. Nature 401(6750):293–297
Galan JE (1996) Molecular genetic bases of Salmonella entry into host cells. Mol Microbiol 20:263–271
Galán JE (2011) Salmonella interactions with host cells: type III secretion at work. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:53–86 Review
Galan JE, Zhou D (2000) Striking a balance: modulation of the actin cytoskeleton by Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(16):8754–8761
Galkin VE, Orlova A, VanLoock MS, Zhou D, Galán JE, Egelman EH (2002) The bacterial protein SipA polymerizes G-actin and mimics muscle nebulin. Nat Struct Biol 9(7):518–521
Garcia-del Portillo F, Zwick MB, Leung KY, Finlay BB (1993) Salmonella induces the formation of filamentous structures containing lysosomal membrane glycoproteins in epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(22):10544–10548
Giacomodonato MN, Uzzau S, Bacciu D, Caccuri R, Sarnacki SH, Rubino S, Cerquetti MC (2007) SipA, SopA, SopB, SopD and SopE2 effector proteins of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium are synthesized at late stages of infection in mice. Microbiology 153(Pt 4):1221–1228
Graham SM, Molyneux EM, Walsh AL, Cheesbrough JS, Molyneux ME, Hart CA (2000) Nontyphoidal Salmonella infections of children in tropical Africa. Pediatr Infect Dis J 19:1189–1196
Haraga A, Miller SI (2003) A Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium translocated leucine-rich repeat effector protein inhibits NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression. Infect Immun 71(7):4052–4058
Hardt WD, Chen LM, Schuebel KE, Bustelo XR, Galán JE (1998) S. typhimurium encodes an activator of Rho GTPases that induces membrane ruffling and nuclear responses in host cells. Cell 93(5):815–826
Henry T, Couillault C, Rockenfeller P, Boucrot E, Dumont A, Schroeder N, Hermant A, Knodler LA, Lecine P, Steele-Mortimer O, Borg JP, Gorvel JP, Méresse S (2006) The Salmonella effector protein PipB2 is a linker for kinesin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(36):13497–13502 Epub 2006 Aug 25
Hensel M, Shea JE, Gleeson C, Jones MD, Dalton E, Holden DW (1995) Simultaneous identification of bacterial virulence genes by negative selection. Science 269(5222):400–403
Hess J, Ladel C, Miko D, Kaufmann SH (1996) Salmonella typhimurium aroA-infection in gene-targeted immunodeficient mice: major role of CD4+ TCR-αβ cells and IFN-gamma in bacterial clearance independent of intracellular location. J Immunol 156:3321–3326
Hobbie S, Chen LM, Davis RJ, Galán JE (1997) Involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in the nuclear responses and cytokine production induced by Salmonella typhimurium in cultured intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol 159(11):5550–5559
Jones MA, Wood MW, Mullan PB, Watson PR, Wallis TS, Galyov EE (1998) Secreted effector proteins of Salmonella dublin act in concert to induce enteritis. Infect Immun 66(12):5799–5804
Kage H, Takaya A, Ohya M, Yamamoto T (2008) Coordinated regulation of expression of Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 and flagellar type III secretion systems by ATP-dependent ClpXP protease. J Bacteriol 190(7):2470–2478
Kerrinnes T, Zelas ZB, Streckel W, Faber F, Tietze E, Tschäpe H, Yaron S (2009) CsrA and CsrB are required for the post-transcriptional control of the virulence-associated effector protein AvrA of Salmonella enterica. Int J Med Microbiol 299(5):333–341 Epub 2008 Nov 29
Knodler LA, Steele-Mortimer O (2005) The Salmonella effector PipB2 affects late endosome/lysosome distribution to mediate Sif extension. Mol Biol Cell 16(9):4108–4123
Knodler LA, Winfree S, Drecktrah D, Ireland R, Steele-Mortimer O (2009) Ubiquitination of the bacterial inositol phosphatase, SopB, regulates its biological activity at the plasma membrane. Cell Microbiol 11(11):1652–1670 Epub 2009 Jul 13
Kubori T, Galán JE (2003) Temporal regulation of salmonella virulence effector function by proteasome-dependent protein degradation. Cell 115(3):333–342
Kuhle V, Abrahams GL, Hensel M (2006) Intracellular Salmonella enterica redirect exocytic transport processes in a Salmonella pathogenicity island 2-dependent manner. Traffic 7(6):716–730 Epub 2006 Apr 21
Lawley TD, Chan K, Thompson LJ, Kim CC, Govoni GR, Monack DM (2006) Genome-wide screen for Salmonella genes required for long-term systemic infection of the mouse. PLoS Pathog 2(2):e11 Epub 2006 Feb 24
Lee CA, Silva M, Siber AM, Kelly AJ, Galyov E, McCormick BA (2000) A secreted Salmonella protein induces a proinflammatory response in epithelial cells, which promotes neutrophil migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(22):12283–12288
Lesnick ML, Reiner NE, Fierer J, Guiney DG (2001) The Salmonella spvB virulence gene encodes an enzyme that ADP-ribosylates actin and destabilizes the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. Mol Microbiol 39(6):1464–1470
Liao AP, Petrof EO, Kuppireddi S, Zhao Y, Xia Y, Claud EC, Sun J (2008) Salmonella type III effector AvrA stabilizes cell tight junctions to inhibit inflammation in intestinal epithelial cells. PLoS One 3(6):e2369
Lin D, Rao CV, Slauch JM (2008) The Salmonella SPI1 type three secretion system responds to periplasmic disulfide bond status via the flagellar apparatus and the RcsCDB system. J Bacteriol 190(1):87–97 Epub 2007 Oct 19
Liu X, Lu R, Wu S, Sun J (2010) Salmonella regulation of intestinal stem cells through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. FEBS Lett 584(5):911–916 Epub 2010 Jan 19
López-Garrido J, Casadesús J (2010) Regulation of Salmonella enterica pathogenicity island 1 by DNA adenine methylation. Genetics 184(3):637–649 Epub 2009 Dec 14
Mariathasan S, Newton K, Monack DM, Vucic D, French DM, Lee WP, Roose-Girma M, Erickson S, Dixit VM (2004) Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors ASC and Ipaf. Nature 430(6996):213–218 Epub 2004 Jun 9
Mastroeni P, Harrison JA, Robinson JH, Clare S, Khan S, Maskell DJ, Dougan G, Hormaeche CE (1998) Interleukin-12 is required for control of the growth of attenuated aromatic-compound-dependent salmonellae in BALB/c mice: role of gamma interferon and macrophage activation. Infect Immun 66:4767–4776
McCormick BA, Colgan SP, Delp-Archer C, Miller SI, Madara JL (1993) Salmonella typhimurium attachment to human intestinal epithelial monolayers: transcellular signalling to subepithelial neutrophils. J Cell Biol 123(4):895–907
McGhie EJ, Hayward RD, Koronakis V (2001) Cooperation between actin-binding proteins of invasive Salmonella: SipA potentiates SipC nucleation and bundling of actin. EMBO J 20(9):2131–2139
Miao EA, Brittnacher M, Haraga A, Jeng RL, Welch MD, Miller SI (2003) Salmonella effectors translocated across the vacuolar membrane interact with the actin cytoskeleton. Mol Microbiol 48(2):401–415
Mota LJ, Ramsden AE, Liu M, Castle JD, Holden DW (2009) SCAMP3 is a component of the Salmonella-induced tubular network and reveals an interaction between bacterial effectors and post-Golgi trafficking. Cell Microbiol 11(8):1236–1253
Mrsny RJ, Gewirtz AT, Siccardi D, Savidge T, Hurley BP, Madara JL, McCormick BA (2004) Identification of hepoxilin A3 in inflammatory events: a required role in neutrophil migration across intestinal epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(19):7421–7426 Epub 2004 May 3
Myeni SK, Zhou D (2010) The C terminus of SipC binds and bundles F-actin to promote Salmonella invasion. J Biol Chem 285(18):13357–13363 Epub 2010 Mar 8
Nikolaus T, Deiwick J, Rappl C, Freeman J, Schröder W, Miller S, Hensel M (2001) SseBCD Proteins Are Secreted by the Type III Secretion System of Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 2 and Function as a Translocon. J Bacteriol 183(20):6036–6045
Norris FA, Wilson MP, Wallis TS, Galyov EE, Majerus PW (1998) SopB, a protein required for virulence of Salmonella dublin, is an inositol phosphate phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(24):140579
O’Brien AD, Rosenstreich DL, Scher I, Campbell GH, MacDermott RP, Formal SB (1980) Genetic control of susceptibility to Salmonella typhimurium in mice: role of the LPS gene. J Immunol 124:20–24
Ohlson MB, Huang Z, Alto NM, Blanc MP, Dixon JE, Chai J, Miller SI (2008) Structure and function of Salmonella SifA indicate that its interactions with SKIP, SseJ, and RhoA family GTPases induce endosomal tubulation. Cell Host Microbe 4(5):434–446
Patel JC, Galán JE (2006) Differential activation and function of Rho GTPases during Salmonella-host cell interactions. J Cell Biol 175(3):453–463 Epub 2006 Oct 30
Prost LR, Sanowar S, Miller SI (2007) Salmonella sensing of anti-microbial mechanisms to promote survival within macrophages. Immunol Rev 219:55–65
Ribet D, Hamon M, Gouin E, Nahori MA, Impens F, Neyret-Kahn H, Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J, Dejean A, Cossart P (2010) Listeria monocytogenes impairs SUMOylation for efficient infection. Nature 464(7292):1192–1195
Rogers LD, Kristensen AR, Boyle EC, Robinson DP, Ly RT, Finlay BB, Foster LJ (2008) Identification of cognate host targets and specific ubiquitylation sites on the Salmonella SPI-1 effector SopB/SigD. J Proteomics 71(1):97–108 Epub 2008 Feb 5
Salcedo SP, Holden DW (2003) SseG, a virulence protein that targets Salmonella to the Golgi network. EMBO J 22(19):5003–5014
Samudrala R, Heffron F, McDermott JE (2009) Accurate prediction of secreted substrates and identification of a conserved putative secretion signal for type III secretion systems. PLoS Pathog 5(4):e1000375 Epub 2009 Apr 24
Sherry AE, Inglis NF, Stevenson A, Fraser-Pitt D, Everest P, Smith DG, Roberts M (2010) Characterisation of proteins extracted from the surface of Salmonella Typhimurium grown under SPI-2-inducing conditions by LC-ESI/MS/MS sequencing. Proteomics 11(3):361–370
Srikanth CV, Wall DM, Maldonado-Contreras A, Shi HN, Zhou D, Demma Z, Mumy KL, McCormick BA (2010) Salmonella pathogenesis and processing of secreted effectors by caspase-3. Science 330(6002):390–393
Stebbins CE, Galan JE (2003) Priming virulence factors for delivery into the host. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:738–744
Stein MA, Leung KY, Zwick M, Garcia-del Portillo F, Finlay BB (1996) Identification of a Salmonella virulence gene required for formation of filamentous structures containing lysosomal membrane glycoproteins within epithelial cells. Mol Microbiol 20(1):151–164
Stender S, Friebel A, Linder S, Rohde M, Mirold S, Hardt WD (2000) Identification of SopE2 from Salmonella typhimurium, a conserved guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Cdc42 of the host cell. Mol Microbiol 36(6):1206–1221
Van Engelenburg SB, Palmer AE (2008) Quantification of real-time Salmonella effector type III secretion kinetics reveals differential secretion rates for SopE2 and SptP. Chem Biol 15(6):619–628
Wall DM, Nadeau WJ, Pazos MA, Shi HN, Galyov EE, McCormick BA (2007) Identification of the Salmonella enterica serotype typhimurium SipA domain responsible for inducing neutrophil recruitment across the intestinal epithelium. Cell Microbiol 9(9):2299–2313 Epub 2007 May 18
Worley MJ, Ching KH, Heffron F (2000) Salmonella SsrB activates a global regulon of horizontally acquired genes. Mol Microbiol 36(3):749–761
Wu S, Ye Z, Liu X, Zhao Y, Xia Y, Steiner A, Petrof EO, Claud EC, Sun J (2010) Salmonella typhimurium infection increases p53 acetylation in intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298(5):G784–G794 Epub 2010 Mar 11
Ye Z, Petrof EO, Boone D, Claud EC, Sun J (2007) Salmonella effector AvrA regulation of colonic epithelial cell inflammation by deubiquitination. Am J Pathol 171(3):882–892 Epub 2007 Aug 9. Erratum in: Am J Pathol. 2009 May; 174(5):1981–1982
Zhou D, Mooseker MS, Galán JE (1999) Role of the S. typhimurium actin-binding protein SipA in bacterial internalization. Science 283(5410):2092–2095
Zhou D, Mooseker MS, Galán JE (1999) An invasion-associated Salmonella protein modulates the actin-bundling activity of plastin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(18):10176–10181
Zhou D, Chen LM, Hernandez L, Shears SB, Galán JE (2001) A Salmonella inositol polyphosphatase acts in conjunction with other bacterial effectors to promote host cell actin cytoskeleton rearrangements and bacterial internalization. Mol Microbiol 39(2):248–259 Erratum in: Mol Microbiol Jun 40(6):1461
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK56754 and DK33506), and the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America to B.A.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srikanth, C.V., Mercado-Lubo, R., Hallstrom, K. et al. Salmonella effector proteins and host-cell responses. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 3687–3697 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0841-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0841-0