Abstract.
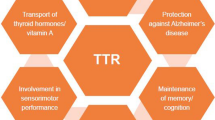
Transthyretin (formerly called prealbumin) plays important physiological roles as a transporter of thyroxine and retinol-binding protein. X-ray structural studies have provided information on the active conformation of the protein and the site of binding of both ligands. Transthyretin is also one of the precursor proteins commonly found in amyloid deposits. Both wild-type and single-amino-acid-substituted variants have been identified in amyloid deposits, the variants being more amyloidogenic. Sequencing of the gene and the resulting production of a transgenic mouse model have resulted in progress toward solving the mechanism of amyloid formation and detecting the variant gene in individuals at risk.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 23 January 2001; received after revision 4 April 2001; accepted 30 April 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamilton, J., Benson, M. Transthyretin: a review from a structural perspective. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 1491–1521 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000791
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00000791