Abstract
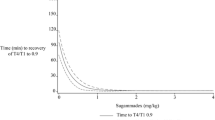
Background and Objective: Sugammadex facilitates rapid reversal of rocuronium- and vecuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade. This study aimed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of high doses of sugammadex (up to 96 mg/kg) in healthy subjects.
Methods: In this randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled, single-centre study, 13 healthy adults were scheduled to receive three single intravenous doses of sugammadex in ascending order (32, 64 and 96 mg/kg) and placebo (interspersed between sugammadex doses), each separated by a 1-week washout period. Subjects were randomized to one of four treatment sequences, receiving doses as constant rate infusions over 5 minutes. Safety was assessed by adverse events, 12-lead ECGs, vital signs, and blood and urine laboratory parameters; pharmacokinetics were evaluated from blood and urine sugammadex concentrations.
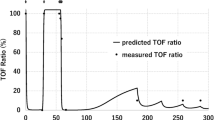
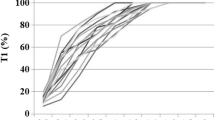
Results: Sugammadex was well tolerated in 12 of the 13 subjects, with adverse events being generally mild, of limited duration and more frequent at higher doses. The most common adverse event was dysgeusia; there were no serious adverse events. One subject was withdrawn from the study after experiencing several adverse events following first exposure to sugammadex, related to a probable hypersensitivity reaction to sugammadex. Pharmacokinetics were dose linear over the dose range studied (32–96 mg/kg), and 90–93% of the sugammadex dose was excreted unchanged in urine within 48 hours.
Conclusion: High doses of sugammadex (up to 96 mg/kg) were well tolerated in 12 of the 13 subjects. One male subject experienced several adverse events associated with a probable hypersensitivity reaction to sugammadex. Pharmacokinetics were dose linear over the range 32–96 mg/kg, with elimination predominantly via the renal route.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy GS. Residual neuromuscular blockade: incidence, assessment, and relevance in the postoperative period. Minerva Anestesiol 2006 Mar; 72(3): 97–109
EMA. European Public Assessment Report (EPAR). Bridion. EPAR summary for the public, updated June 2010 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000885/WC500052310.pdf [Accessed 2010 Jul 19]
Bom A, Bradley M, Cameron K, et al. A novel concept of reversing neuromuscular block: chemical encapsulation of rocuronium bromide by a cyclodextrin-based synthetic host. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2002 Jan; 41(2): 266–70
Epemolu O, Bom A, Hope F, et al. Reversal of neuromuscular blockade and simultaneous increase in plasma rocuronium concentration after the intravenous infusion of the novel reversal agent Org 25969. Anesthesiology 2003 Sept; 99(3): 632–7
deBoer HD, vanEgmond J, van de Pol F, et al. Reversal of profound rocuronium neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex in anesthetized rhesus monkeys. Anesthesiology 2006 Apr; 104(4): 718–23
Gijsenbergh F, Ramael S, Houwing N, et al. First human exposure of Org 25969, a novel agent to reverse the action of rocuronium bromide. Anesthesiology 2005 Oct; 103(4): 695–703
Shields M, Giovanelli M, Mirakhur RK, et al. Org 25969 (sugammadex), a selective relaxant binding agent for antagonism of prolonged rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block. Br J Anaesth 2006 Jan; 96(1): 36–43
Sorgenfrei IF, Norrild K, Larsen PB, et al. Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block by the selective relaxant binding agent sugammadex: a dose-finding and safety study. Anesthesiology 2006 Apr; 104(4): 667–74
Suy K, Morias K, Cammu G, et al. Sugammadex, a selective relaxant binding agent, offers effective reversal of moderate rocuronium- or vecuronium-induced neuromuscular block. Anesthesiology 2007 Feb; 106(6): 283–8
deBoer HD, Driessen JJ, Marcus MA, et al. Reversal of rocuronium-induced (1.2mg/kg) profound neuromuscular block by sugammadex: a multicenter, dose-finding and safety study. Anesthesiology 2007 Aug; 107(2): 239–44
Groudine SB, Soto R, Lien C, et al. A randomized, dose-finding, phase II study of the selective relaxant binding drug, sugammadex, capable of safely reversing profound rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block. Anesth Analg 2007 Mar; 104(3): 555–62
Sacan O, White PF, Tufanogullari B, et al. Sugammadex reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade: a comparison with neostigmine-glycopyrrolate and edrophonium-atropine. Anesth Analg 2007 Mar; 104(3): 569–74
Sparr HJ, Vermeyen KM, Beaufort AM, et al. Early reversal of profound rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block by sugammadex in a randomized multicenter study: efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics. Anesthesiology 2007 May; 106(5): 935–43
Vanacker BF, Vermeyen KM, Struys MMRF, et al. Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block with the novel drug sugammadex is equally effective under maintenance anesthesia with propofol or sevoflurane. Anesth Analg 2007 Mar; 104(3): 563–8
Cammu G, DeKam PJ, Demeyer I, et al. Safety and tolerability of single intravenous doses of sugammadex administered simultaneously with rocuronium or vecuronium in healthy volunteers. Br J Anaesth 2008 Mar; 100(3): 373–9
Molina AL, deBoer HD, Klimek M, et al. Reversal of rocuronium-induced (1.2mg/kg) profound neuromuscular block by accidental high dose of sugammadex (40mg/kg). Br J Anaesth 2007 May; 98(5): 624–7
deKam PJ, vanKuijk J, Prohn M, et al. Effects of sugammadex doses up to 32 mg/kg alone or in combination with rocuronium or vecuronium on QTc prolongation: a thorough QTc study. Clin Drug Investig 2010; 30(9): 599–611
deKam P-J, vanKuijk J, Smeets J, et al. Single IV sugammadex doses up to 32 mg/kg are not associated with QT/QTc prolongation (abstract). Anesthesiology 2007; 107: A1580
Organon USA. FDA Anesthetic and Life Support Advisory Committee Meeting: briefing document (background package) for sugammadex sodium injection [online]. Available from URL: http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/08/slides/2008-4346s1-01-Schering-Plough-corebackup.pdf [Accessed 2009 June 30]
Stella VJ, He Q. Cyclodextrins. Toxicol Pathol 2008; 36(1): 30–42
Peeters P, Passier P, Smeets J, et al. Sugammadex is cleared rapidly and predominantly in an unchanged form via renal excretion (abstract). Clin Pharmacol Ther 2009; 85: S83
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by MSD, Oss, the Netherlands. Pierre Peeters, Michiel van den Heuvel, Emiel van Heumen and Alex Zwiers are all employees of MSD (Oss, the Netherlands). Paul Passier and Jean Smeets were previously employees of MSD and are currently employed by Astellas (Leiderdorp, the Netherlands) and LAP&P Consultants BV (Leiden, the Netherlands), respectively. Thijs van Iersel, the Principal Investigator of the trial, was previously an employee of MSD, but was employed by Xendo (Groningen, the Netherlands) at the time of the start of the trial.
Pharmacokinetic calculations for this manuscript were performed by Dennis Doorstam (MSD, Oss, the Netherlands). Medical writing assistance was provided by Neil Venn (Prime Medica, Knutsford, UK) during the preparation of this manuscript.
The design and conduct of the study, as well as opinions on analysis, conclusions and interpretation of the study data, are the responsibility of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peeters, P.A.M., van den Heuvel, M.W., Heumen, E.v. et al. Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Sugammadex Using Single High Doses (Up to 96 mg/kg) in Healthy Adult Subjects. Clin. Drug Investig. 30, 867–874 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03256915
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03256915