Summary
IL-18 binding protein (BP) neutralizes the activity of IL-18, a cytokine implicated in psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We investigated the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of recombinant human IL-18 BP (r-hIL-18 BP) in healthy volunteers and subjects with psoriasis or RA in four phase I studies.
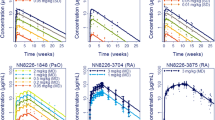
A) Healthy volunteers (n=24) were randomised to receive a single subcutaneous (sc) injection of r-hIL-18 BP (20,70,210 or 350 mg) or placebo. B) Healthy volunteers (n=10) were randomised to receive six sc injections of r-hIL-18 BP (35 or 175 mg, 48 h between injections) or placebo. C) Subjects with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis (n=35) were randomised to receive r-hIL-18 BP (20,160 or 320 mg, sc tiw) or placebo for 6 weeks. D) Subjects with active, moderate-to-severe RA (n=36) were randomised to receive r-hIL-18 BP (20,80,160 mg, sc tiw) or placebo for 6 weeks. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety were assessed in all four studies.
r-hIL-18 BP showed a dose-dependent pharmacokinetic profile, with a peak serum concentration of 6–48 hours. With repeated sc injections tiw, a steady state was achieved in 1–2 weeks among subjects with psoriasis or RA. The majority of adverse events were mild or moderate in severity. Injection site reactions were the most frequently reported event in subjects with psoriasis or RA. r-hIL-18 BP displays dose-dependent pharmacokinetics, has a favourable safety profile and is well-tolerated in healthy volunteers and in subjects with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis or active, moderate-to-severe RA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. De Rie, M.A., Meinardi, M.M. & Bos, J.D. (1990). Analysis of side-effects of medium- and low-dose cyclosporin maintenance therapy in psoriasis.British Journal of Dermatology, 123, 347–353.
Whiting-O’Keefe, Q.E., Fye, K.H. & Sack, K.D. (1991). Methotrexate and histologic hepatic abnormalities: a meta-analysis.American Journal of Medicine, 90, 711–716.
Caldwell, J.R. & Furst, D.E. (1991). The efficacy and safety of low-dose corticosteroids for rheumatoid arthritis.Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 21, 1–11.
Bresnihan, B., Roux-Lombard, P., Murphy, E., Kane, D., FitzGerald, O. & Dayer, J.M. (2002). Serum interleukin 18 andinterleukin 18 binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis.Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 61, 726–729.
Dinarello, C.A. (2004). Interleukin-18 and the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America, 30, 417–434, ix.
Gracie, J.A., Forsey, R.J., Chan, W.L., Gilmour, A., Leung, B.P., Greer, M.R., Kennedy, K., Carter, R., Wei, X.Q., Xu, D., Field, M., Foulis, A., Liew, F.Y. & McInnes, I.B. (1999). A proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis.Journal of Clinical Investigation, 104, 1393–1401.
Gangemi, S., Merendino, R.A., Guameri, F., Minciullo, P.L., DiLorenzo, G., Pacor, M. & Cannavo, S.P. (2003). Serum levels of interleukin-18 and s-ICAM-1 in patients affected by psoriasis: preliminary considerations.Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, 17, 42–16.
Ohta, Y., Hamada, Y. & Katsuoka, K. (2001). Expression of IL-18 in psoriasis.Archives of Dermatological Research, 293, 334–342.
Kohno, K. & Kurimoto, M. (1998). Interleukin 18, a cytokine which resembles IL-1 structurally and IL-12 functionally but exerts its effect independently of both.Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology, 86, 11–15.
Micallef, M.J., Ohtsuki, T., Kohno, K., Tanabe, F., Ushio, S., Namba, M., Tanimoto, T., Torigoe, K., Fujii, M., Ikeda, M., Fukuda, S. & Kurimoto, M. (1996). Interferon-gamma-inducing factor enhances T helper 1 cytokine production by stimulated human T cells: synergism with interleukin-12 for interferon-gamma production.European Journal of Immunology, 26, 1647–1651.
Okamura, H., Tsutsui, H., Kashiwamura, S., Yoshimoto, T. & Nakanishi, K. (1998). Interleukin-18: a novel cytokine that augments both innate and acquired immunity.Advances in Immunology, 70, 281–312.
Puren, A.J., Fantuzzi, G., Gu, Y., Su, M.S. & Dinarello, C.A. (1998). Interleukin-18 (IFNgamma-inducing factor) induces IL-8 and IL-lbeta via TNFalpha production from non- CD14+ human blood mononuclear cells.Journal of Clinical Investigation, 101, 711–721.
Ushio, S., Namba, M., Okura, T., Hattori, K., Nukada, Y., Akita, K., Tanabe, F., Konishi, K., Micallef, M., Fujii, M., Torigoe, K., Tanimoto, T., Fukuda, S., Ikeda, M., Okamura, H. & Kurimoto, M. (1996). Cloning of the cDNA for human IFN-gamma-inducing factor, expression in Escherichia coli, and studies on the biologic activities of the protein.Journal of immunology, 156, 4274–4279.
Okamura, H., Tsutsi, H., Komatsu, T., Yutsudo, M., Hakura, A., Tanimoto, T., Torigoe, K., Okura, T., Nukada, Y., Hattori, K. & et al. (1995). Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-gamma production by T cells.Nature, 378, 88–91.
Takeda, K., Tsutsui, H., Yoshimoto, T., Adachi, O., Yoshida, N., Kishimoto, T., Okamura, H., Nakanishi, K. & Akira, S. (1998). Defective NK cell activity and Th1 response in IL-18-deficient mice.Immunity, 8, 383–390.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
IL-18 BP Study GroupCanada: Professor Robert Bissonnette, Professor Kim Papp, Professor Neil Shear; Croatia: Professor Bozidar Curkovic;Germany: Professor Wolfram Sterry;Serbia and Montenegro: Professor Aleksandar Dimic, Professor Vladimir Mircetic;Slovak Republic: Dr Zlata Kmecova, Professor Josef Ravensky;Slovenia: Professor Blaz Rozman;The Netherlands: Professor Paul Tak;UK: Dr Iain Mclnnes, Dr Anthony Priestley, Dr Amran Saifulanwar, Dr Rene Van der Merwe.
Please send reprint requests to: Andrew Desson, SERONO International S.A. 15 bis, Chemin des Mines, 1202 Geneva, Switzerland
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tak, P.P., Bacchi, M. & Bertolino, M. Pharmacokinetics of IL-18 binding protein in healthy volunteers and subjects with rheumatoid arthritis or plaque psoriasis. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 31, 109–116 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191127
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191127