Abstract
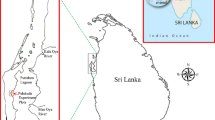
Sedimentation rate and nutrient concentrations were assessed in 1989 at four sites of differing stream morphometry in the Kakagon Sloughs, a Lake Superior coastal wetland in northern Wisconsin dominated by northern wild-rice (Zizania palustris). Pre-weighed sediment traps were placed at each site along deep-to-shallow water zones. Accrued sediment was collected during five time periods corresponding to differing stages of growth in wild-rice stands. There were higher sedimentation rates at the river sites (straight sections and inside and outside curves) when compared to the backwater site. Differences were also observed among depths and at the different time periods, demonstrating the influence of vegetation on the sedimentation process in this wetland complex. Higher sedimentation rates took place closest to the vegetation-open water interface (deep zones). However, in shallow zones, a significant proportion of the annual sedimentation took place during the submersed and floating leaf stages, showing the importance of these time periods for providing an annual input of sediment to large areas of riverine habitat. Of nutrients tested, both TKN and NO3-N had lower concentrations in the period following wild-rice stem elongation. These data suggest that the early growth habit of wild-rice (submersed and floating stages) promotes pulses of nutrient-rich sediment, which are necessary for the later nutrient-demanding stages of stem elongation and grain formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aiken, S. G., P. F. Lee, D. Punter, and J. M. Stewart. 1988. Wild Rice in Canada. NC Press, Ioronto, Ontario, Canada.
Archibald, O.W., B. J. Weichel, and J. E. Fitzgibbon. 1985. Factors in the ecology of wild rice in northern Saskatchewan. The Canadian Geographer 29:100–112.
Barko, J. W. and R. M. Smart. 1980. Mobilization of sediment phosphorus by submersed freshwater macrophytes. Freshwater Biology 10:229–238.
Brooks, R. P. 1989. An overview of ecological functions and economic values of wetlands. p. 11–20.In S.K. Majumdar, R. P. Brooks, F. J. Brenner, and R. W. Tiner, Jr. (eds.) Wetlands Ecology and Conservation: Emphasis in Pennsylvania. The Pennsylvania Academy of Science. Easton, PA, USA.
Carpenter, S. R. and D. M. Lodge. 1986. Effects of submerged macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquatic Botany 26: 341–370.
Dean, R. G. 1979. Effects of vegetation on shoreline erosional processes. p. 416–426.In P. E. Greeson, J. R. Clark, and J. E. Clark (eds.) Wetland Functions and Values: The State of Our Understanding. American Water Resources Association. Minneapolis, MN, USA.
Dore, W. G. 1969. Wild-Rice. Research Branch-Canada Department of Agriculture, Publication 1393, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Gordon, N. D., T. A. McMahon, and B. L. Finlayson. 1992. Stream Hydrology: An Introduction For Ecologists. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, New York, NY, USA.
Jeffries, M. and D. Mills. 1990. Freshwater Ecology: Principles and Applications. Biddles Limited of Guildford and Kings. Lynn, UK.
Jenks, A. E. 1901. The Wild Rice Gatherers of the Upper Lakes: A Study in American Primitive Economics. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC, USA.
Keenan, T. J. and P. F. Lee. 1988. Ecological relationships of wild rice,Zizania aquatica. 7. Sediment nutrient depletion following introduction of wild rice to a shallow boreal lake. Canadian Journal of Botany 66:236–241.
Kemp, W. M., W. R. Boynton, and R. R. Twilley. 1984. Influences of submersed vascular plants on ecological processes in upper Chesapeake Bay. p. 368–394.In V.S. Kennedy (ed.) The Estuary as a Filter, Academic Press, New York, NY, USA.
Klopatek, J. M. 1978. Nutrient dynamics of freshwater riverine marshes and the role of emergent macrophyte. p. 195–216.In R.E. Good, D.F. Whigham, and R.L. Simpson (eds.) Freshwater Wetlands. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA.
Lee, P. F. and J. M. Stewart. 1983. Ecological relationships of wild rice,Zizania aquatica. 2. Sediment-plant tissue nutrient relationships. Canadian Journal of Botany 61:1775–1784.
Leopold, L. B., M. G. Wolman, and J. P. Miller. 1964. Fluvial Processes in Geomorphology. W.H. Freeman, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Meeker, J. E. 1993. The ecology of “wild” wild-rice (Zizania palustris var.palustris) in the Kakagon Sloughs, a riverine wetland on Lake Superior. Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, USA.
Oelke E. A. 1982. Wild rice production in Minnesota. Extension Bulletin 464. University of Minnesota, Agricultural Extension Service, Minneapolis, MN. USA.
Peden, D. G. 1982. Factors associated with growth of wild rice in northern Saskatchewan. Arctic 35:307–311.
Posey, M. H. 1988. Community changes associated with the spread of an introduced seagrass,Zostera japonica. Ecology 69:974–983.
Richard, G. A. 1987. Seasonal and environmental variations in sediment accretion in a Long Island salt marsh. Estuaries 1: 29–35.
Richards, K. S. 1982. Rivers, Form and Process in Alluvial Channels. Metheun, London, UK.
Sculthorpe, C. D. 1967. The Biology of Aquatic Vascular Plants. William Clowes and Sons, London, UK.
Systat®. 1992. Version 5.2 Edition, Systat. Inc. Evanston, IL, USA. Thomas, A. G. and J. M. Stewart. 1969. The effect of different water depths on the growth of wild rice. Canadian Journal of Botany 47:1525–1531.
Tukey, J. W. 1977. Exploratory Data Analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meeker, J.E. Wild-rice and sedimentation processes in a Lake Superior coastal wetland. Wetlands 16, 219–231 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160695
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160695