Abstract
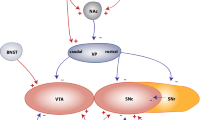
The detailed anatomy of the monoamine pathways of the rat, first described by the students of Nils-Åke Hillarp in Sweden, provided the basis for a neurocircuitry targeted pharmacology, leading to important therapeutic breakthroughs. Progress was achieved by the introduction of accurate lesion techniques based on selective neurotoxins. Systematic intracerebral injections of 6-hydroxydopamine let Urban Ungerstedt at the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, to propose the first stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain; and the ‘Rotational Behaviour’, as a classical model for screening drugs useful for alleviating Parkinson’s disease and other neuropathologies. The direction of the rotational behaviour induced by drugs systematically administrated to unilaterally 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats reveals their mechanism of action at dopamine synapses, as demonstrated when rotational behaviour was combined with microdialysis. The model was useful for proposing a role of dopamine receptors in the gating of the flow of information integrated and/or modulated by the basal ganglia, through different efferent pathways; notably the striatopallidal system, via D2 receptors, and the striatonigral system, via D1 receptors. The role of other dopamine receptor subtypes on rotational behaviour has not yet been clarified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RN (1978)In vivo electrochemical recording- a new neurophysiological approach.Trends Neurosci. 1, 160–163.
Agnati LF, K Fuxe, M Zoli, I Ozini, A Härfstrand, G Toffano and F Ferraguti (1986) A correlation analysis of the regional distribution of central enkephalin and beta-endorphin immu-noreactive terminals and of opiate receptors in adult and old male rats. Evidence for the existence of two main types of communication in the central nervous system: the volume transmission and the wiring transmission.Acta Physiol. Scand. 128, 201–207.
Andén N-E, A Carlsson, A Dahlström, K Fuxe, N-Å Hillarp and K Larsson (1964) Demonstration and mapping out of nigro-neostriatal dopamine neurons.Life Sci. 3, 523–530.
Andén N-E, A Dalhström, K Fuxe and K Larsson (1966) Functional role of the nigro-neostriatal dopamine neurons.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 24, 264–274.
Andén N-E, A Rubenson, K Fuxe and T Hökfelt (1967) Evidence for dopamine receptor stimulation by apomorphine.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 19, 627–629.
Arnt J, KP Bogeso, J Hyttel and E Meier (1988) Relative dopamine D1 and D2 receptor affinity and efficacy determine whether dopamine agonists induce hyperactivity or oral stereotypy in rats.Pharmacol. Toxicol. 62, 121–130.
Bentivoglio M and M Morelli (2005) The organization and circuits of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and the distribution of dopamine receptors in the brain, In:Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy:Dopamine (Björklund A and T Hökfelt, Eds.) (Elsevier BV:The Netherlands), Vol.21, 1–107.
Bunzow JR, HHM Van Tol, DK Grandy, P Albert, A Salon, MD Christie, CA Machida, KA Neve and O Civelli (1988) Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA.Nature 336, 781–783.
Campbell GA, MJ Eckardt and FF Weight (1985) Dopaminergic mechanisms in subthalamic nucleus of rat: analysis using horseradish peroxidase and microiontophoresis.Brain Res. 333, 261–270.
Carlsson A, K Fuxe, B Hamberger and M Lindqvist (1966) Biochemical and histochemical studies on the effects of imipramine-like drugs and (+)-amphetamine on central and peripheral catecholamine neurons.Acta Physiol. Scand. 67, 481–497.
Chevalier G, AM Tierry, T Shibazaki and J Feger (1981) Evidence for a GABAergic inhibitory nigrotectal pathway in the rat.Neurosci. Lett. 21, 67–70.
Christensson-Nylander I, M Herrera-Marschitz, W Staines, T Hökfelt, L Terenius, U Ungerstedt, C Cuello, WH Oerteland M Goldstein (1986) Striato-nigral dynorphin and substance P pathways in the rat. I. Biochemical and immunohisto-chemical evidence.Exp. Brain Res. 64, 169–192.
Corrodi H, K Fuxe, T Hökfelt, P Lidbrink and U Ungerstedt (1973) Effect of ergot drugs on central catecholamine neurons: evidence for stimulation of dopamine neurons.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 25, 409–412.
Cuello AC and G Paxinos (1978) Evidence for a long leuenkephalin striatopallidal pathway in rat brain.Nature 271, 178–180.
Dahlström A and K Fuxe (1964) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. I. Demonstration of monoamines in the cell bodies of brain stem neurons.Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl.232, 1–55.
Dahlström A and K Fuxe (1965) Evidence for the existence of monoamine-containing neurons in the central nervous system. II. Experimentally induced changes in the intraneuronal amine levels of bulbospinal neuron systems.Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl.247, 1–36.
Dearry J, JA Gingrich, P Falardeau, RTJ Fremau, MD Bates and MG Caron (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of the gene for a human D1 dopamine receptor.Nature 347, 72–76.
Delgado JMR, FV De Feudis, RH Roth, DK Ryugo and BM Mitruka (1972) Dialytrode for long-term intracerebral perfusion in awake monkeys.Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. 198, 9–21.
Diaz J, D Lévesque, CH Lammers, M Griffon, M-P Martres, JC Schwartz and P Sokoloff (1995) Phenotypical characterization of neurons expressing the D3 receptor in the rat brain.Neuroscience 65, 731–745.
DiChiara G, M Olianas, M Del Fiaco, PF Spano and A Tagliamonte (1977) Intranigral kainic acid is evidence that nigral non-dopaminergic neurons control posture.Nature 268, 743–745.
DiChiara G, ML Porceddu, M Morelli, ML Mulas and GL Gessa (1979) Evidence for a GABAergic projection from the substantia nigra to the ventromedial thalamus and to the superior colliculus of the rat.Brain Res. 176, 273–284.
Ernst AM (1967) Mode of action of apomorphine and dexamphet-amine on gnawing compulsion in rats.Psychopharmacology 10, 316–323.
Ferre S, WT O’Connor, K Fuxe and U Ungerstedt (1993) The striato-pallidal neuron: a main locus for adenosine-dopamine interactions in the brain.J. Neurosci. 13, 5402–5406.
Fuxe K and U Ungerstedt (1970) Histochemical biochemical and functional studies on central monoamine neurons after acute and chronic amphetamine administration, In:Amphetamine and Related Compounds (Costa E, Ed.) (Raven Press:New York), pp 257–288.
Gaddum JH (1961) Push-pull cannulae.J. Physiol. (London) 155, 1–2.
Garcia-Munoz M, NM Nicolaou, IF Tulloch, AK Wright and GW Arbuthnott (1977) Feedback loop or output pathway in striato-nigral fibers?Nature 265, 363–365.
Gerfen CR and CJ Wilson (1996) The basal ganglia. Chapter II, In:Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Vol 12:Integrated Systems of the CNS. Part III (Swanson LW, A Björklund and T Hökfelt, Eds.) (Elsevier Science BV:The Netherlands), pp 371–468.
Glowinski J (1974) Properties and function of intraneuronal monoamine compartments in central aminergic neurons, In:Handbook of Psychopharmacology (Iversen LL, S Iversen and SH Snyder, Eds.) (Plenum Press:New York), pp 139–167.
Goldstein M, A Lieberman, JY Lew, T Asano, MR Rosenfeld and MH Makman (1980) Interaction of pergolide with central dopaminergic receptors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 3725–3728.
Haber SN, HJ Groenewegen, EA Grove and WJH Nauta (1985) Efferent connections of the ventral pallidum: evidence of a dual striato pallidofugal pathway.J. Comp. Neurol. 235, 322–335.
Hallman H and G Jonsson (1984) Studies on central dopamine neurons. Regional characterization of dopamine turnover.Med. Biol. 62, 198–209.
Herrera-Marschitz M (1986) Neuropharmacology and functional anatomy of the basal ganglia. Karolinska Institutet-Thesis, Stockholm, pp 1–79.
Herrera-Marschitz M and U Ungerstedt (1984a) Evidence that apomorphine and pergolide induce rotation in rats by different actions on D1 and D2 receptor sites.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 98, 165–176.
Herrera-Marschitz M and U Ungerstedt (1984b) Evidence striatal efferents relate to different dopamine receptors.Brain Res. 323, 269–278.
Herrera-Marschitz M and U Ungerstedt (1985) Effect of the dopamine D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 on rotational behaviour induced by apomorphine and pergolide in 6-hydroxydo-pamine denervated rats.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 109, 349–354.
Herrera-Marschitz M, J Hyttel and U Ungerstedt (1984) The dopamine D-1 antagonist SCH 23390 inhibits apomorphine but not pergolide induced rotation.Acta Physiol. Scand. 122, 427–428.
Herrera-Marschitz M, T Hökfelt and U Ungerstedt (1985a) A rotational model sensitive to D-1 but not to D-2 dopamine receptor stimulation.Acta Physiol. Scand. (Suppl. 124),542, 181.
Herrera-Marschitz M, C Forster and U Ungerstedt (1985b) Rotational behaviour elicited by intracerebral injections of apomorphine and pergolide in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. I: Comparisons between systemic and intrastriatal injections.Acta Physiol. Scand. 125, 519–527.
Herrera-Marschitz M, H Utsumi and U Ungerstedt (1990) Scoliosis in rats with experimentally-induced hemiparkin-sonism: dependence upon striatal dopamine denervation.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 53, 39–43.
Herrera-Marschitz M, JJ Meana, WT O’Connor, M Goiny, MS Reid and U Ungerstedt (1992) Neuronal dependence of extracellular dopamine, acetylcholine, glutamate, aspartate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) measured simultaneously from rat neostriatum usingin vivo microdialysis, reciprocal interactions.Amino Acids 2, 157–179.
Herrera-Marschitz M, Z-B You, M Goiny, JJ Meana, R Silveira, O Godukhin, Y Chen, S Espinoza, E Pettersson, F Loidl, G Lubec, K Andersson, I Nylander, L Terenius and U Ungerstedt (1996) On the origin of extracellular glutamate levels monitored in the basal ganglia byin vivo microdialysis.J. Neurochem. 66, 1726–1735.
Herrera-Marschitz M, M Goiny, Z-B You, JJ Meana, E Pettersson, R Rodriguez-Puertas, Z-Q Xu, L Terenius, T Hökfelt and U Ungerstedt (1997) On the release of glutamate and aspartate in the basal ganglia of the rat: interactions with monoamines and neuropeptides.Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21, 489–495.
Hopkins DA and LW Niessen (1976) Substantia nigra projections to the reticulata formation, superior colliculus and central gray in the rat, cat and monkey.Neurosci. Lett. 2, 253–259.
Hurd YL and U Ungerstedt (1989) Influence of a carrier transport process onin vivo release and metabolism of dopamine: dependence on extracellular Na+.Life Sci. 45, 283–293.
Hyttel J (1983) SCH 23390- the first selective dopamine D-1 antagonist.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 91, 153–154.
Hyttel J (1986) Dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors. Characterization and differential effects of neuroleptics.Acta Pharm. Suecica Suppl. 1, 426-439.
Hökfelt T and U Ungerstedt (1973) Specificity of 6-hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of central monoamine neurons: an electron and fluorescence microscopic study with special reference to intracerebral injection on the nigro-striatal dopamine system.Brain Res. 60, 269–297.
Imperato S and G DiChiara (1984) Trans-striatal dialysis coupled to reverse performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection: a new method for the study of thein vivo release of endogenous dopamine and metabolites.J. Neurosci. 4, 960–977.
Iorio LC, A Barnett, FH Leitz, VP Houser and CA Korduba (1983) SCH 23390, a potential benzazepine antipsychot- ic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 226, 462–468.
Jones DL and GJ Mogenson (1980) Nucleus accumbens to globus pallidus GABA projection subserving ambulatory activity.Am. J. Physiol. 238, 65–69.
Jonsson G, H Hallman, I Mefford and RN Adams (1980) The use of liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection for the determination of adrenaline and other biogenic- monoamines in the CNS, In:Central Adrenaline Neurons (Fuxe K, M Goldstein, B Hökfelt and T Hökfelt, Eds.) (Pergamon Press:Oxford-New York), pp 59–71.
Kilpatrick IC, MS Starr, A Flechter, TA James and NK MacLeod (1980) Evidence for a GABAergic nigrothalamic pathway in the rat.Exp. Brain Res. 40, 45–54.
Kilpatrick IC, GL Collingridge and MS Starr (1982) Evidence for the participation of nigrotectal ?-aminobutyrate-containing neurones in striatal and nigral-derived circling in the rat.Neuroscience 7, 207–222.
Kita H, HT Chang and ST Kitai (1983) Pallidal inputs to sub-thalamus: intracellular analysis.Brain Res. 264, 255–265.
Kretschmer BD, M Goiny and M Herrera-Marschitz (2000) Effect of intracerebral administration of NMD A and AMPA on dopamine and glutamate release in the ventral pallidum on motor behaviour.J. Neurochem. 74, 2049–2057.
Langer SZ (1966) The degeneration contraction of the nictitating membrane in the un-anesthetized cat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 151, 66–72.
Loopuijt LD and D Van Der Kooy (1985) Organization of the striatum: collateralization of its efferent axons.Brain Res. 348, 86–99.
Marshall JF and U Ungerstedt (1977) Striatal efferent fibers play a role in maintaining rotational behaviour in the rat.Science 198, 62–64.
Mogenson GJ and MA Nielsen (1983) Evidence that an accumbens to subpallidal GABAergic projection contributes to locomotor activity.Brain Res. Bull. 11, 309–314.
Monsma FJ Jr, LC Manhan, LD McVittie, CR Gerfen and DR Sibley (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of a D1 dopamine receptor linked to adenylyl cyclase activation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 6723–6727.
Osborne PG, WT O’Connor, KL Drew and U Ungerstedt (1990) Anin vivo microdialysis characterization of extracellular dopamine and GABA in dorsolateral striatum of awake freely moving and anesthetised rats.J. Neurosci. Meth. 34, 99–105.
Paxinos G and C Watson (1982)The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic Press: San Diego, CA).
Pendleton RG, L Samler, C Kaiser and PT Ridley (1978) Studies on renal dopamine receptors with a new agonist.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 51, 19–28.
Pycock CK and CD Marsden (1978) The rotating rodent: a two component system?Eur. J. Pharmacol. 47, 167–175.
Reid M, M Herrera-Marschitz, T Hökfelt, L Terenius and U Ungerstedt (1988) Differential modulation of striatal dopamine release by intranigral injection of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), dynorphin A and substance P.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 147, 411–420.
Reid M, M Herrera-Marschitz, T Hökfelt, N Lindefors, H Persson and U Ungerstedt (1990) Striatonigral GABA, dynorphin, substance P and neurokinin A modulation of striatal dopamine: evidence for direct regulatory mechanisms.Exp. Brain Res. 82, 293–303.
Robertson HA (1992) Dopamine receptor interactions: some implications for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.Trends Neurosci. 15, 201–206.
Romero CA, DA Bustamante, G Zapata-Torres, M Goiny, B Cassels and M Herrera-Marschitz (2006) Neurochemical and behavioural characterization of alkoxyamphetamine derivatives in rats.Neurotoxicity Res. 10, 11–22.
Rouzaire-Dubois B, C Hammond, B Hamon and J Ferger (1980) Pharmacological blockade of the globus pallidus-induced inhibitory response of subthalamic cells in the rat.Brain Res. 200, 321–329.
Schwarcz R, K Fuxe, LF Agnati, T Hökfelt and JT Coyle (1979a) Rotational behaviour in rats with unilateral striatal kainic acid lesions: a behavioural model for studies on intact dopamine receptors.Brain Res. 170, 485–495.
Schwarcz R, T Hökfelt, K Fuxe, G Jonsson, M Goldstein and L Terenius (1979b) Ibotenic acid-induced neuronal degeneration: a morphological and neurochemical study.Exp. Brain Res. 37, 199–216.
Seeman P (1981) Brain dopamine receptors.Pharmacol. Rev. 32, 229–313.
Temlett JA, NP Quinn, PG Jenner, CD Marsden, E Purcher, AM Bonnet, Y Agid, R Markstein and X Lataste (1989) Antiparkinsonian activity of CY 208-243, a partial D-1 dopamine receptor agonist, in MPTP-treated marmosets and patients with Parkinson’s disease.Mov. Disord. 4, 261–265.
Trabucchi M, R Longoni, S Fresia and PF Spano (1975) Sulpiride: a study of the effects on dopamine receptors in rat neostriatum and limbic forebrain.Life Sci. 17, 1551–1556.
Tranzer JP and H Thoenen (1968) An electron microscopic study of selective, acute degeneration of sympathetic erve terminals after administration of 6-hydroxydopamine.Experientia 24, 155–156.
Tsurata K, EA Frey, CW Grewe, TE Cote, RL Eskay and JW Kebabian (1981) Evidence that LY-141865 specifically stimulate the D2 dopamine receptor.Nature 292, 463–465.
Ungerstedt U (1971a) Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathway in the rat brain.Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl.367, 1–48.
Ungerstedt U (1971b) Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxydopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system.Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl.367, 69–93.
Ungerstedt U (1971c) Striatal dopamine release after amphetamine or nerve degeneration revealed by rotational behaviour.Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl.367, 49–68.
Ungerstedt U (1976) 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopamine pathway: the turning syndrome.Pharmacol. Ther. Behav. 2, 37–40
Ungerstedt U (1991) Microdialysis — principles and applications for studies in animals and man.J. Intern. Med. 230, 365–373.
Ungerstedt U and GW Arbuthnott (1970) Quantitative recording of rotational behaviour in rats after 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the nigrostriatal dopamine system.Brain Res. 24, 85–493.
Ungerstedt U and M Herrera-Marschitz (1981) Behavioural pharmacology of dopamine receptor mechanisms, In:Chemical Neurotransmission 75 years (Stjärne L, P Hedqvist, H Lagercrantz and Å Wennmalm, Eds.) (Academic Press:New York), pp 481–494.
Ungerstedt U and C Pycock (1974) Functional correlates of dopamine neurotransmission.Bull. Schweiz. Acad. Med. Wiss. 1278, 1–5.
Ungerstedt U, M Herrera-Marschitz, U Jungnelius, L Ståhle, U Tossman and T Zetterström (1982) Dopamine synaptic mechanisms reflected in studies combining behavioural recordings and brain dialysis.Adv. Biosci. 37, 219–231.
Van Der Kooy D, T Hattori, K Shannak and O Hornykiewicz (1981) The pallido-subthalamic projection in rat: anatomical and biochemical studies.Brain Res. 204, 253–240.
Vincent SR, T Hattori and EG McGeer (1978) The nigrotectal projection: a biochemical and ultrastructural characterization.Brain Res. 151, 159–164.
Westerink BHC, HM Hofsteed, G Damsma and GB de Vries (1988) The significance of extracellular calcium for the release of dopamine, acetylcholine and amino acids in conscious rats evaluated by brain microdialysis.Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 337, 373–378.
You Z-B, M Herrera-Marschitz, E Brodin, JJ Meana, P Morino, T Hökfelt, R Silveira, M Goiny and U Ungerstedt (1994a) On the origin of striatal cholecystokinin release: studies within vivo microdialysis.J. Neurochem. 62, 76–85.
You Z-B, I Nylander, M Herrera-Marschitz, WT O’Connor, M Goiny and L Terenius (1994b) The striatonigral dynorphin pathway of the rat studied within vivo microdialysis. I. Effects of K+-depolarization, lesions and peptidase inhibition.Neuroscience 63, 415–425.
You Z-B, M Herrera-Marschitz, I Nylander, WT O’Connor, M Goiny, U Ungerstedt and L Terenius (1994c) The striatonigral dynorphin pathway of the rat studied within vivo microdialysis. II. Effects of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists.Neuroscience 63, 427–434.
Zetterström T (1986) Pharmacological analysis of central dopaminergic neurotransmission using a novelin vivo brain perfusion method. Karolinska Institutet-Thesis, Stockholm, pp 1–45.
Zetterström T, T Sharp, CA Marsden and U Ungerstedt (1983)In vivo measurement of dopamine and its metabolites studied by intracerebral dialysis: changes after D-amphetamine.Neurochem. 41, 1769–1773.
Zetterström T, M Herrera-Marschitz and U Ungerstedt (1986) Simultaneous measurement of dopamine release and rotational behaviour in 6-hydroxydopamine denervated rats using intracerebral dialysis.Brain Res. 376, 1–7.
Zhou QJ, DK Grandy, L Thambi, JA Kushner, HHM Van Tol, R Cone, D Pribnow, J Salon, JR Bunzow and O Civelli (1990) Cloning and expression of human and rat D1 dopamine receptors.Nature 347, 76–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera-Marschitz, M., Bustamante, D., Morales, P. et al. Exploring neurocircuitries of the basal ganglia by intracerebral administration of selective neurotoxins. neurotox res 11, 169–182 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033566
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033566