Abstract
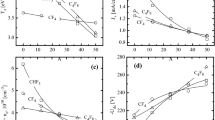
Picosecond mid-IR USPL induced surface damage on a Gallium Phosphate (GaP) and Calcium Fluoride (CaF2) is reported. A semiconductor GaP and a dielectric material CaF2, that are transparent over3–10μm, were exposed to one picosecond mid-IR light (4.7μm) to investigate laser-induced surface morphological changes on the target The initiation of damage along the polishing scratch line of GaP and the random location of damage digs on the CaF2 suggests that the mid-IR picosecond laser-induced damage on targets started from intrinsic surface defects. Multiple pulse irradiations produced periodic corrugated surface structures (ripples) perpendicular to the polarization of light on both GaP and CaF2. In terms of the orientation and the spacing between ripples, observed ripples have common features with previously reported ripples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhmanov, S. A., Emel’yanov, V. I., Koroteev, N. I. and Seminogov, V. N., 1985, “Interaction of Powerful Laser Radiation with the Surfaces of Semiconductors and Metals: Nonlinear Optical Effects and Nonlinear Optical Diagnostics,” Sovietphysics: Uspekhi, Vol. 28, pp. 1084–1124.
Ashkenasi, D., Rosenfeld, A., Varel, H., Wahmer, M. and Campbell, E. E. B., 1997, “Laser Processing of Sapphire with Picosecond and Sub-Picosecond Pulses,”Applied Surface Science, Vol. 120, pp. 65–80.
Baurele, D., 2000a,Laser processing and chemistry, Chapter 12, Berlin, Springer.
Baurele, D., 2000b,Laser processing and che-mistry, Chapter 21, Berlin, Springer.
Birnbaun, M., 1965, “Semiconductor Surface Damage Produced by Ruby Lasers,”Journal of Applied Physics, Vol. 36, pp. 3688–3689.
Chang, W., Choi, M., Kim, J., Cho, S. and Whang, K., 2004, “Nanoscale Patterning Using Femtosecond Laser and Self-Assembled Monolayers(SAMs),”Journal of Korean Society of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 28, pp. 1270–1275.
Chichkov, B. N., Momma, C., Nolte, S., von Alvensleben, F. and Tunnermann, A., 1996, “Femtosecond, Picosecond and Nanosecond Laser Ablation of Solids,”Applied Physics A, Vol. 63, pp. 109–115.
Gusev, V. E. and Karabutov, A. A., 1993,Laser Optoacoustics, New York: AIP Press.
Keilmann, F. and Bai, Y. H., 1982, “Periodic Surface Structures Frozen into CO2 Laser-Melted Quartz,”Applied Physics A, Vol. 29, pp. 9–18.
Kittel, C., 1996,Introduction to solid state physics, 7th ed., Wiley, New York.
Koechner, W., 2000,Solid State Laser Engineering, Chapter 11, Berlin, Springer.
Neev, J., Da Silva, L. B., Feit, M. D., Perry, M. D., Rubenchik, A. M. and Stuart, B. C., 1996, “Ultrashort Pulse Lasers for Hard Tissue Ablation,”IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, Vol. 2, pp. 790–800.
Oraevsky, A. A., Da Silva, L. B., Rubenchik, A. M., Feit, M. D., Glinsky, M. E., Perry, M. D., Mammini, B. M., Small, W. IV and Stuart, B. C., 1996, “Tissues With Nanosecond-to-Femtosecond Laser Pulses: Rel-ative Role of Linear and. Nonlinear Absorption, “IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, Vol. 2, pp. 801–809.
Oraevsky, A. A., Jacques, S. L. and Tittel, F. K. “Measurements of Tissue Optical Properties by Means of Time-Resolved Detection of Laser-Induced Transient Stress,”Applied Optics, Vol. 36, pp. 402–415.
Simanovskii, D., Schwettman, H. A., Lee, H. and Welch, A. J., 2003, “Mid-Infrared Optical Break-down in Dielectrics,”Physical Review Letters, Vol. 91, No. 10,107601(1–4).
Spooner, G. J. R., Juhasz, T., Traub, I. R., Djotyan, G., Horvath, C., Sacks, Z., Marre, G., Miller, D. and Wil-liams, A. R., 2000, “Commercial and Biomedical Applications of Ultrafast Lasers,”Proceedings of SPIE, Vol. 3934, pp. 62–72.
Stoian, R., Ashkenasi, D., Rosenfeld, A., Wittmann, M., Kelly, R. and Campbell, E. E. B., 2000, “The Dynamics of Ion Expulsion in Ultrashort Pulse Laser Sputtering of A12O3,”Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, Vol. 166-167, pp. 682–690.
Vasquez, M. J., Halada, G. P., Clayton, C. R. and Gouma, P. I., 1999, “Fabrication of Nanostructured Al CuMg Thin Film by Femtosecond Pulsed Laser Ablation,”Thin Solid Films, Vol. 458, pp. 37–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H. Picosecond mid-IR laser induced surface damage on Gallium Phosphate (GaP) and Calcium Fluoride(CaF2). J Mech Sci Technol 21, 1077–1082 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027657
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03027657