Abstract
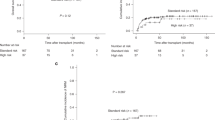
Little evidence exists in Asian countries regarding the incidence, immunologic characteristics, and clinical outcomes of adult patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) and -negative (Ph-) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). In this study, we prospectively studied 324 Thai adult acute leukemia patients, 79 (24%) of whom were identified as having ALL. Immunophenotyping was performed by 5-parameter flow cytometry, and karyotyping was conducted by standard banding methods. The Ph chromosome was detected in 18.5% of cases. The mean age of Ph+ ALL patients was 29 years (50% male), and that of Ph- ALL patients was 33 years (62% female). The Ph+ ALL patients had significantly higher white blood cell (WBC) counts (mean, 93 x 109/L), with 67% having WBC counts higher than 50x 109/L. In contrast, most Ph- ALL patients had WBC counts lower than 50x109/L (mean, 36x109/L; P< .05). CD10 and CD34 were more highly expressed in the Ph+ ALL patients (mean expression, 83% and 87%, respectively) than in the Ph- ALL patients (45% and 57%;P < .005).The aberrant expression of myeloid antigens, including CD33 and CD13, was also significantly observed in the Ph+ ALL patients. The median survival time of Ph+ ALL patients was 8 months, compared with 22 months for the Ph- ALL patients. In conclusion, immunophenotyping results showed that Ph+ ALL in Thai adults arises from B-cells at an earlier stage of development. Extreme leukocytosis, a younger age, male sex, high expression levels of CD10 and CD34, aberrant myeloid antigens, and poorer rates of survival appeared to be associated with the Ph chromosome in Thai adult ALL cases.The incidence of the Ph chromosome among Thai adult ALL patients was not different from that found in Western countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young JL Jr, Ries LG, Silverberg E, Horm JW, Miller RW. Cancer incidence, survival, and mortality for children younger than age 15 years.Cancer. 1986;58:598–602.
Pui CH. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Pediatr Clin North Am. 1997;44:831–846.
Kantarjian HM. Adult acute lymphocytic leukemia: critical review of current knowledge.Am J Med. 1994;97:176–184.
Faderl S, Albitar M. Insights into the biologic and molecular abnormalities in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14:1267–1288.
Campana D, Behm FG. Immunophenotyping of leukemia.J Immunol Methods. 2000;243:59–75.
Huh YO, Ibrahim S. Immunophenotypes in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: role of flow cytometry in diagnosis and monitoring of disease.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14:1251–1265.
Rowley JD. A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining [letter].Nature. 1973;243:290–293.
Groffen J, Heisterkamp N. The chimeric BCR-ABL gene.Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 1997;10:187–201.
Udomsakdi-Auewarakul C, U-Pratya Y, Boonmoh S, Vatanavicharn S. Detection of molecular variants of BCR-ABL gene in blood and bone marrow of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia by reversetranscriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).J Med Assoc Thai. 2000;83:928–935.
Radich JP. Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphocytic leukemia.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2001;15:21–36.
Arico M, Valsecchi MG, Camitta B, et al. Outcome of treatment in children with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.N Engl J Med. 2000;342:998–1006.
Hoelzer D. Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults.Semin Hematol. 1994;31:1–15.
Gokbuget N, Hoelzer D, Arnold R, et al. Treatment of Adult ALL according to protocols of the German Multicenter Study Group for Adult ALL (GMALL).Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14:1307–1325.
Mitelman F, ed.ISCN 1995:An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature 1995. Basel, Switzerland: S Karger AG; 1995.
Borowitz MJ, Guenther KL, Shults KE, Stelzer GT. Immunophenotyping of acute leukemia by flow cytometric analysis: use of CD45 and right-angle light scatter to gate on leukemic blasts in three-color analysis.Am J Clin Pathol. 1993;100:534–540.
Kishimoto T, Kikutani H, von dem Borne AEG, et al. eds.Leucocyte Typing VI: White Cell Differentiation Antigens. New York, NY: Garland; 1997.
Bene MC, Castoldi G, Knapp W, et al. Proposal for the immunological classification of acute leukemias: European Group for the Immunological Characterization of Leukemias (EGIL).Leukemia. 1995;9:1783–1786.
Buyse ME, Staquet MJ, Sylvester RJ, eds.Cancer Clinical Trials: Methods and Practice. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 1992.
Gee TS, Haghbin M, Dowling MD, Cunningham I, Middleman MP, Clarkson BD. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults and children: differences in response with similar therapeutic regimens.Cancer. 1976;37:1256–1264.
Copelan EA, McGuire EA. The biology and treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults.Blood. 1995;85:1151–1168.
Secker-Walker LM, Prentice HG, Durrant J, Richards S, Hall E, Harrison G. Cytogenetics adds independent prognostic information in adults with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia on MRC trial UKALL XA: MRC Adult Leukaemia Working Party.Br J Haematol. 1997;96:601–610.
Dombret H, Gabert J, Boiron JM, et al. Outcome of treatment in adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: results of the prospective multicenter LALA-94 trial.Blood. 2002;100:2357–2366.
Walters R, Kantarjian HM, Keating MJ, et al. The importance of cytogenetic studies in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia.Am J Med. 1990;89:579–587.
Westbrook CA, Hooberman AL, Spino C, et al. Clinical significance of the BCR-ABL fusion gene in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B study (8762).Blood. 1992;80:2983–2990.
Preti HA, O’Brien S, Giralt S, Beran M, Pierce S, Kantarjian HM. Philadelphia-chromosome-positive adult acute lymphocytic leukemia: characteristics, treatment results, and prognosis in 41 patients.Am J Med. 1994;97:60–65.
Larson RA, Dodge RK, Burns CP, et al. A five-drug remission induction regimen with intensive consolidation for adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Cancer and Leukemia Group B study 8811.Blood. 1995;85:2025–2037.
Wetzler M, Dodge RK, Mrozek K, et al. Prospective karyotype analysis in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: the Cancer and Leukemia Group B experience.Blood. 1999;93:3983–3993.Immunophenotypic Analysis of Thai Adult ALL Cases
Faderl S, Kantarjian HM, Thomas DA, et al. Outcome of Philadelphia chromosome-positive adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;36:263–273.
Annino L, Ferrari A, Cedrone M, et al. Adult Philadelphiachromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia: experience of treatments during a ten-year period.Leukemia. 1994;8:664–667.
Bloomfield CD, Secker-Walker LM, Goldman Al, et al. Six-year follow-up of the clinical significance of karyotype in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1989;40:171–185.
Fenaux P, Lai JL, Morel P, et al. Cytogenetics and their prognostic value in childhood and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) excluding L3.Hematol Oncol. 1989;7:307–317.
Specchia G, Mininni D, Guerrasio A, Palumbo G, Pastore D, Liso V. Ph positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: molecular and clinical studies.Leuk Lymphoma. 1995;18(suppl 1):37–42.
Groupe Français de Cytogénétique Hématologique. Cytogenetic abnormalities in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: correlations with hematologic findings and outcome: a collaborative study of the Groupe Français de Cytogénétique Hématologique.Blood. 1996;87:3135–3142.
Ko BS, Tang JL, Tsai W, et al. Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Taiwan.Ann Hematol. 2001;80:510–515.
Boucheix C, David B, Sebban C, et al. Immunophenotype of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia, clinical parameters and outcomes: an analysis of a prospective trial, including 562 tested patients (LALA87).Blood. 1994;84:1603–1612.
Preti HA, Huh YO, O’Brien SM, et al. Myeloid markers in adult acute lymphocytic leukemia: correlations with patient and disease characteristics and with prognosis.Cancer. 1995;76:1564–1570.
Tabernero MD, Bortoluci AM, Alaejos I, et al. Adult precursor B-ALL with BCR/ABL gene rearrangements displays a unique immunophenotype based on the pattern of CD10, CD34, CD13 and CD38 expression.Leukemia. 2001;15:406–414.
Cascavilla N, Musto P, D’Arena G, Ladogana S, Matera R, Carotenuto M. Adult and childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: clinico-biological differences based on CD34 antigen expression.Haematologica. 1997;82:31–37.
Thomas X, Archimbaud E, Charrin C, Magaud JP, Fiere D. CD34 expression is associated with major adverse prognostic factors in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Leukemia. 1995;9:249–253.
Khaldi HS, Chyang KL, Medeiros LJ, et al. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: survey of immunophenotype, French-American-British classification, frequency of myeloid antigen expression, and karyotypic abnormalities in 210 pediatric and adult cases.Am J Clin Pathol. 1998;111:467–476.
Annino L, Vegna ML, Camera A, et al. Treatment of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): long-term follow-up of the GIMEMA ALL 0288 randomized study.Blood. 2002;99:863–871.
Zhang MJ, Hoelzer D, Horowitz MM, et al. Long-term follow-up of adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia in first remission treated with chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation: the Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Working Committee.Ann Intern Med. 1995;123:428–431.
Drucker BJ, Sawyers CL, Kantarjian H, et al. Activity of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in the blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia with the Philadelphia chromosome.N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1038–1042.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Udomsakdi-Auewarakul, C., Promsuwicha, O., Tocharoentanaphol, C. et al. Immunophenotypes and Outcome of Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive and -Negative Thai Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int J Hematol 78, 337–343 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983559
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983559