Abstract
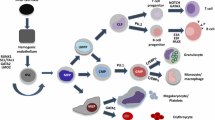
It has been well established that a number of transcription factors play critical roles in regulating the fate of hematopoietic stem cell populations. One of them is the leukemia-associated transcription factor acute myeloid leukemia 1 (AML1; also known as runt-related transcription factor 1, or RUNX1). This gene was originally cloned from the breakpoint of the t(8;21) reciprocal chromosome translocation and was later recognized as one of the most frequent targets of leukemia-associated gene aberrations. Gene-targeting experiments revealed that transcriptionally active AML1 is essential for the establishment of definitive hematopoiesis. More specifically, this gene functions in the emergence of the hematopoietic progenitor cells from the hemogenic endothelium by budding in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region, and its expression points to the sites with strong potential for the emergence of hematopoietic stem cells. This review discusses aspects of the biologic properties of AML1 in early hematopoietic development.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Okuda, T., Nishimura, M., Nakao, M. et al. RUNX1/AML1: A Central Player in Hematopoiesis. Int J Hematol 74, 252–257 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982057
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02982057