Abstract
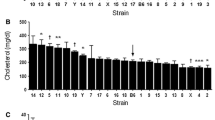
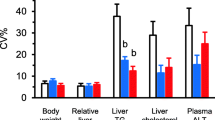
Nine inbred strains of mice, which are progenitors of recombinant inbred sets, were evaluated for aortic lesion formation and plasma and liver lipid levels. This survey was done to determine if a semi-synthetic high-fat diet could elicit the same extent of diet-induced atherosclerosis as that observed in mice fed a natural ingredient highfat diet and to discover strain-specific plasma and liver lipid variants for future genetic characterization. Evaluation of aortic lesions after 18 wk of diet consumption showed that strains C57BL/6J, C57L/J, SWR/J and SM/J were susceptible to atherosclerosis and that A/J, AKR/J, C3H/HeJ, DBA/2J and SJL/J were relatively resistant. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were negatively correlated to lesion formation. Susceptible strains had decreased HDL-C levels when switched from chow to the semi-synthetic high-fat, high cholesterol diet, whereas resistant strains either showed no change or a slight increase in HDL-C levels. The exception to this pattern was found in SM mice, which were susceptible to aortic lesion formation but maintained the same HDL-C level on both chow and high-fat diets. HDL size differed among the strains, and levels of plasma apolipoprotein A-I and A-II correlated with HDL-C levels. Liver damage was not correlated to HDL-C levels or to susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Mice from strain A, which are resistant to atherosclerosis, had evidence of liver damage as observed by elevated levels of plasma alanine aminotransferase activity, by liver histology, by increased liver weight and by exceptionally high hepatic cholesterol content. For all strains, the levels of liver cholesterol and triglycerides were inversely correlated with each other; phospholipids did not vary greatly among strains. No remarkable differences in hepatic fatty acid profile were noted among the strains fed the atherogenic diet, but the fatty acid profile did differ considerably from that found in the diet itself.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
- apo A-I:
-
apolipoprotein A-I
- apo-II:
-
apolipoprotein A-II
- BW:
-
body weight
- EDTA:
-
ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- HDL-C:
-
high-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- LDL-C:
-
low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
- TC:
-
total cholesterol
- VLDL:
-
very low density lipoprotein
References
Lyons, M.F., and Searle, A.G. (eds.) (1989)Genetic Variants and Strains of the Laboratory Mouse, 2nd edn., pp. 632–648, Oxford University Press, New York.
Paigen, B., Morrow, A., Holmes, P.A., Mitchell, D., and Williams, R.A. (1987)Atherosclerosis 68, 231–240.
Roberts, A., and Thompson, J. (1977)Progr. Biochem. Pharmacol. 13, 298–308.
Paigen, B., Morrow, A., Brandon, C., Mitchell, D., and Holmes, P. (1985)Atherosclerosis 57, 65–73.
Paigen, B., Ishida, B.Y., Verstuyft, J., Winters, R.B., and Albee, D. (1990)Arteriosclerosis 10, 316–323.
Nishina, P.M., Verstuyft, J., and Paigen, B. (1990)J. Lipid Res. 31, 859–869.
Izzo, C., Grillo, F., and Murado, E. (1981)Clin. Chem. 27, 371–374.
Mancini, G., Carbonara, A.O., and Heremans, J.F. (1965)Immunochem. 2, 235–254.
Lindgren, F.T. (1975) inAnalyses of Lipids and Lipoproteins (Perkins, E.G., ed.) pp. 204–224, American Oil Chemists’ Society, Champaign.
Blanche, P.G., Gong, G.L., Forte, T.M. and Nichols, A.U. (1981)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 665, 408–419.
Folch, J., Lees, M., and Sloane-Stanley, G.H. (1957)J. Biol. Chem. 226, 497–509.
Fletcher, M.J. (1968)Clin. Chim. Acta 22, 393–397.
Allain, C.C., Poon, L.S., Chang, C.S.G., Richmond, W., and Fu, P.C. (1974)Clin. Chem. 20, 470–475.
Rouser, G. (1970)Lipids, 5, 494–496.
Aubert, R., Perdereau, D., Roubiscoul, M., Herzog, J., and Lemonnier, D. (1988)Lipids 23, 48–54.
Stewart-Phillips, J.L., Lough, J., and Skamene, E. (1989)Clin. Invest. Med. 12, 121–126.
Paigen, B., Mitchell, D., Reue, K., Morrow, A., Lusis, A.J., and LeBoeuf, R.C. (1987)Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 3763–3767.
Paigen, B., Nesbitt, M.N., Mitchell, D., Albee, D., and LeBoeuf, R.C. (1989)Genetics, 122, 163–168.
Rubin, E.M., Krauss, R.M., Spangler, E.A., Verstuyft, J.G., and Clift, S.M. (1991)Nature 353, 265–269.
Hwa, J.J., Zollman, S., Warden, C.H., Taylor, B.A., Edwards, P.A., Fogelman, A.M., and Lusis, A.J. (1992)J. Lipid Res. 33, 711–725.
Ishida, B.Y., Blanche, P.J., Nichols, A.V., and Yashar, M. (1991)J. Lipid Res. 32, 559–568.
Jiao, S., Cole, T., Kitchens, T.T., Pfleger, B., and Schonfeld, G. (1990)Metabolism 39, 155–160.
Woollett, L.A., Spady, B.K., and Dietschy, J.M. (1989)J. Clin. Invest. 84, 119–128.
Srivastava, R.A.K., Jiao, S., Tang, J., Pfleger, B.A., Kitchens, R.T., and Schonfeild, G. (1991)Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1086, 29–43.
Beynen, A.C., Katan, M.B., and Van Zutphen, L.F.M. (1987)Adv. Lipid Res., 22, 115–171.
Lusis, A.J., Taylor, B.A., Quon, D., Zollman, S., and LeBoeuf, R.C. (1987)J. Biol. Chem. 262, 7594–7604.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Nishina, P.M., Wang, J., Toyofuku, W. et al. Atherosclerosis and plasma and liver lipids in nine inbred strains of mice. Lipids 28, 599–605 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536053
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02536053