Summary
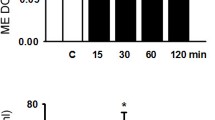
Two atypical neuroleptic agents, clozapine and fluperlapine, produced rapid elevations in plasma PRL concentrations that were similar in magnitude to those produced by haloperidol. However, the PRL response to clozapine or fluperlapine was of much shorter duration than that elicited by haloperidol. Clozapine, but neither fluperlapine nor haloperidol, produced a rapid increase in the activity of tuberoinfundibular dopamine (TIDA) neurons, as evidenced by an enhanced accumulation of dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) in the median eminence after the inhibition of DOPA decarboxylase. The clozapine-induced increase in DOPA accumulation was evident within 30 minutes after its administration and persisted for at least 4 hours. The clozapine-induced increase in the activity of TIDA neurons may account, in part, for the abbreviated PRL response to this neuroleptic. In addition, ability to produce a short-lived increase in PRL secretion in the rat appears to be common to the atypicl neuroleptic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartholini G, Haefely W, Jalfre M, Keller HH, Pletscher A (1972) Effects of clozapine on central catecholaminergic neuron systems. Br J Pharmacol 46: 736
Ben-Jonathan N, Oliver C, Mical RS, Porter JC (1977) Dopamine in hypophysial portal plasma of the rat during the estrous cycle and throughout pregnancy. Endocrinology 100: 542–548
Bjerkenstedt L, Gullberg B, HÄrnyrd C, Sedvall G (1979) Relationship between clinical and biochemical effects of melperone and thiothixene in psychotic women. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr 227: 181–192
Bjerkenstedt L, Eneroth P, HÄrnyrd C, Sedvall G (1977) Effects of melperone and thiothixene on prolactin levels in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of psychotic women. Arch Psychiat Nervenkr 224: 281–293
Caron MG, Beaulieu M, Raymond V, Gagné B, Drouin J, Lefkowitz RJ, Labrie F (1978) Dopaminergic receptors in the anterior pituitary gland. J Biol Chem 253: 2244–2253
Chiodo CA, Bunney BS (1983) Typical and atypical neuroleptics; differential effects of chronic administration on the activity of A 9 and A 10 midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neuroscience 3: 1607–1619
Clemens JA, Smalstig EG, Sawyer BD (1974) Antipsychotic drugs stimulate prolactin release. Psychopharmacology 40: 123–127
Creese I, Schneider R, Snyder SH (1977)3H-spiroperidol labels dopamine receptors in pituitary and brain. Eur J Pharmacol 46: 377–381
Cronin MJ, Roberts JM, Weiner RI (1978) Dopamine and dihydroergocryptine binding to the anterior pituitary and other brain areas of the rat and sheep. Endocrinology 103: 302–309
Cuello AC, Horn AS, Mackay AVP, Iversen LL (1974) Catecholamines in the median eminence: new evidence for a major noradrenergic input. Nature 243: 465–467
Demarest KT, Moore KE (1979) Comparison of dopamine synthesis regulation in terminals of nigrostriatal, mesolimbic, tuberoinfundibular and tuberohypophyseal neurons. J Neural Transm 46: 263–277
Demarest KT, Moore KE (1980) Accumulation of L-dopa in the median eminence: An index of tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic nerve activity. Endocrinology 106: 463–468
Demarest KT, Moore KE (1981) Sexual differences in the sensitivity of tuberoinfundibular dopamine neurons to the actions of prolactin. Neuroendocrinology 33: 230–234
Demarest KT, Riegle GD, Moore KE (1984) Prolactin-induced activation of tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons: evidence for both a rapid tonic and a delayed induction component. Neuroendocrinology 38: 467–475
Dieterle D, Eben E, EinhÄupi K, Hippius H, Klein H, Rüther E, Schmauss M (1984) The effect of fluperlapine in acute psychotic patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 17: 57–60
Eichenberger E (1984) Pharmacology of fluperlapine compared with clozapine. Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res 34: 110–113
Fink H, Morgenstern R, Oelssmer W (1984) Clozapine — a serotonin antagonist. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20: 513–517
Fischer-Cornellsen KA (1984) Fluperlapine in 104 schizophrenic patients. Open multicenter trial. Arzneimittelforschung 34: 125–130
Gibbs DM, Neill JD (1978) Dopamine levels in hypophysial stalk blood in the rat are sufficient to inhibit prolactin secretionin vivo. Endocrinology 102: 1895–1900
Gudelsky GA (1981) Tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons and the regulation of prolactin secretion. Psychoneuroendocrinology 6: 3–16
Gudelsky GA, Moore KE (1976) A comparison of the effects of haloperidol on dopamine turnover in the striatum, olfactory tubercle and median eminence of the rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 202: 149–156
Gudelsky GA, Porter JC (1980) Release of dopamine from tuberoinfundibular neurons into pituitary stalk blood following prolactin or haloperidol administration. Endocrinology 106: 526–529
Korsgaard S, Noring U, Gerlach J (1984) Fluperlapine in tardive dyskinesia and parkinsonism. Psychopharmacology 84: 76–79
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AJ, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
MacLeod RM (1976) In: Martini L, Ganong WF (eds) Frontiers in neuroendocrinology. Raven Press, New York, pp 169–194
Marco E, Mao CC, Cheney DL, Reruelta A, Costa E (1976) The effects of antipsychotics on the turnover rate of GABA and acetylcholine in rat brain nuclei. Nature 264: 363–365
McMillen BA, Shore PA (1978) Comparative effects of clozapine and alphaadrenoreceptor blocking drugs on regional noradrenaline metabolism in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 52: 225–230
Meltzer HY, Daniels S, Fang VS (1976) Clozapine increases rat serum prolactin levels. Life Sci 17: 339–342
Meltzer HY, Goode DJ, Schyve PM, Young M, Fang VS (1979 a) Effect of clozapine on human serum prolactin levels. Am J Psychiat 136: 1550–1555
Meltzer HY, So R, Miller RJ, Fang VS (1979 b) Comparison of the effects of substituted benzamides and standard neuroleptics on the binding of3H-spiroperidol in the rat pituitary and striatum within vivo effects on rat prolactin secretion. Life Sci 25: 573–584
Miller RJ, Hiley CR (1974) Anti-muscarinic properties of neuroleptics and drug induced parkinsonism. Nature 248: 596–597
Nair NPV, Lal S, Cervantes C, Yassa R, Guyda H (1979) Effect of clozapine or apomorphine-induced growth hormone secretion and serum prolactin concentration in schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 5: 136–142
Pelham RW, Munsat TL (1979) Identification of direct competition for, and indirect influences on striatal muscarinic cholinergic receptors:In vitro 3H-quinuclidinyl benzilate binding in rats. Brain Res 171: 473–480
Sachar EJ, Gruen PH, Altman N, Halpern FS, Frantz AG (1976) In: Sachar EJ (ed) Hormones, behavior and psychopathology. Raven Press, New York, pp 161–176
Selmanoff M (1985) Rapid effects of hyperprolactinemia on basal prolactin secretion and dopamine turnover in the medial and lateral median eminence. Endocrinology 116: 1943–1952
Stille G, Lauener H, Eichenberg F (1971) The pharmacology of 8-chloro-11-(4-methyl-L-piperazinyl)-5H-dibenzo[b,e][1,4] diazepine (clozapine). Il Farmaco 26: 603–625
Weeks JR, Davis JD (1964) Chronic intravenous cannulas for rats. J Appl Physiol 19: 540–541
White FJ, Wang RY (1983) Differential effects of classical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on A 9 and A 10 dopamine neurons. Science 221: 1054–1057
Wiesel F-A, Bjerkenstedt L, Skett P (1978) Effect of melperone, two of its metabolites and thiothixene on central monoamine metabolism and prolactin levels in rodents. Acta pharmacol toxicol 43: 129–136
Wilk S, Watson E, Stanley ME (1975) Differential sensitivity of two dopaminergic structures in rat brain to haloperidol and to clozapine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 195: 265–270
Woggon B, Angst J, Bartels N, Heinrich K, Hippius H, Koukkon M, Kiebs E, Küfferle B, Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Poldinger W, Ruther E, Schied HW (1984) Antipsychotic efficacy of fluperlapine: an open multicenter trial. Neuropsychobiology 11: 116–120
York DH (1975) In: Iversen LE, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Biogenic amine receptors. Plenum Press, New York, pp 23–61
Young MA, Meltzer HY (1980) RMI-81582, a novel antipsychotic drug. Psychopharmacology 67: 101–106
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gudelsky, G.A., Koenig, J.I., Simonovic, M. et al. Differential effects of haloperidol, clozapine, and fluperlapine on tuberoinfundibular dopamine neurons and prolactin secretion in the rat. J. Neural Transmission 68, 227–240 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098500
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02098500