Abstract
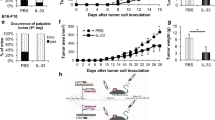
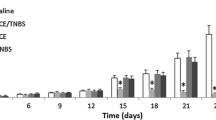
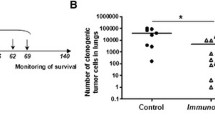
Two immunomodulatory protocols were evaluated for their ability to inhibit lung colonization by mouse mammary tumor line 4T07. Preimmunization with tumor cells or pretreatment with poly I : C were equally effective at inhibiting lung colonization but a clonogenic tumor cell assay demonstrated that the treatments reduced tumor cell burden at different steps during the metastatic process. Poly I : C pretreatment accelerated tumor cell clearance based on the recovery of clonogenic tumor cells from lungs dispersed within 6 h post-arrest. Preimmunization inhibited the subsequent replication of tumor cells which survived and established in the lung, as indicated by the expansion of clonogenic cell numbers between 1 day and 7 days post-arrest. Histologic examination of serial sections of lungs demonstrated that very few (6%) of the tumor cells were extravascular 6 h post-tumor cell injection. By 24 h and 168 h the percentages of tumor cells which were extravascular had increased to 62% and 86%, respectively. Thus, poly I : C pretreatment appears to enhance killing of tumor cells prior to extravasation, whereas preimmunization appears to inhibit tumor cells after extravasation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, J. M., andParker, E. T., 1979, Host immune treatments affecting artificial pulmonary metastases: interpretation of loss of radioactivity labelled cells from lungs.International Journal of Cancer,40, 677–688.
Crissman, J. D., Hatfield, J. S., Schaldenbrand, M., Sloane, B. F., andHonn, K. V., 1985, Arrest and extravasation of B16 amelanotic melanoma in murine lungs.Laboratory Investigation,53, 470–478.
Fidler, I. J., 1978, Tumor heterogeneity and the biology of cancer invasion and metastasis.Cancer Research,38, 2651–2660.
Fidler, I. J., Gersten, D. M., andRiggs, C. W., 1977, Relationship of host immune status to tumor cell arrest, distribution and survival in experimental metastasis.Cancer,40, 46–55.
Fidler, I. J., andHart, I. R., 1982, Biological diversity in metastatic neoplasms: origins and implications.Science,217, 998–1003.
Fulton, A. M., 1987, Interactions of natural effector cells and prostaglandins in the control of metastasis.Journal of the National Cancer Institute,78, 735–741.
Glaves, D., andWeiss, L., 1975, Effect of host sensitization on patterns of metastasis.Transplantation Proceedings,7, 253–257.
Hoover, H. C., andKetcham, A. S., 1975, Metastasis of metastases.American Journal of Surgery,130, 405–411.
Jones, D. S., Wallace, A. C., andFraser, E. E., 1971, Sequence of events in experimental metastasis of Walker 256 tumor: light, immunofluorescent, and electron microscopic.Journal of the National Cancer Institute,46, 493–504.
Liotta, L. A., andDeLisi, C., 1977, Method for quantitating tumor cell removal and tumor cell-invasive capacity in experimental metastases.Cancer Research,37, 4003–4008.
Miller, B. E., Aslakson, C. J., andMiller, F. R., 1990, Efficient recovery of clonogenic stem cells from solid tumors and occult metastatic deposits.Invasion and Metastasis,10, 101–112.
Miller, B. E., Miller, F. R., Wilburn, D., andHeppner, G. H., 1988, Dominance of a tumor subpopulation line in mixed heterogeneous mouse mammary tumors.Cancer Research,48, 5747–5753.
Miller, F. R., andHeppner, G. H., 1979, Immunologic heterogeneity of tumor cell subpopulations from a single mouse mammary tumor.Journal of the National Cancer Institute,63, 1457–1463.
Miller, F. R., andHeppner, G. H., 1982, Tumor immunity in the mammary gland.Cancer Immunology and Immunotherpay,12, 173–176.
Miller, F. R., McInerney, D. J., Rogers, C., Aitken, D. R., andWei, W.-Z., 1986, Use of drug resistance markers to recover clonogenic tumor cells from occult metastases in host tissue.Invasion and Metastasis,6, 197–208.
Miller, F. R., Miller, B. E., andHeppner, G. H., 1983, Characterization of metastatic heterogeneity amoung subpopulations of a single mouse mammary tumor: heterogeneity in phenotypic stability.Invasion and Metastasis,3, 22–31.
Vaage, J., 1989, A survey ofin vivo growth characteristics and spontaneous metastasizing potentials of C3H mouse mammary tumors.International Journal of Cancer,43, 910–914.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aslakson, C.J., McEachern, D., Conaway, D.H. et al. Inhibition of lung colonization at two different steps in the metastatic sequence. Clin Exp Metast 9, 139–150 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01756385
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01756385