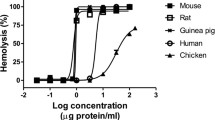
Summary
Fluorescein-labelled epidermolytic toxin (FTC-toxin) ofStaphylococcus aureus and ferritin—toxin conjugate have been prepared and purified. FTC-toxin bound selectively to cryostat and resin-impregnated sections of neonatal mouse skin. Binding was localized at the keratohyalin granules and in the stratum corneum. In an epidermal cell (granular, spinous and basal) preparation, only keratohyalin granules of the granular cells bound FTC-toxin. Ferritin—toxin conjugate bound to skin sections at the same two sites as FTC-toxin and was competitive with the binding of free toxin. Keratohyalin granules in unstained sections had a novel ‘patched’ appearance under the electron microscope, and the ferritin—toxin conjugate bound preferentially to the electron-lucent areas. In the stratum corneum it was shown by quantitative estimation that the target density decreased as the surface of the tissue was approached.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ANDERSON, P. J. (1967) Purification and quantitation of glutaraldehyde and its effect on several enzyme activities in skeletal muscle.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 15, 652–61.
AINSWORTH, S. K. & KARNOVSKY, M. J. (1972) An ultrastructural staining method for enhancing the size and electron opacity of ferritin in thin sections.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 20, 225–9.
BAILEY, C. J., DE AZAVEDO, J. & ARBUTHNOTT, J. P. (1980) A comparative study of two serotypes of epidermolytic toxin fromStaphylococcus aureus.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 624, 111–20.
BAKER, D. H., DIMOND, R. L. & WUEPPER, K. D. (1978) The epidermolytic toxin ofStaphylococcus aureus: its failure to bind to cells and its detection in blister fluids of patients with bullous impetigo.J. Invest. Dermatol. 71, 274–5.
BONNEVILLE, M. A. (1968) Observations on epidermal differentiation in the fetal rat.Amer. J. Anat. 123, 147–64.
ELIAS, P. M., FRITSCH, P., DAHL, M. V. & WOLFF, K. (1975) Staphylococcal toxic epidermal necrolysis: Pathogenesis and studies on the subcellular site of action of exfoliatin.J. Invest. Dermatol. 65, 501–12.
ELIAS, P. M., FRITSCH, P. & EPSTEIN, E. H. (1977) Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and recent microbiological and biochemical developments.Arch. Dermatol. 113, 207–19.
ENGVALL, E. & PERLMANN, P. (1972) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA III. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labelled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen coated tubes.J. Immunol. 109, 129–35.
FARBMANN, A. I. (1966) Morphological variability of keratohyalin.Anat. Rec. 154, 275–86.
FREER, J. H. & ARBUTHNOTT, J. P. (1982) Toxins ofStaphylococcus aureus.Pharmacol. Therapeut. 19, 55–106.
GALFRE, G. & MILSTEIN, C. (1981) Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures.Methods Enzymol. 73, 25–6.
GOMMANS, J. M., BERGERS, M., VAN ERP, P. E. J., VAN DEN HURK, J. J. M. A., MIER, P. D. & ROELFZEMA, H. (1979) Studies on the plasma membrane of normal and psoriatic keratinocytes.Brit. J. Dermatol. 101, 407–12.
HARDING, C. R. & SCOTT, I. R. (1983) Histidine-rich proteins (filaggrins): structural and functional heterogeneity during epidermal differentiation.J. Mol. Biol. 170, 651–73.
JARRETT, A. (1973) The physiology and pathophysiology of the skin. InThe Epidermis vol 1 (edited by JARRETT, A.), pp. 12–14. New York: Academic Press.
JOHNSON, A. D., SPERO, L., CADES, J. S. & DE CICCO, B. T. (1979) Purification and characterization of different types of exfoliative toxin fromS. aureus.Infect. Immun. 24, 679–84.
JOHNSON, G. D. & NOGUEIRA ARAUJO, G. M. DE C. (1981) A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluoresence during microscopy.J. Immunol. Methods 43, 349–50.
KAKIMI, S., FUKUYAMA, K., & EPSTEIN, W. L. (1980) A study of ultrathin frozen sections of granular cells in newborn rat epidermis.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 70, 8–14.
KONDO, I., SAKURAI, S. & SARAI, Y. (1976) Staphylococcal exfoliation A and B. InStaphylococci and Staphylococal Diseases (edited by JELJASZEWITZ, J.) pp. 489–98. Stuttgart: Gustav Fisher.
LILLIBRIDGE, C. B., MELISH, M. E. & GLASGOW, L. A. (1972) Site of action of exfoliative toxin in the Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome.Pediatrics,50, 728–38.
MALTOSY, A. G. & MALTOSY, M. N. (1970) The chemical nature of keratohyalin granules of the epidermis.J. Cell Biol. 47, 593–603.
MCLAY, A. L. C., ARBUTHNOTT, J. P. & LYELL, A. (1975) Action of Staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin on mouse skin: an electron microscopic study.J. Invest. Dermatol. 65, 423–8.
MELISH, M. E. & GLASGOW, L. A. (1970) The Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: development of an experimental model.New. Eng. J. Med. 282, 1114–19.
MONTAGNA, W. & PARAKKAL, P. F. (1974)The Structure and Function of Skin, 3rd edn., pp. 57–60. New York, London: Academic Press.
ROGOLSKY, M. (1979) Nonenteric toxins ofStaphylococcus aureus.Microbiol. Rev. 43, 320–60.
SCOTT, I. R. & HARDING, C. R. (1981) Studies of the synthesis and degradation of a high molecular weight, histidine-rich phosphoprotein from mammalian epidermis.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 669, 65–78.
SMITH, T. P. & BAILEY, C. J. (1986) Epidermolytic toxin fromStaphylococcus aureus binds to filaggrins.FEBS Letts. 194, 309–12.
STEINERT, P. M., CANTIERI, J. S., TELLER, D. C., LONSDALE-ECCLES, J. D. & DALE, B. A. (1981) Characterization of a class of cationic proteins that specifically interact with intermediate filaments.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, 4097–101.
SUZUKI, S., TSUYAMA, S., SUGANUMA, T., YAMAMOTO, N. & MURATTA, F. (1981) Postembedding staining of Brunner's gland with lectin—ferritin conjugates.J. Histochem. Cytochem. 29, 946–52.
VAN NOORDEN, S. & POLAK, J. M. (1983) Immunocytochemistry today: techniques and practice. InImmunocytochemistry, Practical Applications in Pathology and Biology (edited by POLAK, J. M. & VAN NOORDEN, S.) pp. 11–42. Bristol, London, Boston: John Wright & Sons.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, T.P., John, D.A. & Bailey, C.J. The binding of epidermolytic toxin fromStaphylococcus aureus to mouse epidermal tissue. Histochem J 19, 137–149 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01695138
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01695138