Abstract
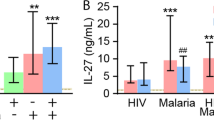
Apart from cellular immunity and immunopathology, various cytokines have been implicated in malaria-associated immunosuppression. In this study, serum levels of transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) were determined with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 37 patients with acutePlasmodium falciparum malaria prior to, during, and after therapy and in 17 healthy controls in Bangkok, Thailand. Patients were treated with artesunate and mefloquine. TGF-β serum levels were found decreased prior to treatment (14±11 pg/ml versus 63±15 pg/ml in healthy controls;P<0.05). The serum concentrations of TGF-β increased after initiation of treatment and were within normal range on day 21. Serum levels of both tumor necrosis factor-ga (TNF-α) and soluble TNF-receptor 55 kDa were inversely correlated to serum levels of TGF-β (r= −0.667 andr=}-0.592, n=37; respectively,P < 0.05 for both). No correlation between parasitemia and serum levels of TGF-β could be found. The results are compatible with a decreased production and release, an enhanced clearance or utilization, or tissue accumulation of TGF-β in acuteP. falciparum malaria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sher A, Gazzinelli RT, Oswald IP, Clerici M, Kullberg M, Pearce EJ, Berzofsky JA, Mosmann TR, James SL, Morse HC, Shearer GM: Role of T-cell derived cytokines in the downregulation of immune-responses in parasitic and retroviral infection. Immunol Rev 127:183–204, 1992
Silva JS, Twardzik DR, Reed SG: Regulation ofTrypanosoma cruzii infectionsin vitro andin vivo by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med 174:59, 1991
King CL, Mahanty S, Kumaraswami W, Abrams JS, Regunathan J, Jamarayan K, Ottesen EA, Nutman TB: Cytokine control of parasite-specific anergy in human lymphatic filariasis. Preferential induction of a regulatory T helper type 2 lymphocyte subset. J Clin Invest 92:1667–1673, 1993
Barral-Netto M, Barrai A, Brownell LE, Skeiky YAW, Ellings-worth LR, Twardzik DR, Reed SG: Transforming growth factor-β in leishmania infection: An important parasite escape mechanism. Science 257:545–548, 1992
de Kossodo S, Grau GE: Profiles of cytokine production in relation with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. J Immunol 151:4811–4820, 1993
de Kossodo S, Grau GE: Role of cytokines and adhesion molecules in malaria immunopathology. Stem Cells Dayt 11:41–48, 1993
Roberts AB, Sporn MB: The transforming growth factor-βs. Handb Exp Pharmacol 95(I):419–472
Sporn MB, Roberts AB, Wakefield LM, de Crombrugghe B: Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol 105:1039–1045, 1991
Lebman DA, Lee FD, Coifman RL: Mechanism for transforming growth factorβ and IL-2 enhancement of IgA expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated B cell cultures. J Immunol 144:952–959, 1990
Sonoda E, Matsumoto R, Hitoshi Y, Ishii, Sugimoto, Araki S, Tominaga A, Yamaguchi N, Takatsu: Transforming growth factorβ induces IgA production and acts additively with interleukin 5 for IgA production. J Exp Med 170:1415–1420, 1989
Oswald IP, Cazzinelli RT, Sher A, James SL: IL-10 synergizes with IL-4 and transforming growth factors to inhibit macrophage cytotoxic activity. J Immunol 148:3578–3582, 1992
Ding A, Nathan CF, Graycar J, Derynck R, Stuehr DJ, Srimal S: Macrophage deactivating factor and transforming growth factors-β1, -β2, and -β3 inhibit induction of macrophage nitrogen oxide synthesis by IFN-γ. J Immunol 145:940–944, 1990
Bogdan C, Nathan C: Modulation of macrophage function by transforming growth factor-β, interleukin-4, and interleukin-10. Ann NY Acad Sci 685:713–739, 1993
Looareesuwan S, Kyle DE, Viravan C, Vanijanonta S, Wilairatana P: Treatment of patients with recrudescent malaria with a sequential combination of artesunate and mefloquine. Am J Trop Med 47:794–799, 1992
Harpa ZR, Edelmann R, Wassermann SS, Levine MM, Davis JR, Sztein MB: Serum cytokine profiles in experimental human malaria. J Clin Invest 90:515–523, 1993
Mshana RN, Boucandi J, Mshana NM, Mayombo J, Mendome G: Cytokines in the pathogenesis of malaria: Levels of IL-1, IL-4, IL-6, TNFα, and IFNγ in plasma of healthy individuals and malaria patients in a holoendemic area. J Clin Lab Immunol 34:313–139, 1991
Naotunne TDS, Karunaweera ND, Del Guidice G, Kularatne MU, Grau GE, Carter R, Mendis KN: Cytokines kill malaria parasites during infection crisis: Extracellular complementary factors are essential. J Exp Med 173:523–529, 1991
Schafield L, Ferreira A, Nussenzweig V, Nussenzweig RS: Antimalarial activity of TNF and IFNα and IFNγ. Fed Proc 46:760, 1987
Taverne J, Tavernier J, Fiers W, Playfair JHL: Recombinant tumour necrosis factor inhibits malaria parasitesin vivo but notin vitro. Clin Exp Immunol 64:1–4, 1987
Kumaratilake JM, Ferrante A, Rzepcyk KL: The role of T-lymphocytes in immunity toP. falciparum: Enhancement of neutrophil-mediated killing by lymphotoxin and IFN-γ: Comparisons with TNF parasite effects. J Immunol 146:762–767, 1991
Orago ASSO, Facer CA: Cytotoxicity of human NK cell subsets forPlasmodium falciparum erythrocytic schizonts: Stimulation with cytokines and inhibition with neomycin. Clin Exp Immunol 86:22–29, 1991
Kuranaweera ND, Carter R, Grau GB, Kwiatkowski D, del Giudice G, Mendis KN: Tumour necrosis-dependent killing effects during paroxysm in non-immunePlasmodium vivax malaria patients. Clin Exp Immunol 88:499–506, 1992
Grau GE, Bieler G, Pointaire P, de Kossodo S, Tacchini-Lotier F, Kassalli P, Piquet P, Lambert PH: Significance of cytokine production and adhesion molecules in malaria immunopathology. Immunol Lett 25:189–194, 1990
Orago ASS, Facer CA: Cytokine-induced inhibition ofPlasmodium falciparum erythrocytic growthin vitro. Clin Exp Immunol 91:287–294, 1993
Ferreira A, Schofield L, Enea V, Schellekeus H, van der Meide P, Collins WE, Nussenzweig RS, Nussenzweig V: Inhibition of development of exo-erythrocytic forms of malaria parasites by interferon-γ. Science 232:881–884, 1986
Graninger W, Thalhammer F, Hollenstein U, Zotter GM, Kremsner PG: Serum protein concentrations inPlasmodium falciparum malaria. Acta Trop 52:121–128, 1992
Ho M, Webster HK, Looareesuwan S, Supanarnond W, Philips RE, Chanthavanich P, Warrell DA: Antigen-specific immunosuppression in human malaria due toPlasmodium falciparum. J Infect Dis 153:763–771, 1986
Ho M, Webster HK, Green B, Looareesuwan S, Kongchareon S, White N: Defective production of and response to IL-2 in acute falciparum malaria. J Immunol 441:2755–2759, 1988
Kremsner PG, Zotter GM, Feldmeier H, Graninger W, Rocha RM, Jansen-Rosseck R, Bienzle U: Immune responses in patients during and afterPlasmodium falciparum infection. J Infect Dis 161:1025–1028, 1990
Kremsner PG, Feldmeier H, Zotter GM, Jansen-Rosseck R, Graninger W, Rocha RM, Bienzle U: Immunological alterations in uncomplicatedPlasmodium falciparum malaria. Relationship between parasitemia and indicators of macrophage activation. Acta Trop 46:351–359, 1989
Chizzolini C, Grau GE, Geinoz A, Schrijvers D: T-lymphocyte gamma interferon production induced byPlasmodium falciparum antigen is high in recently infected non-immune and low in immune subjects. Clin Exp Immunol 79:95–99, 1990
Grau GE, Taylor TE, Molyneux ME, Wirima JJ, Vasalli P, Hommel M, Lambert PH: Tumor necrosis factor and disease severity in children withPlasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med 320:1586–1591, 1989
Kern P, Hemmer CJ, Van Damme J, Gruss HS, Dietrich M: Elevated tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 serum levels as markers for complicatedPlasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Med 87:139–143, 1989
Grau GE, Heremans H, Piquet PF, Pointaire P, Allet B, Lambert PH, Billian A, Vassalli P: Monoclonal antibody against interferon can prevent experimental cerebral malaria and its associated overproduction of tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5572–5574, 1989
Kviatkowski D, Hill AUS, Sambon I, Twumasi P, Castracane J, Manoque KR, Erami A, Brewster DR, Greenwood BM: TNF concentration in fatal cerebral, non-fatal cerebral, and uncomplicatedPlasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet 336:1201–1204, 1990
Flynn RM, Paliadino MA: TNF and TGF-beta: The opposite sides of the avenue. Tumor Necrosis Factors 131, 1992
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenisch, C., Parschalk, B., Burgmann, H. et al. Decreased serum levels of TGF-β in patients with acutePlasmodium falciparum malaria. J Clin Immunol 15, 69–73 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01541734
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01541734