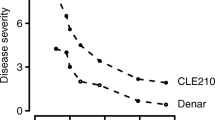
Abstract
Powdery mildew, caused byEryisphe graminis f. sp.hordei, is one of the most important diseases of barley (Hordeum vulgare). A number of loci conditioning resistance to this disease have been reported previously. The objective of this study was to use molecular markers to identify chromosomal regions containing genes for powdery mildew resistance and to estimate the resistance effect of each locus. A set of 28 F1 hybrids and eight parental lines from a barley diallel study was inoculated with each of five isolates ofE. graminis. The parents were surveyed for restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) at 84 marker loci that cover about 1100 cM of the barley genome. The RFLP genotypes of the F1s were deduced from those of the parents. A total of 27 loci, distributed on six of the seven barley chromosomes, detected significant resistance effects to at least one of the five isolates. Almost all the chromosomal regions previously reported to carry genes for powdery mildew resistance were detected, plus the possible existence of 1 additional locus on chromosome 7. The analysis indicated that additive genetic effects are the most important component in conditioning powdery mildew resistance. However, there is also a considerable amount of dominance effects at most loci, and even overdominance is likely to be present at a number of loci. These results suggest that quantitative differences are likely to exist among alleles even at loci which are considered to carry major genes for resistance, and minor effects may be prevalent in cultivars that are not known to carry major genes for resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dudley JW, Saghai Maroof MA, Rufener GK (1991) Molecular markers and grouping of parents in maize breeding programs. Crop Sci 31:718–723
Geiger HH, Heun M (1989) Genetics of quantitative resistance to fungal diseases. Annu Rev Phytopathol 27:317–341
Giese H, Holm-Jensen AG, Jensen HP, Jensen J (1993) Localization of theLaevigatum powdery mildew resistance gene to barley chromosome 2 by the use of RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 85:897–900
Hayashi J, Heta H (1985) Association of a mildew resistance geneJm1h in Hanna 906 with chromosome 6. Barley Genet Newsl 15:46–47
Heun M (1987a) Combining ability and heterosis for quantitative powdery mildew resistance in barley. Plant Breed 99:234–238
Heun M (1987b) Genetics of quantitative resistance in barley againstErysiphe graminis f. sp.hordei. Barley Genet 5:593–600
Heun M (1993) Mapping quantitative powdery mildew resistance of barley using an RFLP map. Genome 35:1019–1025
Heun M, Kennedy AE, Anderson JA, Lapitan NLV, Sorrells ME, Tanksley SD (1991) Construction of a restriction fragment length polymorphism map for barley (Hordeum vulgare). Genome 34:437–447
Hilbers S, Fischbeck G, Jahoor A (1992) Localization of theLaevigatum resistance geneMILa against powdery mildew in the barley genome by the use of RFLP markers. Plant Breed 109:335–338
Hinze K, Thompson RD, Ritter E, Salamini F, Schulze-Lefert P (1991) Restriction fragment length polymorphism-mediated targeting of theml-o resistance locus in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:3691–3695
Jensen J, Jorgensen JH, Jensen HP, Giese H, Doll H (1980) Linkage of the Hordein lociHor1 andHor2 with the powdery mildew resistance lociMl-k andMl-a on barley chromosome 5. Theor Appl Genet 58:27–31
Kleinhofs A, Kilian A, Saghai Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Hayes P, Chen FQ, Lapitan N, Fenwick A, Blake TK, Kanazin V, Ananiev E, Dahleen L, Kudrna D, Bollinger J, Knapp SJ, Liu B, Sorrells M, Heun M, Franckowiak JD, Hoffman D, Skadsen R, Steffenson BJ (1993) A molecular, isozyme and morphological map of the barley (Hordeum vulgare) genome. Theor Appl Genet 86:705–712
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Lee M, Godshalk EB, Lamkey KR, Woodman WW (1989) Association of restriction fragment length polymorphisms among maize inbreds with agronomic performance of their crosses. Crop Sci 29:1067–1071
Melchinger AE, Boppenmaier J, Dhillon BS, Pollmer WG, Herrman RG (1992) Genetic diversity for RFLPs in European maize inbreds: II. Relation to performance of hybrids within versus between heterotic groups for forage traits. Theor Appl Genet 82:672–681
Saghai Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Schuller C, Backes G, Fischbeck G, Jahoor A (1992) RFLP markers to identify the alleles on theMla locus conferring powdery mildew resistance in barley. Theor Appl Genet 84:330–338
Shin JS, Chao S, Corpuz L, Blake T (1990) A partial map of the barley genome incorporating restriction fragment length polymorphism, polymerase chain reaction, isozymes, and morphological marker loci. Genome 33:803–810
Smith OS, Smith JSC, Bowen SL, Tenborg RA, Wall SJ (1990) Similarities among a group of elite maize inbreds as measured by pedigree, F1 grain yield, grain yield, heterosis, and RFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 80:833–840
Sogaard B, Wettstein-Knowles P (1987) Barley: Genes and chromosomes Carlsberg Research Commun 52:123–196
Ward JH (1963) Hierarchal grouping to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc 58:236–244
Wettstein-Knowles P (1993) Barley (Hordeum vulgare) 2N=14. In: O'Brien SJ (ed) Genetic maps: locus maps of complex genomes. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Zhang Q, Saghai Maroof MA, Kleinhofs A (1993) Comparative diversity analysis of RFLPs and isozymes within and among populations ofHordeum vulgare ssp.spontaneum. Genetics 134: 909–916
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by A. L. Kahler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maroof, M.A.S., Biyashev, R.M. & Zhang, Q. Molecular marker analyses of powdery mildew resistance in barley. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 88, 733–740 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01253978
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01253978