Abstract
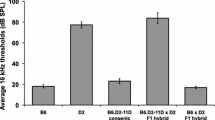
The difference in susceptibility to audiogenic seizures (AGS) between C57BL/6J and DBA/2J inbred strains of mice is due to multiple genetic factors. AGS susceptibility was tested in 21-day-old mice from classical crosses, BXD recombinant inbred (RI) strains, a congenic DBA/2N.B6N-Ah b inbred strain and crosses between the BXD RI strains and DBA/2J. Analysis of these data reveals that the variation in AGS susceptibility between these two strains results from allelic differences at three or more loci. Most of the variation is due to allelic differences at two loci. The first,Asp-1 (formerlyIas), is a major gene located on chromosome 12, betweenAh andD12 Nyul. The second,Asp-2 (formerlyasp), is a minor gene located on chromosome 4, tightly linked tob. The negative correlation of brain stem Ca2+-ATPase activity and AGS susceptibility in the BXD RI strains suggests that the strain difference in Ca2+-ATPase activity is inherited as a polygenic trait and thatAsp-1 andAsp-2 are linked to, or identical to, factors that influence Ca2+-ATPase activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ault, B., and Wang, C. M. (1986). Adenosine inhibits epileptiform activity arising in hippocampal area CA3.Br. J. Pharmacol. 87:695–703.
Bailey, D. W. (1978). Sources of subline divergence and their relative importance for sublines of six major inbred strains of mice. In Morse, H. C., III (ed.),Origins of Inbred Mice, Academic Press, New York, pp. 197–215.
Carey, G. (1988). Inference about genetic correlations.Behav. Genet. 18:329–338.
Cobb, R. R., Stoming, T. A., and Whitney, J. B., III (1987). The aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase (Ah) locus and a novel restriction-fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) are located on mouse chromosome 12.Biochem. Genet. 25:401–413.
Coleman, D. L. (1960). Phenylalanine hydroxylase activity in dilute and nondilute strains of mice.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 91:300–306.
Collins, R. L. (1970). A new genetic locus mapped from behavioral variation in mice: Audiogenic seizure prone (asp).Behav. Genet. 1:99–109.
Collins, R. L. (1972). Audiogenic seizures. In Purpura, D. P., Penry, J. K., Tower, D. B., Woodbury, D. M., and Walter, R. D. (eds),Experimental Models of Epilepsy: A Manual for the Laboratory Worker, Raven Press, New York, pp. 347–372.
Collins, R. L. (1974). Maltese dilution, chromosome 9, and audiogenic seizures in DBA/2 mice: experimental evaluation.Brain Res. 70:541–546.
Collins, R. L., and Fuller, J. L. (1968). Audiogenic seizure prone (asp): A gene affecting behavior in linkage group VIII of the mouse.Science 162:1137–1139.
Davisson, M. T., and Roderick, T. H. (1981). Recombination percentages. In Green, M. C. (ed.),Genetic Variants and Strains of the Laboratory Mouse, Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart, pp. 283–313.
Davisson, M. T., Roderick, T. H., Hillyard, A. L., and Doolittle, D. P. (1988). Linkage map of the mouse.Mouse News Lett. 81:12–19.
D'Eustachio, P. (1984). A genetic map of mouse chromosome 12 composed of polymorphic DNA fragments.J. Exp. Med. 160:827–838.
Dunwiddie, T. V., and Worth, T. (1982). Sedative and anticonvulsant effects of adenosine analogs in mouse and rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 220:70–76.
Ferrendelli, J. A. (1984). Roles of biogenic amines and cyclic nucleotides in seizure mechanisms.Ann. Neurol. 16 (Suppl.):S98-S103.
Fuller, J. L., and Sjursen, F. H., Jr. (1967). Audiogenic seizures in eleven mouse strains.J. Hered. 58:135–140.
Fuller, J. L., Easler, C., and Smith, M. E. (1950). Inheritance of audiogenic seizure susceptibility in the mouse.Genetics 35:622–632.
Ginsburg, B. E., and Miller, D. S. (1963). Genetic factors in audiogenic seizures. In Busnel, R. G. (ed.),Colloques Internationaux du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique No. 112: Psychopathologie, Neuropharmacologie et Biochimie de la Crise Audiogene, Editions du Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, Paris, pp. 217–225.
Ginsberg, B. E., Cowen, J. S., Maxson, S. C., and Sze, P. Y. (1967). Biochemical effects of gene mutations associated with audiogenic seizures.Excerpta Med. Int. Congr. Ser. 175:695–701.
Hall, C. S. (1947). Genetic differences in fatal audiogenic seizures between two inbred strains of house mice.J. Hered. 38:2–6.
Henry, K. R. (1986). Audiogenic seizures in relation to genetically and experimentally produced cochlear pathology. In Fuller, J. L., and Simmel, E. C. (ed.),Perspectives in Behavior Genetics, Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ, pp. 57–93.
Huff, S. D., and Huff, R. L. (1962). Dilute locus and audiogenic seizures in mice.Science 136: 318–319.
Huff, S. D., and Fuller, J. L. (1964). Audiogenic seizures, the dilute locus, and phenylalanine hydroxylase in DBA/1 mice.Science 144:304–305.
Hume, R. I., and Honig, M. G. (1986). Excitatory action of ATP on embryonic chick muscle.J. Neurosci. 6:681–690.
International Committee on Standardized Genetic Nomenclature for Mice (1985). Rules for nomenclature of genes, chromosome anomalies and inbred strains.Mouse News Lett. 72:2–28.
Jahr, C. E., and Jessell, T. M. (1983). ATP excites a subpopulation of rat dorsal horn neurones.Nature 304:730–733.
Laird, H. E., II, Dailey, J. W., and Jobe, P. C. (1984). Neurotransmitter abnormalities in genetically epileptic rodents.Fed. Proc. 43:2505–2509.
Legraverend, C., Karenlampi, S. O., Bigelow, S. W., Lalley, P. A., Kozak, C. A., Womack, J. E., and Nebert, D. W. (1984). Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction by benzo[a]anthracene: Regulatory gene localized to the distal portion of mouse chromosome 17.Genetics 107:447–461.
Maitre, M., Ciesielski, L., Lehmann, A., Kempf, E., and Mandel, P. (1974). Protective effect of adenosine and nicotinamide against audiogenic seizure.Biochem. Pharmacol. 23:2807–2816.
Nebert, D. W., (1980). Pharmacogenetics: An approach to understanding chemical and biological aspects of cancer.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 64:1279–1290.
Neumann, P. E., Seyfried, T. N., and Collins, R. L. (1989). Nomenclature changes for audiogenic seizure susceptibility genes.Mouse News Lett. 83:157.
Palayoor, S. T., and Seyfried, T. N. (1984). Genetic association between Ca2+-ATPase activity and audiogenic seizures in mice.J. Neurochem. 42:1771–1774.
Palayoor, S. T., Seyfried, T. N., and Bernard, D. J. (1986). Calcium ATPase activities in synaptic plasma membranes of seizure-prone mice.J. Neurochem. 46:1370–1375.
Roderick, T., and Davisson, M. T. (1987). Nomenclature change: Ias to asp-1.Mouse News Lett. 77:106.
Schlesinger, K., Elston, R. C., and Boggan, W. (1966). The genetics of sound induced seizure in inbred mice.Genetics 54:95–103.
Seyfried, T. N. (1979). Audiogenic seizures in mice.Fed. Proc. 38:2399–2404.
Seyfried, T. N. (1982a). Convulsive disorders. In Foster, H. L., Small, J. D., and Fox, J. C. (eds.),The Mouse in Biomedical Research, Vol. 4, Academic Press, Orlando, FL, pp. 97–124.
Seyfried, T. N. (1982b). Developmental genetics of audiogenic seizure susceptibility in mice. In Anderson, V. E., Hauser, W. A., Penry, J. K., and Sing, C. F. (eds.),Genetic Basis of the Epilepsies, Raven Press, New York, pp. 199–210.
Seyfried, T. N. (1983). Genetic heterogeneity for the development of audiogenic seizures in mice.Brain Res. 271:325–329.
Seyfried, T. N., and Glaser, G. H. (1981). Genetic linkage between the Ah locus and a major gene that inhibits susceptibility to audiogenic seizures in mice.Genetics 99:117–126.
Seyfried, T. N., Glaser, G. H., and Yu, R. K. (1978). Cerebral, cerebellar and brainstem gangliosides in mice susceptible to audiogenic seizures.J. Neurochem. 31:21–27.
Seyfried, T. N., Yu, R. K., and Glaser, G. H. (1980). Genetic analysis of audiogneic seizures susceptibility in C57BL/6J×DBA/2J recombinant inbred strains of mice.Genetics 94:701–718.
Seyfried, T. N., Glaser, G. H., Yu, R. K., and Palayoor, S. T. (1986). Inherited convulsive disorders in mice. In Delgado-Escueta, A. V., Ward, A. A., Jr., Woodbury, D. M., and Porter, J. R. (eds.),Advances in Neurology, Vol. 44, Raven Press, New York, pp. 115–133.
Silver, J. (1985). Confidence limits for estimates of gene linkage based on analysis of recombinant inbred strains.J. Hered. 76:436–440.
Taylor, B. A. (1988). BXD-32 RI strain contaminated.Mouse News Lett. 81:72.
Wieraszko, A., and Seyfried, T. N. (1989). Increased amount of extracellular ATP in stimulated hippocampal slices of seizure prone mice.Neurosci. Lett. 106:287–293.
Wieraszko, A., Goldsmith, G., and Seyfried, T. N. (1989). Stimulation dependent release of ATP from hippocampal slices.Brain Res. 485:244–250.
Witt, G., and Hall, C. S. (1949). The genetics of audiogenic seizures in the house mouse.J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 42:58–63.
Wood, A. W., and Taylor, B. A. (1979). Genetic regulation of coumarin hydroxylase activity in mice: Evidence for single locus control on chromosome 7.J. Biol. Chem. 254:5647–5661.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by grants from the HRC Foundation, NIH (NS 20820, NS 23355, and NS 24826), and NSF (BNS 8305449).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neumann, P.E., Seyfried, T.N. Mapping of two genes that influence susceptibility to audiogenic seizures in crosses of C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Behav Genet 20, 307–323 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067798
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01067798