Abstract
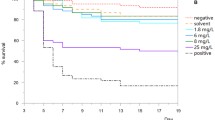
Medicago sativa L. (Leguminosae) sprayed withO,O-dimethylS-(N-methylcarbamoylmethyl) phosphorodithioate (dimethoate) had only 0.5 ppm of dimethoate in pollen one day later, but 3 ppm in nectar one week later, and 1 ppm in nectar two weeks later. As little as 1 ppm added to syrup fed to caged workers ofApis mellifera L. (Apidae) inhibited cholinesterase and reduced survival. Bees given a choice between treated and untreated syrups showed no preference; this suggests that the levels of dimethoate found in nectar are toxic and not repellent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, L. D., and A. S. Deal: Cygon. Honeybee problem on onions. Univ. Calif. Riverside. Mimeo. Field Report (1965).
Anonymous: Pesticide use report by commodity 1976. State of California, Dept. of Food and Agriculture, Sacramento (1977).
Barker, R. J., and G. D. Waller: Sublethal effects of parathion, methyl parathion or formulated methoprene fed to colonies of honey bees. Environ. Entomol.7, 569 (1978).
Ellman, G. L., R. D. Courtney, V. Andres, Jr., and R. M. Featherstone: A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol.7, 88 (1961).
Hameed, S. F., R. L. Adlakha, and S. P. Giamza: Relative toxicity of some insecticides to the workers ofApis mellifera L. Madras Agric. J.60, 552 (1973).
Jaycox, E. R.: Effect on honey bees of nectar from systemic insecticide-treated plants. J. Econ. Entomol.57, 3 (1964).
Johansen, C. A.: Pesticides and pollinators. Annu. Rev. Entomol.22, 177 (1977).
Lord, K. A., M. A. May, and J. H. Stevenson: The secretion of the systemic insecticides dimethoate and phorate into nectar. Ann. Appl. Biol.61, 19 (1968).
Mizuta, H. M., and C. A. Johansen: The hazard of plant-systemic insecticides to nectar-collecting bees. Washington Agric. Exp. Stn., Pullman, Tech. Bull. 72 (1972).
Palmer-Jones, T., I. W. Forster, and G. L. Jeffery: Effect on honey bees of Rogor and Endothion applied from the air as sprays to brassicas. J. Agri. Res.2, 475 (1959).
Saini, M. L., and A. D. Khurana: Persistent toxicity of some systemic insecticides to little honey bee. Pesticides1, 24 (1968).
Stevenson, J. H.: Laboratory studies on the acute contact and oral toxicities of insecticides to honeybees. Ann. Appl. Biol.61, 467 (1968).
Wafa, A. K., M. K. Ahmed, and A. M. Shoeb: Toxicity of field applications of phosphorus insecticides to the honeybee. Bull. Entomol. Soc. Egypt, Econ. Ser.1, 155 (1966).
Waller, G. D., and R. J. Barker: Effects of dimethoate on honey bee colonies. J. Econ. Entomol. (in press) (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barker, R.J., Lehner, Y. & Kunzmann, M.R. Pesticides and honey bees: Nectar and pollen contamination in alfalfa treated with dimethoate. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 9, 125–133 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055368
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055368