Abstract
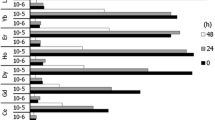
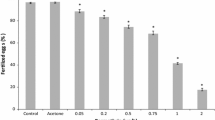
The gametes and embryos of three sea urchin species were exposed to cadmium chloride at concentrations ranging from 10−8 M to 10−3 M. When zygotes were reared in the presence of Cd2+, skeletal differentiation displayed some severe abnormalities or was suppressed, as a function of Cd2+ level. The embryotoxic action of Cd2+ was inversely related to salinity and to Ca2+ concentration. Cadmium-exposed larvae displayed similar abnormalities if Cd2+ was present throughout development or only after hatching, while pre-hatching exposure produced no developmental defects. No aberrations in mitotic figures were observed in cleaving eggs following acute exposure to Cd2+. The pretreatment of sperm or eggs did not affect the ensuing development of embryos, both for acutely toxic Cd2+ levels (up to 10−2M), and for prolonged exposures in relatively low Cd2+ levels. The fertilization rate was differently affected depending on whether sperm or eggs were pretreated;i.e., the exposure of eggs to Cd2+ promoted fertilization at relatively high Cd2+ levels. If sperm was exposed to Cd2+, a depression of fertilizing capacity was observed at high Cd2+ levels, while lower Cd2+ levels, displayed an opposite action, resulting in an increase in fertilization rate after prolonged sperm exposure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauchinger, M., E. Schmid, H. J. Einbrodt, and J. Dresp: Chromosome aberrations in lymphocytes after occupational exposure to lead and cadmium. Mutation Res.40, 57 (1976).
Bresch, H., R. Spielhoff, U. Mohr, and H. Barkemeyer: Use of the sea urchin egg for quick screen testing of the biological activities of substances. I. Influence of fractions of a tobacco smoke condensate on early development. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.141, 747 (1972).
Bui, T. H., J. Lindsten, and G. F. Nordberg: Chromosome analysis of lymphocytes from cadmium workers and Itai Itai patients. Environ. Res.9, 187 (1975).
Chernoff, N.: Teratogenic effects of cadmium in rats. Teratology8, 29 (1973).
de Angelis, E., and G. G. Giordano: Sea urchin egg development under the action of benzo(a)pyrene and 7,12-dimethylbenz-(a)anthracene. Cancer Res.39, 1275 (1974).
Deknudt, G., and A. Léonard: Cytogenetic investigations on leucocytes of workers from a cadmium plant. Environ. Physiol. Biochem.5, 319 (1975).
Deknudt, G., and G. B. Gerber: Chromosomal aberrations in bone-marrow cells of mice given a normal and a calcium-deficient diet supplemented with various heavy metals. Mutation Res.68, 163 (1979).
Engel, D. W., and B. A. Fowler: Factors influencing cadmium accumulation and its toxicity to marine organisms. Environ. Health Persp.28, 81 (1979).
Hagström, B. E., and B. Hagström: The effect of decreased and increased temperatures on fertilization. Exp. Cell Res.16, 174 (1959).
Hagström, B. E., and S. Lönning: The sea urchin as a testing object in toxicology. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol.32, Suppl. 1 (1973).
—: The effects of Esso Corexit 9527 on the fertilizing capacity of spermatozoa. Mar. Poll. Bull.8, 136 (1977).
Larsson, S. E., and M. Piscator: Effect of cadmium on skeletal tissue in normal and calcium-deficient rats. Israel J. Med. Sci.7, 495 (1971).
Layton, W. M., Jr. and M. W. Layton: Cadmium-induced limb defects in mice: Strain associated differences in sensitivity. Teratology19, 229 (1979).
O'Riordan, M. L., E. G. Hughes, and H. J. Evans: Chromosome studies on blood lymphocytes of men occupationally exposed to cadmium. Mutation Res.58, 305 (1978).
Pagano, G., A. Esposito, G. G. Giordano, and B. E. Hagström: Embryotoxic and teratogenic effects of styrene and its derivatives on sea urchin development. Scand J. Work Environ. Health4, Suppl. 1, 136 (1978).
Parizek, J.: The peculiar toxicity of cadmium during pregnancy-an experimental “toxaemia of pregnancy” induced by cadmium salts. J. Reprod. Fertil.9, 111 (1965).
Rosenkranz, P. G., D. R. Gordon, W. T. Speck, and H.S. Rosenkranz: Developmental abnormalities in the American sea urchin induced by povidone-iodine, a widely used vaginal antiseptic. Mutation Res.77, 387 (1980).
Rünnström, J.: Veränderungen der Plasmakolloide bei der Entwicklungserregung des Seeigelseies. Protoplasma4, 388 (1928).
Samarawickrama, G. P., and M. Webb: Acute effects of cadmium on the pregnant rat and embryo-fetal development. Environ. Health Persp.28, 245 (1979).
Umeda, M., and M. Nishimura: Inducibility of chromosomal aberrations by metal compounds in cultured mammalian cells. Mutation Res.67, 221 (1979).
Voyer, R. A., J. F. Heltsche, and R. A. Kraus: Hatching success and larval mortality in an estaurine teieost,Menidia menidia (Linnaeus), exposed to cadmium in constant and fluctuating salinity regimes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol.23, 475 (1979)
Wolverton, B. C., and R. C. McDonald: Bioaccumulation and detection of trace levels of cadium in aquatic systems byEichhornia crassipes. Environ. Health Persp.27, 161 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagano, G., Esposito, A. & Giordano, G.G. Fertilization and larval development in sea urchins following exposure of gametes and embryos to cadmium. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 11, 47–55 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055185
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01055185