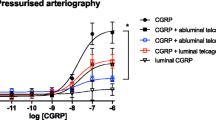
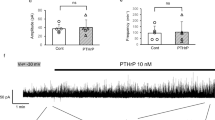
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) on the K+ channels of vascular smooth muscle cells. Cultured smooth muscle cells from a porcine coronary artery were studied using the patch-clamp technique. Extracellular application of 100 nM CGRP activated two types of K+ channels the Ca2+-activated K+ channel (KCa channel) and the ATP-sensitive K+ channel (KATP channel) in cell-attached patch configurations. In cells pretreated with Rp-cAMPS, a membrane-permeable inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), extracellular application of 100 nM CGRP could not activate the KCa or KATP channel, indicating that the activation of the K+ channels by CGRP occurs in connection with PKA. In the cell-attached patch configurations, extracellular application of 1 mM dibutyryl cAMP, a membrane permeable cAMP, activated KCa and KATP channels. In inside-out patch configurations, application of PKA to the cytosolic side activated both the KCa and KATP channels. These results indicate that CGRP modulates the K+ channels of vascular smooth muscle cells via adenylate cyclase, i.e., cAMP-PKA pathway, and contributes to control of vascular tone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brain SD, Williams TJ, Tippins JR, Morris HR, MacIntyre I (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide is a potent vasodilator. Nature 313: 54–56
Brayden JE, Nelson MT (1992) Regulation of arterial tone by activation of calcium-dependent potassium channels. Science 256: 532–535
Edwards RM, Stack EJ, Trizna W (1991) Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates adenylate cyclase and relaxes intracerebral arterioles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257: 1020–1024
Emeson RB, Hedjran F, Yeakley JM, Guise JW, Rosenfeld MG (1989) Alternative production of calcitonin and CGRP mRNA is regulated at the calcitonin-specific splice acceptor. Nature 341: 76–80
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patchclamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391: 85–100
Ishikawa T, Okamura N, Saito A, Masaki T, Goto K (1988) Positive inotropic effect of calcitonin gene-related peptide mediated by cyclic AMP in guinea pig heart. Circ Res 63: 726–734
Jansen I, Mortensen A, Edvinsson L (1992) Characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptors in human cerebral vessels: vasomotor responses and cAMP accumulation. Ann NY Acad Sci 657: 435–440
Kageyama M, Yanagisawa T, Taira N (1993) Calcitonin gene-related peptide relaxes porcine coronary arteries via cyclic AMP-dependent mechnisms, but not activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265: 490–497
McCulloch J, Uddman R, Kingman TA, Edvinsson L (1986) Calcitonin generelated peptide: Functional role in cerebrovascular regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 5731–5735
Minami K, Fukuzawa K, Nakaya Y (1993) Protein kinase C inhibits the Ca2+-activated K+ channel of cultured porcine coronary artery smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 190: 263–269
Minami K, Fukuzawa K, Nakaya Y, Zeng X, Inoue I (1993) Mechanism of activation of the Ca2+-activated K+ channel by cyclic AMP in cultured porcine coronary artery smooth musole cells. Life Sci 53: 1129–1135
Miyoshi H, Nakaya Y (1993) Activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in cultured smooth muscle cells of porcine coronary artery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193: 240–247
Miyoshi Y, Nakaya Y, Wakatsuki T, Nakaya S, Fujino K, Saito K, Inoue I (1992) Endothelin blocks ATP-sensitive K+ channels and depolarizes smooth muscle cells of porcine coronary artery. Circ Res 70: 612–616
Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, Rodrigo J, Allen JM, Rosenfeld MG, Polak JM, Bloom SR (1985) Calcitonin generelated peptide in cardiovascular tissues of the rat. Neuroscience 14: 947–954
Nelson MT, Huang Y, Brayden JE, Hescheler J, Standen NB (1990) Arterial dilations in response to calcitonin generelated peptide involve activation of K+ channels. Nature 344: 770–773
Nelson MT, Patlak JB Worley JF, Standen NB (1990) Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol 259: C3-C18
Quayle JM, Bonev AD, Brayden JE, Nelson MT (1994) Calcitonin generelated peptide activated ATP-sensitive K+ currents in rabbit arterial smooth muscle via protein kinase A. J Physiol 475: 9–13
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod J, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 304: 129–135
Ross R (1971) The smooth muscle cell. J Cell Biol 50:172–186
Wakatsuki T, Nakaya Y, Inoue I (1992) Vasopressin modulates K+-channel activities of cultured smooth muscle cells from porcine coronary artery. Am J Physiol 263: H491-H496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyoshi, H., Nakaya, Y. Calcitonin gene-related peptide activates the K+ channels of vascular smooth muscle cells via adenylate cyclase. Basic Res Cardiol 90, 332–336 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00797911
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00797911