Summary
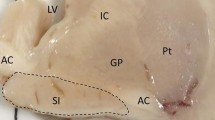
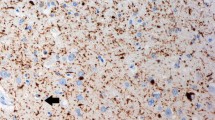
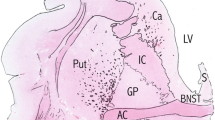
The nucleus basalis of Meynert, the major source of cholinergic innervation of the cerebral cortex, was morphometrically investigated in 58 cases of neuropsychiatric disorders and compated to 14 controls. The results demonstrate a loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer's disease (70%), paralysis agitans (77%), and Korsakoff's disease (47%) but no marked reduction of neurons in postencephalitic parkinsonism, Huntington's disease, chronic alcoholism without dementia, schizophrenia and infantile brain damage. Neurons of the three subdivisions of the nucleus basalis of Meynert (the nucleus septi medialis, the nucleus of the diagonal band of Broca and the nucleus basalis Meynert neurons in the substantia innominata) may be affected in a different manner in different patients within a single group homogeneous with respect to the usual clinical and neuropathological diagnostic criteria. Cell loss in the basal forebrain is restricted to the large neurons of the nucleus basalis, the immediately adjacent neurons of the globus pallidus externus not being affected. The selective degeneration of these neurons provides the morphological correlate of the cortical cholinergic deficiency in these neuropathological conditions. The degeneration of this discrete cholinergic neuronal population in several disorders of higher cortical function is probably directly related to the progressive deterioration of memory and cognitive processes in affected patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antuono P, Sorbi S, Bracco L, Fusco T (1980) A discrete sampling technique in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type and alcoholic dementia: study of the cholinergic system. In: Amaducci L, Davison AN, Antuono P (eds) Aging of the brain and dementia. Raven Press, New York, pp 151–158
Averback P (1981) Lesions of the nucleus ansae peduncularis in neuropsychiatric disease. Arch Neurol 38:230–235
Bigl V, Woolf NJ, Butcher LL (1982) Cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain to frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital and cingulate cortices: a combined fluorescent tracer and acetylcholinesterase analysis. Brain Res Bull 8:727–750
Bird ED, Barnes J, Iversen LL, Spokes EG, Mackay AVP, Shepherd M (1977) Increased brain dopamine and reduced glutamic acid decarboxylase and choline acethyltransferase activity in schizophrenia and related psychoses. Lancet II:1157–1159
Bowen EP (1976) Behavioural alterations in patients with basal ganglia lesions. In: Yahr M (ed) The basal ganglia Raven Press, New York, pp 169–180
Bowen DM, Davison AN (1978) Changes in brain lysosomal activity, neurotransmitter-related enzymes, and other proteins in senile dementia. In: Katzman R, Terry RD, Bick KL (eds) Alzheimer's disease. Raven Press, New York, pp 421–424
Bowen DM, Smith CB, White P, Davidson AN (1976) Neurotransmitter-related enzymes and indices of hypoxia in senile dementia and other abiotrophies. Brain 99:459–496
Brockhaus H (1942) Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen über den Basalkernkomplex. J Psychol Neurol 51:57–95
Buttlar-Brentano K von (1952) Pathohistologische Feststellungen am Basalkern Schizophrener. J Nerv Ment Dis 116:646–653
Buttlar-Brentano K von (1955) Das Parkinsonsyndrom im Lichte der lebensgeschichtlichen Veränderungen des Nucleus basalis. J Hirnforsch 2:55–76
Davies P, Maloney AJF (1976) Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet II:1403
Davis KL, Yesavage JA (1979) Brain acetylcholine and disorders of memory. In: Davis KL, Berger PA (eds) Brain acetylcholine and neuropsychiatric disease. Plenum Press, New York, pp 205–213
De Kosky ST, Bass NH (1980) Effects of aging and senile dementia on the microchemical pathology of human cerebral cortex. In: Amaducci L, Davison AN, Antuono P (eds) Aging of the brain and dementia. Raven Press, New York, pp 33–38
De Long M (1972) Activity of basal ganglia neurons during movement. Brain Res 4:127–135
Divac J (1975) Magnocellular nuclei of the basal forebrain project to neocortex, brain stem and olfactory bulb. Review of some functional correlates. Brain Res 93:385–398
Fuld PA (1976) Storage retention and retrieval in Korsakoff's syndrome. Neuropsychologia 14:225–236
Fulton JF, Ingraham FD (1929) Emotional disturbances following experimental lesions of the base of the brain (prechiasmal). J Physiol (Lond) 67:27–28
Gorry JR (1963) Studies on the comparative anatomy of the ganglion basale of Meynert. Acta Anat 55:51–104
Hassler R (1938) Zur Pathologie der Paralysis agitans und des postenzephalitischen Parkinsonismus. J Psychol Neurol 48:387–476
Hassler R (1965) Extrapyramidal control of the speed of behavior and its change by primary age prcesses. In: Welford AT, Birrin JT (eds) Behavior, aging, and the nervous system. Thomas, Springfield, IL, pp 284–306
Johnston MV, McKinney N, Coyle JT (1979) Evidence for a cholinergic projection to neocortex from neurons in basal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5392–5396
Jones EG, Burton H, Saper CB, Swanson LW (1976) Midbrain, diencephalic and cortical relationship of the nucleus basalis of Meynert and associated structures in primates. J Comp Neurol 167:385–397
Kimura H, McGeer PL, Peng F, McGeer EG (1980) Choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons in rodent brain demonstrated by immunohistochemistry. Science 208:1057–1059
Kimura H, McGeer PL, Peng F, McGeer EG (1981) The central cholinergic system studied by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry in the cat. J Comp Neurol 200:151–201
Kitt CA, Price DL, De Long MR, Struble RG, Mitchell SJ, Hedreen JC (1982) The nucleus basalis of Meynert. Projections to the cortex, amygdala and hippocampus. Abstr Ann Meet Soc Neurosci 8:212
Lehman J, Nagy JI, Atmadja S, Fibiger HC (1980) The nucleus basalis magnocellularis: the origin of a cholinergic projection to the neocortex of the rat. Neuroscience 5:1161–1174
Lewy, FH (1923) Die Lehre vom Tonus und der Bewegung. Springer, Berlin
Linseman MA (1974) Inhibitory unit activity of the ventral forebrain during both appetitive and aversive Pavlovian conditioning. Brain Res 80:146–151
Lo Conte G, Casamenti F, Bigl V, Milaneschi E, Pepeu G (1982) Effect of magnocellular forebrain nuclei lesions on acetylcholin output from the cerebral cortex electrocorticogram and behaviour. Arch Ital Biol 120:176–188
Marchbanks RM (1982) Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 39:9–15
McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1976) Enzymes associated with the metabolism of catecholamines, ACh and GABA in human cortex and patients with Parkinson's disease and Huntington's chorea. J Neurochem 26:65–76
McGinty DJ, Sterman MB (1968) Sleep suppression after basal forebrain lesions in the cat. Science 160:1253–1255
Mesulam M, van Hoesen GW (1976) Acetylcholinesterase-rich projections from the basal forebrain of the rhesus monkey to neocortex. Brain Res 109:152–157
Meudell P, Butters N, Montgomery K (1978) Role of rehearsal in the short-term memory performance of patients with Korsakoff's and Huntington's disease. Neuropsychologia 16:507–510
Meyer U, Wenk H, Bigl V (1979) Cholinergic connections in the CNS of rats determined by lesions technique and quantitative histochemistry. In: Matthies H, Krug M, Popov N (eds) Biological aspects of learning, memory formation and ontogeny of the CNS. Proceedings of the Fifth International Neurobiological Symposium, Magdeburg, June 6–9, 1977. Akademie-Verlag, Berlin
Meynert T (1872) Vom Gehirn der Säugetiere. In: Stricker's Handbuch der Lehre von den Geweben des Menschen, Bd. 2. Engelmann, Leipzig
Nakano I, Hirano A (1982) Loss of large neurons of the medial septal nucleus in an autopsy case of Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 41:341
Nakano I, Hirano A (1982) Neuron loss in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in paralysis agitans and parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam. Ann Neurol 12:96
Nakano I, Hirano A (1983) Neuron loss in the Nucleus basalis of Meynert in parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam. Ann Neurol 13:87–91
Obrist WD, Busse EW, Eisdorfer C, Kleemeier RW (1962) Relation of the electroencephalogram to intellectual function in senescence. J Gerontol 17:197–206
Richter JA, Perry EK, Tomlinson BE (1980) Acetylcholine and choline levels in post-mortem human brain tissue: preliminary observations in Alzheimer's disease. Life Sci 26:1683–1689
Robinson BW, Mishkin M (1968) Alimentary responses to forebrain stimulation in monkey. Exp Brain Res 4:330–366
Rolls ET, Sanqhera MK, Roper-Hall A (1979) The latency of activation of neurons in the lateral hypothalamus and substantia innominata during feeding in the monkey. Brain Res 164:121–135
Rossor MN, Svendsen C, Hunt SP, Mountjoy CQ, Roth M, Iversen LL (1982) The substantia innominata in Alzheimer's disease: A histochemical and biochemical study of cholinergic marker enzymes. Neurosci Lett 28:217–222
Ruberg M, Ploska A, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y (1982) Muscarinic binding and choline acetyltransferase activity in parkinsonian subjects with reference to dementia. Brain Res 232:129–139
Siegel J, Wang RY (1974) Electroencephalographic, behavioral, and single-unit effects produced by stimulation of forebrain inhibitory structures in cats. Exp Neurol 42:28–50
Slaby AE, Wyatt RJ (1974) Dementia in the presenium. Thomas, Springfield, IL
Smith CM, Swash M (1978) Possible biochemical basis of memory disorder in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 3:471–473
Soininen H, Partanen JV, Puranen M, Riekkinen PJ (1982) EEG and computed tomography in the investigation of patients with senile dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 45:711–714
Spokes GS (1982) Huntington's chorea. In: Giuffrida Stella AM, Gombos G, Benzi G, Bachelard HS (eds) Basic and clinical aspects of molecular neurobiology. Proc 4th Meet Eur Soc Neurochem. Catania, pp 65–75
Terry RD (1978) Senile dementia. Fed Proc 37:2837–2840
Terry RD, Davies P (1980) Dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Rev Neurosci 3:77–95
Terry RD, Fitzgerald C, Peck A, Millner J, Farmer P (1977) Cortical cell counts in senile dementia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 36:633
Tomlinson BF, Blessed G, Roth M (1970) Observations on the brains of demented old people. J Neurol Sci 11:205–242
Uhl GR, McKinney M, Hedreen JC, White III CL, Coyle JT, Whitehouse PJ, Price DL (1982) Dementia pugilistica: loss of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons and cortical cholinergic markers. Ann Neurol 12:99
Wang HS (1977) Dementia of old age. In: Smith WL, Kinsbourne M (eds) Aging and dementia. Spectrum, New York, pp 1–24
Wenk H, Bigl V, Meyer U (1980) Cholinergic projections from magnocellular nuclei of the basal forebrain to cortical areas in rats. Brain Res Rev 2:295–316
Wenk H, Bigl V, Meyer U, Biesold D (1981) Cholinergic pathways to the cerebral cortex in rats. In: Pepeu G, Ladinsky H (eds) Cholinergic mechanisms. Phylogenetic aspects, central and peripheral synapses, and clinical significance. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 673–683
Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Clark AW, Coyle JT, De Long MR (1981) Alzheimer disease: evidence for selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the nucleus basalis. Ann Neurol 10:122–126
Whitehouse PJ, Price DL, Sruble RG, Clark AW, Coyle JT, De Long MR (1982) Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia: loss of neurons in the basal forebrain. Science 215:1237–1239
Yates CM, Simpson J, Maloney AFJ, Gordon A, Reid AH (1980) Alzheimer-like cholinergic deficiency in Down's syndrome. Lancet II:979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arendt, T., Bigl, V., Arendt, A. et al. Loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer's disease, paralysis agitans and Korsakoff's disease. Acta Neuropathol 61, 101–108 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00697388
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00697388