Abstract
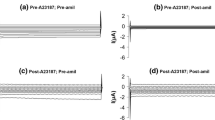
Using the patch-clamp technique, Na+ selective channels were observed in the luminal membrane of rabbit straight proximal tubule segments. In the cell-attached configuration (NaCl-Ringers in pipette and bath) influx of Na+ ions from the pipette into the cell through fluctuating channels was observed was observed. The current-voltage curve of these Na+ channels yielded a zero-current potential of 84.3±30.9 mV (n=10), reflecting the electrochemical driving force for Na+ influx under resting conditions. The single channel conductance was 12.0±2.1 pS (n=13). In inside-out oriented cell-excised patches the single channel conductance was not significantly different with NaCl-Ringers on both sides. At clamp potentials ranging from +50 mV to −50 mV the single channel current was ohmic and channel kinetics were independent of the voltage. With KCl-Ringers on the bath side (corresponding to cell interior), the zero current potential was 62±19 mV (n=4), indicating a high selectivity of Na+ over K+ ions. Addition of 10−5 mol/l amiloride to the bathing solution decreased the mean channel open time slightly. This effect was more pronounced with 10−4 mol/l amiloride, whereas the single channel conductance was unaffected by the diuretic. 10−3 mol/l amiloride caused a complete block of the channel. It is concluded that amiloride sensitive Na+ channels, with similar properties to those observed in tight epithelia, contribute to Na+ reabsorbtion in the straight portion of proximal tubules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bello-Reuss E (1982) Electrical properties of the basolateral membrane of the straight portion of the rabbit proximal renal tubule. J Physiol 326:49–63
Cardinal J, Lapointe JY, Laprade R (1984) Luminal and peritubular ionic substitutions and intracellular potential of the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol 247:F352-F364
Elgavish GA, Elgavish A (1985) Evidence from23Na NMR studies for the existence of sodium-channels in the brush border membrane of the renal proximal tubule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 128:746–753
Fenwick E, Marty A, Neher E (1982) A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. J Physiol 331:577–597
Frömter E (1975) Magnitude and significance of the paracellular shunt path in rat kidney proximal tubule. In: Kramer M, Lauterbach F (eds) Intestinal permeation. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp 393–405
Frömter E (1984) Viewing the kidney through microelectrodes. Am J Physiol 247:F695-F705
Gögelein H, Greger R (1984) Single channel recordings from basolateral and apical membranes of renal proximal tubules. Pflügers Arch 401:424–426
Greger R, Hampel W (1981) A modified system for in vitro perfusion of isolated renal tubules. Pflügers Arch 189:175–176
Hamil OP, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp technique for high resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hamilton KL, Eaton DC (1985) Single-channel recordings from amiloride-sensitive epithelial sodium channel. Am J Physiol 249:C200-C207
Lindemann B, Van Driessche W (1977) Sodium specific membrane channels of frog skin are pores: current fluctuations reveal high turnover. Science 195:292–294
Marty A, Neher E (1983) Tight-seal whole-cell recording. In: Sakmann B, Neher E (eds) Single-channel recording. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 107–122
Moran A, Moran N (1984) Amiloride-sensitive channels in LLC-PK1 apical membranes. Fed Proc 43:447
Palmer LG, Frindt G (1985) Single channels in the apical membrane of rabbit cortical collecting tubule. Vth European Colloquium on Renal Physiology, Frankfurt/Main, p 12
Reinhardt R, Garty H, Lindemann B (1985) Sodium single channel events observed after fusion of membrane vesicles from toad urinary bladder to planar bilayers. Vth European Colloquium on Renal Physiology, Frankfurt/Main, p 135
Sabolic I, Burckhardt G (1984) Effect of the preparation method on Na+−H+ exchange and ion permeabilities in rat renal brush-border membranes. Biochim Biophys acta 772:140–148
Sariban-Sohraby S, Latorre R, Burg M, Olans L, Benos D (1984) Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channels reconstituted into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature 308:80–82
Sheik MI, Kragh-Hansen U, Roigaard-Petersen H (1985) Localization of the proximal tubular Na+/H+ exchange system. Vth European Colloquium on Renal Physiology, Frankfurt/Main, p 215
Ullrich KJ, Cassola AC, Papavassiliou F, Frömter E, Hopfer U (1982) Induction by low Na+ diet of amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport in the proximal convolution of the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch 392:R14
Völkl H, Greger R (1985) Effects of phlorrhizin and temperature changes on basolateral membrane potential on isolated in vitro perfused proximal tubules of mouse kidney. Pflügers Arch 403:R39
Warnock DG, Eveloff J (1982) NaCl entry mechanisms in the luminal membrane of the renal tubule. Am J Physiol 242:F561-F574
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gögelein, H., Greger, R. Na+ selective channels in the apical membrane of rabbit late proximal tubules (pars recta). Pflugers Arch. 406, 198–203 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586683
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00586683