Abstract
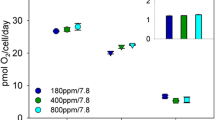
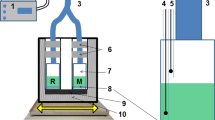
An automatically operated method for high precision measurements of steady-state photosynthesis by macroalgae was developed. Changes in pH and oxygen content of seawater passing the algae in a flowthrough system, could be measured with extremely high accuracy over very long periods of time. The method is especially suitable for measurements on flowthrough systems with high rates of water exchanges (i.e. short retention time), and can be used to study exchange processes for marine plants, animals and small ecosystems. Since the same measuring unit is used for several flowthrough chambers, the method is very suitable for comparisons between different species, or between differently pretreated specimens of the same species (e.g. in toxicological studies). The method was used to study the ratio: [oxygen production] to [CO2+H+ uptake] at different light intensities for several macroalgae belonging to different systematic groups and from different habitats. At lower photosynthetic rates this ratio was similar for all of the algae studied (1.17±0.02). For brown algae of the fucacean family, the ratio increased by 0.08 units at higher photosynthetic rates. This increase was thought to be related to the crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM)-like strategies connected to these algae. For all other algae studied, the ratio remained constant or decreased slightly (at most by 0.04 units) at higher photosynthetic rates. The relations between the abovementioned ratio and the photosynthetic quotient are discussed on a theoretical basis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
American Society for Testing and Materials (1983). Standard test methods for carbon dioxide and bicarbonate and carbonate ions in water. ASTM designation: D 513–82
Atkinson, M., Smith, S. V. (1983). C:N:P ratios of benthic marine plants. Limnol. Oceanogr. 28: 568–574
Axelsson, L., Uusitalo, J. (1988). Carbon acquisition strategies for marine macroalgae.I. Utilization of proton exchanges visualized during photosynthesis in a closed system. Mar. Biol. 97: 295–300
Brechignac, F., Andre, M. (1984). Oxygen uptake and photosynthesis of the red macroalga, Chondrus crispus, in seawater. Effects of light and CO2 concentration. Plant Physiol. 75: 919–923
Fogg, G. E. (1981). The ecology of an extracellular metabolite of seaweeds. In: Fogg, G. E., Jones, W. E. (ed.) Proc. 8. Int. Seaweed Symp. United College of North Wales, Menai Bridge, pp. 46–53
Gagne, J. A., Larochelle, J., Cardinal, A. (1979). A solubilization technique to prepare algal tissue for liquid scintillation counting, with reference to Fucus vesiculosus L. Phycologia 18: 168–170
Garret, D. E., Carpenter, J. H. (1966). Comparison and evaluation of currently employed modifications of the Winkler method for determining dissolved oxygen in seawater. A NASCO report. J. mar. Res. 24: 286–318
Hansson, I. (1973). A new set of pH-scales and standard buffers for sea water. Deep-Sea Res. 20: 479–491
Harris, G. P. (1980). The measurement of photosynthesis in natural populations of phytoplankton. In: Morris, J. (ed.) The Physiological Ecology of Phytoplankton. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p. 129–187
Hofslagare, O., Samuelson, G., Hällgren, J., Pejrud, C., and Sjöberg, S. (1985). A comparison between three methods of measuring photosynthetic uptake of inorganic carbon in algae. Photosyntetica 19: 578–585
Hofslagare, O., Samuelson, G., Sjöberg, S., Ingri, N. (1983). A precise potentiometric method for determination of algal activity in an open CO2 system. Plant Cell Envir. 6: 195–201
Joliffe, E. A., Tregunna, E. B. (1970). Studies on HCO −3 ion uptake during photosynthesis in benthic marine algae. Phycologia 9: 293–303
Kerby, N. W., Raven, J. A. (1985). Transport and fixation of inorganic carbon by marine algae. Adv. bot. Res. 11: 71–123
Kremer, P. B. (1981). Carbon metabolism. In: Lobban, C. S., Wynne, M. J. (eds.). The biology of seaweeds. Blackwell Scientific Publications. Oxford, p. 493–533
Lindahl, P. E. B. (1963). The inhibition of the photosynthesis of aquatic plants by tetramethylthiuram disulphide. Symbolae Both. Upsaliensis 17: 1–47
Lucas, W. J. (1983). Photosynthetic assimilation of exogenous HCO −3 by aquatic plants. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 34: 71–104
Öström, B. (1977). Solubility of CO2, total CO2 content and primary production in sea water. Relationships and formulae for calculations. Bot. mar. 20: 69–74
Peterson, B. J. (1980). Aquatic primary productivity and the 14C−CO2 method: a history of the productivity problem. A. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 11: 363–385
Raven, J. A., Osborne, B. A. and Johnston, A. M. (1985). Uptake of CO2 by aquatic vegetation. Plant Cell Envir. 8: 417–425
Richardson, K., Samuelson, G., and Hällgren, J.-H. (1984). The relationship between photosynthesis measured by 14C incorporation and by uptake of inorganic carbon in unicellular algae. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 81: 241–250
Ryberg, H., Axelsson, L. (1985). Specialized organelle arrangement related to a light buffering system in the brown algal family Fucaceae. Physiol. Plant. 64: 25A
Stumm, W., Morgan, J. J. (1981). Aquatic chemistry. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by T. Fenchel, Copenhagen
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Axelsson, L. Changes in pH as a measure of photosynthesis by marine macroalgae. Mar. Biol. 97, 287–294 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391314
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391314