Summary
-
1.
Archerfish (Toxotes chatareus) spit droplets of water at aerial insect prey, knocking them onto the water surface to be eaten. Since the fish's eyes remain completely below the water surface during sighting and spitting the fish must deal with potentially severe refraction effects at the air-water interface. High speed (200 f.p.s.) motion picture films of 480 spitting sequences were analyzed to determine the magnitude of the refraction effect and to suggest how the fish compensate for it.
-
2.
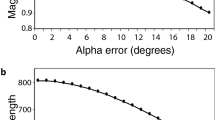
T. chatareus do not shoot from a position directly below the prey, but can correctly set their spitting angle to compensate for the refraction unique to a variety of positions (Fig. 6). The fish can correct (Fig. 14) for large refraction effects on the prey's apparent elevation (Fig. 12) or apparent height (Fig. 13). They may be enabled to do so by a rather precise linear relationship between the real elevation of the prey from the nose and the apparent elevation from the eye which exists during sighting (Fig. 15) and spitting. However, spitting accuracy decreases with increasing prey height (Fig. 7) or range (Fig. 8).
-
3.
The archerfish must also correct for significant curvature of the water droplet's trajectory (Fig. 10). Since shot velocity is relatively constant (Fig. 9) the fish must make this correction via their spitting angle, but the stage in the spitting process at which this occurs is unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekoff, M., Dorr, R.: Predation by “shooting” in archerfish, Toxotes jaculatrix: Accuracy and sequences. Bull. Psychonom. Soc. 7, 167–168 (1976)
Buckley, F.G. Buckley, P.A.: Comparative feeding ecology of wintering adult and juvenile royal terns (Aves: Laridae, Sterninae). Ecology 55, 1053–1063 (1974)
Ficken, R.W., Wilmot, L.B.: Do facial eye-stripes function in avian vision? Amer. Midl. Naturalist 79, 522–523 (1968)
Godfrey, W.E.: The birds of Canada. Nat. Mus. Canada, Bull. 203, 428pp. (1966)
Harris, M.P.: Unusual feeding by the blue-footed boody. Auk 92, 601–602 (1975)
Hediger, H., Heusser, H.: Zum “Schießen” des Schützenfisches, Toxotes jaculatrix. Natur und Volk 91, 237–243 (1961)
Jerkins, F.A., White, H.E.: Fundamentals of optics (2nd ed.) Toronto: McGraw-Hill 1950
Kalleberg, H.: Observations in a stream tank of territoriality and competition in juvenile salmon and trout (Salmo salar L. and S. trutta L.). Inst. Freshwater Res., Drottnigholm, Rept. 39, 55–98 (1958)
Krekorian, C.O., Dunham, D.W.: Preliminary observations on the reproductive and parental behavior of the spraving characid Copeina arnoldi Regan. Z. Tierpsychol. 31, 419–437 (1972)
Lüling, K.H.: Morphologisch-anatomische und histologische Untersuchungen am Auge des Schützenfisches Toxotes jaculatrix (Pallas 1766) (Toxotidae), nebst Bemerkungen zum Spuckgehaben. Z. Morphol. Okol. Tiere 47, 529–610 (1958)
Lüling, K.H.: The archerfish. Sci. Amer. 209, 100–129 (1963)
Milburn, O., Alexander, R.McN.: The performance of the muscles involved in spitting by the archerfish Toxotes. J. Zool., Lond. 180, 243–251 (1976)
Phillips, G.C.: Survival value of the white coloration of gulls and other sea birds. D. Phil. thesis, Oxford Univ. p. 221 (1962)
Salt, G.W., Willard, D.E.: The hunting behavior and success of Forster's tern. Ecology 52, 989–998 (1971)
Schreiber, R.W., Woolfenden, G.E., Curtsinger, W.E.: Prey capture by the Brown Pelican. Auk 92, 649–654 (1975)
Smith, H.M.: The fresh-water fishes of Siam, or Thailand. Bull. Smithsonian Instit. 188, 622 pp. (1945)
Sterba, G.: Freshwater fishes of the world (Translated by D. Tucker) p. 878. London: Vista Books 1962
Timmermans, P.J.A. The preycatching behaviour of the archerfish, Toxotes. Neth. J. Zool. 25, 381 (1975)
Vierke, J.: Das Wasserspucken der Arten der Gattung Colisa (Pisces: Anabantidae). Bonn. Zool. Beitr. 24, 62–104 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dill, L.M. Refraction and the spitting behavior of the archerfish (Toxotes chatareus). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 2, 169–184 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361900
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00361900