Abstract
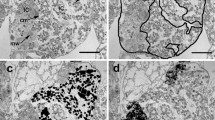
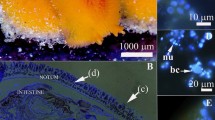
Symbiotic filamentous bacteria thrive in the intestinal caecum of the deposit-feeding echinoid Echinocardium cordatum. Specimens of E. cordatum were collected at Wimereux (Nord Pas-de-Calais, France) in 1991. Their symbiotic bacteria build nodules by forming multilayered mats around detrital particles that enter the caecum. The morphological features of the bacteria are those of Thiothrix, a sulfide-oxidizing genus. The filaments, which may form rosettes, are sheathed and made by a succession of hundreds of rod-shaped bacteria which store elemental sulfur in the presence of external sulfide. Live bacteria are restricted to the outer layers of the nodules. Their sulfide-oxidizing activity was investigated, using a Biological Oxygen Monitor, by measuring the O2-consumption when reduced sulfur compounds are provided. They oxidize thiosulfate and sulfide. Optimal sulfide oxidation occurs at intermediary pO2 (100 to 160 μM O2l-1). Spectrophotometry has confirmed that the sulfur content of the filamentous symbiotic sulfideoxidizing bacteria depends on the presence of external sulfide. This is the first report of symbiotic intradigestive Thiothrixspp.-like bacteria; it lengthens the list of symbioses between sulfide-oxidizing bacteria and invertebrates from sulfide-rich habitats.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bland, J. A., Staley, J. T. (1978). Observation on the biology of Thiothrix. Archs. Microbiol. 117: 79–87
Burgh, M. E. de, Singla, C. L. (1984). Bacterial colonization and endocytosis on the gill of a new limpet species from a hydrothermal vent. Mar. Biol. 84: 1–6
Cavanaugh, C. M. (1983). Symbiotic chemoautotrophic bacteria in marine invertebrates from sulphide-rich habitats. Nature, Lond. 302: 58–61
Cavanaugh, C. M., Gardiner, S. L., Jones, M. L., Jannasch, H. W., Waterbury J. B. (1981). Prokaryotic cells in the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila Jones: possible chemoautotrophic symbionts. Science, N.Y. 213: 340–342
Charlot, G. (1966). Dosage des sulfures solubles en milieu acide fort par l'iode. In: Les méthodes de la chimie analytique, analyse quantitative minérale. Masson et Cie Paris, p. 1023
De Ridder, C. (1986). La nutrition chez les échinodermes psammivores. Etude particulière du spatangide fouisseur Echinocardium cordatum (Pennant) (Echinodermata, Echinoïdea). Université Libre de Bruxelles (Faculté des Sciences) Ph. D. Thesis, Brussels
De Ridder, C., Jangoux, M. (1985). Origine des sédiments ingérés et durée du transit digestif chez l'oursin spatangide, Echinocardium cordatum (Pennant) (Echinodermata) Annls Inst. océanogr. Paris 6: 51–58
De Ridder, C., Jangoux, M., De Vos, L. (1985). Description and significance of a peculiar intradigestive symbiosis between bacteria and a deposit-feeding echinoid. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 96: 65–75
De Ridder, C., Jangoux, M., Van Impe, E. (1985). Food selection and absorption efficiency in the spatangoid echinoid, Echinocardium cordatum (Echinodermata). In: Keegan, B. F., O'Connor, B. D. (eds.) Proc. 5th int. Echinoderm Conf. Galway. Balkema, Rotterdam, p. 507–512
Felbeck, H. (1981). Chemoautotrophic potentials of the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila (Vestimentifera). Science, N. Y. 213: 336–338
Felbeck, H. (1983). Sulfide oxidation and carbon fixation by the gutless clam Solemya reidi: an animal-bacteria symbiosis. J. Comp. Physiol. 152: 3–11
Felbeck, H. (1985). CO2 fixation in the hydrothermal vent tube worm Riftia pachyptila Jones. Physiol. Zoöl. 58: 272–281
Felbeck, H., Childress, J. J., Somero, G. N. (1981). Calvin-Benson cycle and sulfide oxidation enzymes in animals from sulfide-rich habitats. Nature, Lond. 293: 291–293
Fenchel, T., Finlay, B. J. (1989). Kentorphoros: a mouthless ciliate with a symbiotic kitchen garden. Ophelia 30: 75–93
Fenchel, T., Riedl, R. J. (1970). The sulfide system: a new biotic community underneath the oxidized layer of marine sand bottoms. Mar. Biol. 7: 255–268
Gaill, F., Desbruyères, D., Prieur, D. (1987). Bacterial communities associated with “Pompei worms” from the East Pacific Rise hydrothermal vents: SEM, TEM observations. Microb. Ecol. 13: 129–139
Gaill, F., Desbruyères, D., Prieur, D., Gourret, J. P. (1984). Mise en évidence de communautés bactériennes épibiontes du “Ver de Pompei” (Alvinella pompejana). C. r., hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci. Paris 298 (III): 553–558
Giere, O., Langheld, C. (1987). Structural organisation, transfer and biological fate of endosymbiotic bacteria in gutless oligochaetes. Mar. Biol. 93: 641–650
Giere, O., Wirsen, C. O., Schmidt, C., Jannasch, H. W. (1988a). Contrasting effect of sulfide and thiosulfate on symbiotic CO2-assimilation of Phallodrilus leukodermatus (Annelida). Mar. Biol. 97: 413–419
Giere, O., Rhode, B., Dubilier, N. (1988b). Structural peculiarities of the body wall of Tubificoides benedii (Oligochaeta) and possible relations to its life in sulphidic sediments. Zoomorphology 108: 29–39
Harold, R., Stanier, R. Y. (1955). The genera Leucothrix and Thiothrix. Bact. Rev. 19: 49–64
Hazeu, W., Batenburg-van der Vegte, W. H., Bos, P., van der Pas, R. K., Kuenen, J. G. (1988). The production and utilization of intermediary elemental sulfur during the oxidation of reduced sulfur compounds by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Archs Microbiol. 150: 574–579
Jannasch, H. W., Mottl, M. J. (1985). Geomicrobiology of deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Science, N. Y. 229: 717–725
Jannasch, H. W., Wirsen, C. O. (1981). Morphological survey of microbial mats near deep-sea thermal vents. Appl. envirl. Microbiol. 41: 528–538
Jørgensen, B. B., DesMarais, D. J. (1986). Competition for sulfide among colorless and purple sulfur bacteria in cyanobacterial mats. Fedn eur. microbiol. Soc. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 38: 179–186
Jørgensen, B. B., Revsbesch, N. P. (1983). Colorless sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, Beggiatoa spp. and Thiovulum spp., in O2 and H2S microgradients. Appl. envirol Microbiol. 45: 1261–1270
Kuenen, J. G., Bos, P. (1988). Habitats and ecological niches of chemolitho(auto)trophic bacteria. In: Schlegel, H. G., Bowien, B. (eds.) Autotrophic bacteria. Science Tech. Publ., Madison, Wisconsin, p. 53–80
Larkin, J. M. (1980). Isolation of Thiothrix in pure culture and observation of a filamentous epiphyte on Thiothrix. Curr. Microbiol. 4: 155–158
Larkin, J. M., Henk, M. C., Burton, S. D. (1990). Occurrence of a Thiothrix sp. attached to mayfly larvae and presence of parasitic bacteria in the Thiothrix sp. Appl. envirl Microbiol. 56: 357–361
Laubier, L., Desbruyères, D., Chassard-Bouchaud, C. (1983). Microanalytical evidence of sulfur accumulation in a polychaete from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Mar. Biol. Lett. 4: 113–116
Lawrey, N. V., Jani, V., Jensen, T. E. (1981). Identification of the sulfur inclusion body in Beggiatoa alba B18LD by energy-dispersive X-ray microanalysis. Curr. Microbiol. 6: 71–74
Le Pennec, M., Fiala-Medioni, A. (1988). The role of the digestive tract of Calyptogena laubieri and Calyptogena phaseoliformis, vesicomyid bivalves of the subduction zones of Japan. Oceanologica Acta 11: 193–199
Loiseleur, J. (1963). Techniques de laboratoire, Vol 2. Chimie clinique. Masson et Cie, Paris
Nelson, D. C., Wirsen, C. O., Jannash, H. W. (1989). Characterization of large autotrophic Beggiatoa spp. abundant at hydrothermal vents of the Guayamas Bassin. Appl. envirol Microbiol. 55: 2909–2917
Oeschger, R., Schmaljohann, R. (1988). Association of various types of epibacteria with Halicryptus spinulosus (Priapulida). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 48: 285–293
Ott, J. A., Novak, R. (1989). Living at an interface: meiofauna at the oxygen/sulfide boundary of marine sediments. In: Ryland, J. S., Tyler, P. A. (eds.) Reproduction, genetics and distribution of marine organisms. 23rd European Marine Biology Symposium, p. 415–422
Powell, E. N., Crenshaw, M. A., Rieger, R. M. (1979). Adapatations to sulfide in the meiofauna of the sulfide system I. 35S-sulfide accumulation and the presence of a sulfide detoxification system. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 37: 57–76
Prieur, D., Jeanthon, C. (1987). Preliminary study of heterotrophic bacteria isolated from two deep-sea hydrothermal vent invertebrates: Alvinella pompejana (Polychaete) and Bathymodiolus thermophilus (Bivalve). Symbioses 4: 87–98
Rau, G. H., Hedges, J. I. (1979). Carbon-13 depletion in a hydrothermal vent mussel: suggestion of chemosynthetic food source. Science, N. Y. 203: 648–649
Reid, R. G. B., Brand, D. G. (1986). Sulfide-oxydizing symbiosis in lucinaceans: implications for bivalve evolution. Veliger 29 (1): 3–24
Somero, G. N., Childress, J. J., Anderson, A. E. (1989). Transport, metabolism, and detoxification of hydrogen sulfide in animals from sulfide-rich marine environments. CRC critical Rev. aquat. Sci. 1: 591–614
Southward, A. J., Southward, E. C., Dando, P. R., Barrett, R. L., Ling, R. (1986). Chemoautotrophic function of bacterial symbionts in small pogonophora. J. mar. biol. Ass. U. K. 66: 415–437
Strohl, W. R. (1974). Beggiatoales. In: Buchanan, R. E., Gibbons, N. E. (eds.) Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology, 8th edn. The Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, Maryland, p. 2089–2105
Strohl, W. R., Geffers, I., Larkin, J. M. (1981). Structure of the sulfur inclusion envelopes from four Beggiatoas. Curr. Microbiol. 6: 75–79
Temara, A. (1990). Caractères d'une symbiose bactérienne intradigestive chez l'echinide fouisseur Echinocardium cordatum (Echinodermata). Université Libre de Bruxelles (Faculté des Sciences), Master Thesis, Brussels
Temara, A., De Ridder, C. (1990). Features of an intradigestive bacterial symbiosis in the burrowing echinoid Echinocardium cordatum. Belgian J. Zool. 120: 56 (abstract)
Temara, A., De Ridder, C., Kaisin, M. (1991). Presence of an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid in intradigestive bacterial symbionts of a deposit-feeder echinoid (Echinodermata). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 100: 503–505
Vetter, R. D. (1985). Elemental sulfur in the gills of three species of clams containing chemoautotrophic symbiotic bacteria: a possible inorganic energy storage compound. Mar. Biol. 88: 33–42
Vismann, B. (1990). Sulfide detoxification and tolerance in Nereis (Hediste) diversicolor and Nereis (Neanthes) virens (Annelida: Polychaeta). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 59: 229–238
Vismann, B. (1991). Sulfide tolerance: physiological mechanisms and ecological implications. Ophelia. 34: 1–27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Temara, A., de Ridder, C., Kuenen, J.G. et al. Sulfide-oxidizing bacteria in the burrowing echinoid, Echinocardium cordatum (Echinodermata). Marine Biology 115, 179–185 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346333
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346333