Summary
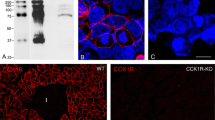
A cobalamin (vitamin B12)-binding protein has recently been identified in canine pancreatic juice which is biochemically, immunochemically and functionally similar to canine gastric intrinsic factor. However, the cellular sources of both this pancreatic intrinsic factor and gastric intrinsic factor in the dog are not known. Antisera raised against canine gastric intrinsic factor have been used to examine the distribution of intrinsic factors in the canine pancreas and stomach. Immunoreactivity was demonstrated in duct cells but not acinar or endocrine cells in the pancreas, and in fundic peptic and pyloric gastric pit cells in stomach. All immunostaining was abolished by preabsorption of the antisera with purified canine gastric and pancreatic intrinsic factors. A cellular source of pancreatic intrinsic factor has not been previously described, and the demonstration of intrinsic factor-like immunoreactivity in two cell types in the canine stomach contrasts with its localization in a single cell type in the gastric mucosa of other mammalian species. Furthermore, immunoreactivity in pancreatic duct cells was detected at much higher dilutions of antisera than those required for staining of peptic and gastric pit cells. This suggests a higher concentration of antigen, and supports previous evidence that the pancreas is a major source of intrinsic factor in the dog.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abels J, Muckerheide MM (1969) Antigenic species specificity of the gastric intrinsic factor. Proc Cent Soc Clin Res 42nd Annual Meeting: 843
Abels J, Muckerheide MM (1970) Absorption of vitamin B12 in dogs. Clin Res 18:530
Abels J, Muckerheide MM, van Kapel J, Lindemans J (1974) A dual role for the dog pancreas in the absorption of vitamin B12. Program, Am Soc Hematol Meeting: 95
Abels J, van Kapel J, Lindemans J (1977) A dual function of the dog pancreas in absorption of vitamin B12 by secretion of a prointrinsic factor and trypsinogen. Neth J Med 20:26
Allen RH, Seetharam B, Allen NC, Podell E, Alpers DH (1978) Correction of cobalamin malabsorption in pancreatic insufficiency with a cobalamin analogue that binds with high affinity to R protein but not to intrinsic factor. In vivo evidence that a failure to partially degrade R protein is responsible for cobalamin malabsorption in pancreatic insufficiency. J Clin Invest 61:1628–1634
Batt RM, Horadagoda NU (1989) Gastric and pancreatic intrinsic factor-mediated absorption of cobalamin in the dog. Am J Physiol 257:9344–9349
Batt RM, Horadagoda NU, McLean L, Morton DB, Simpson K (1989) Identification and characterization of a pancreatic intrinsic factor in the dog. Am J Physiol 256:G517-G523
Batt RM, Morgan JO (1982) Role of serum folate and vitamin B12 concentrations in the differentiation of small intestinal abnormalities in the dog. Res Vet Sci 32:17–22
Carmel R, Abramson SB, Renner IG (1983) Characterization of pure human pancreatic juice: cobalamin content, cobalaminbinding proteins and activity against human R binders of various secretions. Clin Sci 64 193–205
Cheney G, Niemand F (1932) A possible relationship of pancreatic insufficiency to Addison-Biermer (pernicious) anaemia. Arch Int Med 49:925–933
Glass GBJ (1974) Gastric Intrinsic Factor and Other Vitamin B12 Binders: Biochemistry, Physiology, Pathology and Relation to Vitamin B12 Metabolism. Georg Thieme Publishers, Stuttgart
Grasbeck R, Salonen E-M (1976) Vitamin B12. Prog Fd Nutr Sci 2:193–231
Grube D (1980) Immunoreactivities of gastrin (G-) cells. 11 Nonspecific binding of immunoglobulins to G-cells by ionic interactions. Histochemistry 66:149–167
Hill FWG, Osborne AD, Kidder DE (1971) Pancreatic degenerative atrophy in dogs. J Comp Pathol 81:321–330
Horadagoda NU, Batt RM (1985) Purification of canine intrinsic factor by affinity chromatography. Biochem Soc Trans 14:133–134
Horadagoda NU, Batt RM, Vaillant C, Morton DB, Simpson KW (1986) Identification and characterization of a pancreatic intrinsic factor in the dog. Gastroenterology 90:1464
Jacob E, Glass GBJ (1971) Localization of intrinsic factor and complement fixing intrinsic factor-intrinsic factor antibody complex in parietal cell of man. Clin Exp Immunol 8:517–527
Kudo H, Inada M, Ohshio G, Wakatsuki Y, Ogawa K, Hamashima Y, Miyake (1987) Immunohistochemical localization of vitamin B12 R binder in the human digestive tract. Gut 28:339–345
Levine JS, Nakane PK, Allen RH (1980) Immunocytochemical localization of human intrinsic factor: the nonstimulated stomach. Gastroenterology 79:493–502
Levine JS, Nakane PK, Allen RH (1981) Phylogenetic differences in the site of synthesis of intrinsic factor (IF): an immunoelectronmicroscopic study. Gastroenterology 80:1210
Levine JS, Allen RH, Alpers DH, Seetharam B (1984) Immunocytochemical localization of the intrinsic factor-cobalamin receptor in dog ileum: distribution of intracellular receptor during cell maturation. J Cell Biol 98:1111–1118
Levine JS, Magree L, Allen RH, Lusk LB (1985) Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of intrinsic factor in isolated rabbit gastric glands. Gastroenterology 88:1474
Marcoullis G, Nicolas J-P (1983) The interactions of cobalamin in the gastrointestinal tract. In: Glass GBJ, Sherlock P (eds) Progress in Gastroenterology, vol. IV. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 133–172
Marcoullis G, Parmentier Y, Nicolas J-P, Jimenez M, Gerard P (1980a) Cobalamin malabsorption due to nondegradation of R proteins in the human intestine: inhibited cobalamin absorption in exocrine pancreatic dysfunction. J Clin Invest 66:430–440
Marcoullis G, Rothenberg SP, Labombardi VJ (1980b) Preparation and characterization of proteins in the alimentary tract of the dog which bind cobalamin and intrinsic factor. J Biol Chem 255:1824–1829
Sateri H (1975) Investigations on the exocrine pancreatic function in dogs suffering from chronic exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Acta Vet Scand Suppl 53:1–86
Seetharam B, Alpers DH, Allen RH (1981) Isolation and characterization of the ileal receptor for intrinsic factor-cobalamin. J Biol Chem 256:3785–3790
Simons K (1964) Vitamin B12 binders in human body fluid and blood cells. Soc Sci Fennica Com Biol 27:3–94
Simpson KW, Morton DB, Batt RM (1989) Effect of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency on cobalamin absorption in dogs. Am J Vet Res 50:1233–1236
Sternberger LA, Hardy PHJr, Cuculis JJ, Meyer HG (1970) The unlabelled antibody enzyme method of immunohistochemistry. Preparation and properties of soluble antigen-antibody complex (horseradish peroxidase-antihorseradish peroxidase) and its use in identification of spirochetes. J Histochem Cytochem 18:315–333
Taylor IL, Calam J, Rotter JI, Vaillant C, Samloff IM, Cook A, Simkin E, Dockray GJ (1981) Family studies of hypergastrinemic, hyperpepsinogenemic 1 duodenal ulcer. Ann Intern Med 95:421–425
Toskes PP (1983) Intestinal absorption defects of cobalamin (vitamin B1 2) and their differential diagnosis in gastrointestinal disease. In: Glass GBJ, Sherlock P (eds) Progress in Gastroenterology, vol. IV. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 173–188
Toskes PP, Hansell J, Cerda J, Deren JJ (1971) Vitamin B1 2 malabsorption in chronic pancreatic insufficiency. Studies suggesting the presence of a pancreatic “intrinsic factor”. N Engl J Med 284:627–632
Vaillant C, Horadagoda NU, Batt RM (1986) The pancreas is a major source of intrinsic factor in the dog. Can J Physiol Pharmacol July [Suppl]: 154–155
Yamaguchi N, Weisberg H, Glass GBJ (1969) Intestinal vitamin B12 absorption in the dog. Gastroenterology 56:925–935
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaillant, C., Horadagoda, N.U. & Batt, R.M. Cellular localization of intrinsic factor in pancreas and stomach of the dog. Cell Tissue Res 260, 117–122 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297496
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297496