Summary
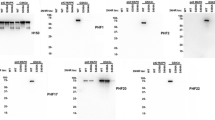
A modified form of the microtubule-associated protein Tau is the major component of the paired helical filaments (PHF) found in Alzheimer's disease. The characterization of these posttranslational Tau modifications is hindered by the lack of sufficient PHF-Tau-specific markers. Here we describe several monoclonal antibodies, prepared by immunization with PHF, two of which showed a selective specificity for PHF-Tau without cross-reactivity with normal Tau. Epitope recognition by these two monoclonals was sensitive to alkaline phosphatase treatment. In Western blotting these monoclonal antibodies reacted specifically with the abnormally phosphorylated epitopes on Alzheimer's disease-associated PHF-Tau. One of the new antibodies can be used for the construction of a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the specific detection of PHF-Tau without cross-reactivity to normal Tau proteins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Binder LI, Frankfurter A, Rebhun LI (1985) The distribution of Tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol 101:1371–1378.
Brion JP, Hanger DP, Bruce MT, Couck AM, Flament-Durand J, Anderton BH (1991) Tau in Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles: N- and C-terminal regions are differentially associated with paired helical filaments and the location of a putative abnormal phosphorylation site. Biochem J 273:127–133
Delacourte A, Flament S, Dibe EM, Hublau P, Sablonnière B, Hémon B, Sherrer V, Defossez A (1990) Pathological proteins Tau 64 and 69 are specifically expressed in the somatodendritic domain of the degenerating cortical neurons during Alzheimer's disease: demonstration with a panel of antibodies against Tau proteins. Acta Neuropathol 80:111–117
Flament S, Delacourte A (1990) Tau marker? (Letter). Nature 346:22
Elament S, Delacourte A, Hémon B, Defossez A (1989) Characterization of two pathological Tau protein variants in Alzheimer brain cortices. J Neurol Sci 92:133–141
Ghanbari HA, Kozuk T, Miller BE, Riesing S (1990) A sandwich enzyme immunoassay for detecting and measuring Alzheimer's disease-associated proteins in human brain tissue. J Clin Lab Anal 4:189–192
Ghanbari HA, Miller BE, Haigler HJ, et al (1990) Biochemical assay of Alzheimer's disease-associated protein(s) in human brain tissue. JAMA 263:2907–2910
Gheuens J, Cras P, Perry G, Boons J, Ceuterick C, Lübke U, Mercken M, Tabaton M, Gambetti PL, Vandermeeren M, Mulvihill P, Siedlak S, Van Heuverswijn H, Martin JJ (1991) Demonstration of a novel neurofilament-associated antigen in the neurofibrillary pathology of Alzheimer and related diseases. Brain Res 558:43–52
Goedert M, Spillantini MG, Jakes R, Rutherford D, Crowther RA (1989) Multiple isoforms of human microtubule-associated protein Tau: sequences and localization in neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 3:519–526
Greenberg S, Davies P (1990) A preparation of Alzheimer paired helical filaments that displays distinct Tau proteins by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5827–5831
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Tung Y-C, Wisniewski HM, Binder LI (1986) Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:4913–4917
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotinperoxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Hui KS, Hui M, Chiu FC, Banay-Schwartz M, Deguzman T, Sacchi RS, Lajtha A (1986) Separation and purification of individual neurofilament proteins by reverse-phase highperformance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 153:230–234
Ihara Y, Nukina N, Miura R, Ogawara M (1986) Phosphorylated tau protein is integrated into paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Biochem (Tokyo) 99:1807–1810
Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Smith AJ, George L, Tung Y, Zaidi T (1989) Identification and localisation of a tau peptide to paired helical filaments of Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5646–5650
Kidd M (1964) Alzheimer's disease: an electron microscopical study. Brain 87:307–327
Köhler G, Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256:495–497
Kondo J, Honda T, Mori H, Hamada Y, Miura R, Ogawara M, Ihara Y (1988) The carboxyl third of Tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron 1:827–834
Kosik KS, Orecchio LD, Binder LI, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VMY, Lee G (1988) Epitopes that span the Tau molecule are shared with paired helical filaments. Neuron 1:817–825
Ksiezak-Reding H, Dickson DW, Davies P, Yen SH (1987) Recognition of Tau epitopes by anti-neurofilament antibodies that bind to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3410–3414
Ksiezak-Reding H, Binder LJ, Yen SH (1990) Alzheimer disease proteins (A68) share epitopes with Tau but show distinct biochemical properties. J Neurosci Res 25:420–430
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee VMY, Balin BJ, Otvos L, Trojanowski J (1991) A68: a major subunit of paired helical filaments and derivated forms of normal Tau. Science 251:675–678
Mercken M, Vandermeeren M, Lübke U, Six J, Boons J, Vanmechelen E, Van De Voorde A, Gheuens J (1992) Affinity purification of human Tau proteins and the construction of a sensitive sandwich ELISA for human Tau detection. J Neurochem 58:548–553
Novak M, Jakes R, Edwards PC, Milstein C, Wischik CM (1991) Difference between the tau protein of Alzheimer paired helical filament core and normal tau revealed by epitope analysis of monoclonal antibodies 423 and 7.51. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5837–5841
Nukina N, Kosik KS, Selkoe DJ (1987) Recognition of Alzheimer paired helical filaments by monoclonal neurofilament antibodies is due to crossreation with Tau protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3415–3419
Pollock NJ, Wood JG (1988) Differential sensitivity of the microtubule-associated protein Tau in Alzheimer's disease tissue to formalin fixation. J Histochem Cytochem 36:1117–1121
Six J, Lübke U, Mercken M, Vandermeeren M, Ceuterick C, Van de Voorde A, Boons J, Gheuens J (1992) Specific monoclonal antibodies against normal microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2) epitopes present in Alzheimer pathological structures do not recognize paired helical filaments. Acta Neuropathol 83:179–189
Sternberger LA, Sternberger NH (1983) Monoclonal antibodies distinguish phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated forms of neurofilaments in situ. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:6126–6130
Trojanowski JQ, Schuck T, Schmidt ML, Lee VMY (1989) Distribution of Tau proteins in the normal human central and peripheral nervous system. J Histochem Cytochem 37:209–215
Vincent IJ, Davies P (1990) Phosphorylation characteristics of the A68 protein in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 531:127–135
Wischik CM, Novak M, Thögersen HC, Edwards PC, Runswick MJ, Jakes R, Walker JE, Milstein C, Roth M, Klug A (1988) Isolation of a fragment of Tau derived from the core of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:4506–4510
Yen SH, Dickson DW, Crowe A, Butler M, Shelanski MI (1987) Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles contain unique epitopes and epitopes in common with heat-stable microtubule-associated proteins Tau and MAP2. Am J Pathol 126:81–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mercken, M., Vandermeeren, M., Lübke, U. et al. Monoclonal antibodies with selective specificity for Alzheimer Tau are directed against phosphatase-sensitive epitopes. Acta Neuropathol 84, 265–272 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227819
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227819