Summary
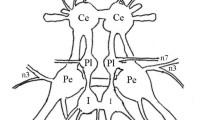
We have used immunohistochemical methods to investigate the morphology of identified, presumptive serotonergic neurons in the antennal lobes and suboesophageal ganglion of the worker honeybee. A large interneuron (deutocerebral giant, DCG) is described that interconnects the deutocerebral antennal and dorsal lobes with the suboesophageal ganglion and descends into the ventral nerve chord. This neuron is accompanied by a second serotonin-immunoreactive interneuron with projections into the protocerebrum. Two pairs of bilateral immunoreactive serial homologues were identified in each of the three suboesophageal neuromeres and were also found in the thoracic ganglia. With the exception of the frontal commissure, no immunoreactive processes could be found in the peripheral nerves of the brain and the suboesophageal ganglion. The morphological studies on the serial homologues were extended by intracellular injections of Lucifer Yellow combined with immunofluorescence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold G, Masson C, Budharugsa S (1985) Comparative study of the antennal lobes and their afferent pathway in the worker bee and the drone (Apis mellifera). Cell Tissue Res 242:593–605
Berridge MJ (1972) The mode of action of 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Exp Biol 56:311–321
Boeckh J, Ernst KD, Sass H, Waldow U (1984) Anatomical and physiological characteristics of individual neurones in the central antennal pathway of insects. J Insect Physiol 30:15–26
Evans PD (1980) Biogenic amines in the insect nervous system. In: Berridge MJ, Treherne JE (eds) Advances in insect physiology. Academic Press, London, 15:317–473
Falck B, Hillarp N A, Thieme G, Torp A (1962) Fluorescence of catecholamines and related compounds condensed with formaldehyde. J Histochem Cytochem 10:348–354
Gaide M (1983) Die Projektionen des Labialund Maxillarnerven im Unterschlundganglion der Biene. Diplomarbeit FU-Berlin
Homberg U (1984) Processing of antennal information in extrinsic mushroom body neurons of the bee brain. J Comp Physiol 154:825–836
Kandel ER, Abrams T, Bernier L, Carew TJ, Hawkins RD, Schwarz JH (1983) Classical conditioning and sensitization share aspects of the same molecular cascade in Aplysia. Cold Spring Harbor Symp 48:821–830
Klemm N (1976) Histochemistry of putative transmitter substances in the insect brain. Prog Neurobiol 7:99–167
Klemm N, Steinbusch HWM, Sundler F (1984) Distribution of serotonin containing neurons and their pathways in the supraoesophageal ganglion of the cockroach Periplaneta americana (L.) as revealed by immunocytochemistry. J Comp Neurol 225:387–395
Kravitz EA, Beltz BS, Glusman S, Goy MF, Harris-Warrick RM, Johnston MF, Livingstone MS, Schwarz TL, Siwicki KK (1983) Neurohormones and lobsters; biochemistry and behavior. TINS 6:345–349
Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1981) The role of serotonin in arousal of feeding behavior of Aplysia. In: Jacobs DL and Gelperin A (eds) Serotonin Neurotransmission and Behavior. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass, and London, pp 255–287
Kuwabara M (1957) Bildung des bedingten Reflexes von Pavlovs Typus bei der Honigbiene (Apis mellifica). Jour Fac Sci Hokkaido Univ Zool 13:458–464
Lent CM, Dickinson MH (1984) Serotonin integrates the feeding behavior of the medicinal leech. J Comp Physiol 154:457–471
Menzel R, Erber J, Masuhr T (1974) Learning and memory in the honeybee. In: Barton Browne L (ed) Experimental analysis of insect behaviour. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 195–217
Mercer AR, Menzel R (1982) The effects of biogenic amines on conditioned and unconditioned responses to olfactory stimuli in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). J Comp Physiol 145:363–368
Mercer A, Mobbs P, Davenport AP, Evans PD (1983) Biogenic amines in the brain of the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Cell Tissue Res 234:655–677
Nässei DR, Elekes K (1985) Serotonergic terminals in the neural sheath of the blowfly nervous system: electron microscopical immunocytochemistry and 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine labelling. Neuroscience 15:293–307
O'Shea M, Evans PD (1979) Potentiation of neuromuscular transmission by octopaminergic neurone in the locust. J Exp Biol 79:169–190
Pareto A (1972) Die zentrale Verteilung der Fühlerafferenzen bei Arbeiterinnen der Honigbiene, Apis mellifica L. Z Zellforsch 131:109–140
Schäfer S, Bicker G (1986) Distribution of GABA-like immunoreactivity in the brain of the honeybee. J Comp Neurol 246:287–300
Schürmann FW, Klemm N (1984) Serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the brain of the honeybee. J Comp Neurol 225:570–580
Sombati S, Hoyle G (1984) Generation of specific behaviors in a locust by local release into neuropile of the natural neuromodulator octopamine. J Neurobiol 15:481–506
Steinbusch HWM, Verhostad AAJ, Joosten HWJ (1978) Localisation of serotonin in the central nervous system by immunohistochemistry. Description of a specific and sensitive technique and some applications. Neuroscience 3:811–819
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, John Wiley and Sons, New York
Suzuki H (1975) Antennal movements induced by odour and central projections of the antennal neurones in the honey bee. J Insect Physiol 21:831–847
Tyrer NM, Turner JD, Altman JS (1984) Identifiable neurons in the locust central nervous system that react with antibodies to serotonin. J Comp Neurol 227:313–330
Walker RJ (1984) 5-Hydroxytryptamine in invertebrates. Comp Biochem Physiol C 79:231–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehder, V., Bicker, G. & Hammer, M. Serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in the antennal lobes and suboesophageal ganglion of the honeybee. Cell Tissue Res. 247, 59–66 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216547
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216547