Abstract
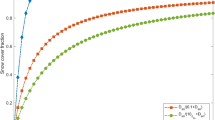
Both observational and numerical studies demonstrate the sensitivity of the atmosphere to variations in the extent and mass of snow cover. There is therefore a need for simple but realistic snow parameterizations in forecast and climate models. A new snow hydrology scheme has recently been developed at Météo-France for use in the ARPEGE climate model and has been successfully tested against local field measurements in stand-alone experiments. This study describes the global validation of the parameterization in a 3-year integration for the present-day climate within the T42L30 version of ARPEGE. Results are compared with those from a control simulation and with available observed climatologies, in order to assess the impact of the new snow parameterization on the simulated surface climate. The seasonal cycle of the Northern Hemisphere snow cover is clearly improved when using the new scheme. The snow pack is still slightly overestimated in winter, but its poleward retreat is better reproduced during the melting season. As a consequence, the modified GCM performs well in simulating the springtime continental heating, which may play a strong role in the simulation of the Asian summer monsoon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett TP, Dümenil L, Schlese U, Roeckner E, Latif M (1989) The effect of Eurasian snow cover on regional and global climate variations. J Atmos Sci 46:661–685
Blanford HF (1884) On the connexion of Himalayan snowfall and seasons of drought in India. Proc R See London 37:322
Brand I, Noilhan J, Bessemoulin P, Mascart P, Haverkamp R, Vauclin M (1993) Bare-ground surface heat and water exchanges under dry conditions: observations and parameterization. Boundary Layer Meteorol 66:173–200
Brun E, Martin E, Simon V, Gendre C, Coleou C (1989) An energy and mass model of snow cover suitable for operational avalanche forecasting. J Glaciol 35:333–342
Brun E, David P, Sudul M, Brunot G (1992) A numerical model to simulate snow-cover stratigraphy for operational avalanche forecasting. J Glaciol 38:13–22
Cariolle D, Déqué M (1986) Southern hemisphere medium-scale waves and total ozone disturbances in a spectral general circulation model. J Geophys Res — Atmos 91:10825–10846
Cess RD, Potter GL, Zhang MH, Blanchet JP, Chalita S, Colman R, Dazlich DA, Del Genio AD, Dymnikov V, Galin V, Jerrett D, Keup E, Lacis AA, Le Treut H, Liang XZ, Mahfouf JF, McAvaney BJ, Meleshko VP, Mitchell JFB, Morcrette JJ, Norris PM, Randall DA, Rikus L, Roeckner E, Royer JF, Schlese U, Scheinin DA, Slingo JM, Sokolov AP, Taylor KE, Washington WM, Wetherald RT, Yagai I (1991) Intercomparison of snow-feedback as produced by 17 general circulation models. Science 253:888–892
Deardorff JW (1978) Efficient prediction of ground surface temperature and moisture, with inclusion of a layer of vegetation. J Geophys Res — Oceans 83:1889–1903
Déqué M, Dreveton C, Braun A, Cariolle D (1994) The ARPEGE/IFS atmosphere model: a contribution to the French community climate modelling. Clim Dyn 10:249–266
Dewey KF (1977) Daily maximum and minimum temperature forecasts and the influence of snow cover. Mon Weather Rev 105:1594–1598
Dolman AJ, Gregory D (1992) The parametrization of rainfall interception in GCMs. Q J R Meteorol Soc 118:455–467
Douville H (1994a) Validation de la climatologie de la neige simulée par la version 1 du modèle Arpège-Climat. Note de Centre GMGEC 31
Douville H (1994b) Développement et validation locale d'une nouvelle paramétrisation du manteau neigeux. Note de Centre GMGEC 36
Eagleson PS, Fennessey NM, Qinliang W, Rodriguez-Iturbe I (1987) Application of spatial Poisson models to air mass thunderstorm rainfall. J Geophys Res — Atmos 92:9661–9678
Foster DJ Jr, Davy RD (1988) Global snow depth climatology, vol USAFETAC/TN - 88/006. USAF Environmental Technical Application Center, Scott Air Force Base, Illinois (Available from the National Climatic Data Center, Asheville, NC 28801)
Foster JL, Chang ATC, Hall DK, Rango A (1991) Derivation of snow water equivalent in boreal forests using microwave radiometry. Arctic 44 (Supp I):147–152
Hahn DG, Shukla J (1976) An apparent relationship between Eurasian snow cover and Indian monsoon rainfall. J Atmos Sci 33:2461–2462
Ingram WJ, Wilson CA, Mitchell JFB (1989) Modelling climate change: an assessment of sea ice and surface albedo feedbacks. J Geophys Res 94:8609–8622
Legates DR, Willmott CJ (1990a) Mean seasonal and spatial variability in gauge-corrected, global precipitation. Int J Climatol 10:111–127
Legates DR, Willmott CJ (1990b) Mean seasonal and spatial variability in global surface air temperature. Theor Appl Climatol 41:11–21
Loth B, Graf HF, Oberhuber JM (1993) Snow cover model for global climate simulations. J Geophys Res — Atmos 98:10451–10464
Louis JF (1979) A parametric model of vertical eddy fluxes in the atmosphere. Boundary Layer Meteorol 17:187–202
Mahfouf JF, Manzi AO, Noilhan J, Giordani H, Déqué M (1995) The land surface scheme ISBA within the Météo-France climate model ARPEGE. Part I: Implementation and preliminary results. J Climate 8:2039–2057
Manabe S (1969) Climate and the ocean circulation: I. The atmospheric circulation and the hydrology of the Earth's surface. Mon Weather Rev 97:739–774
Manzi AO (1993) Introduction d'un schéma des transferts sol-végétation-atmosphère dans un modèle de circulation générale et application à la déforestation Amazonienne. Doctorat Thesis, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse (France)
Manzi AO, Planton S (1994) Implementation of the ISBA parametrization scheme for land surface processes in a GCM — An annual cycle experiment. J Hydrol 155:353–387
Marshall S, Oglesby RJ (1994) An improved snow hydrology for GCMs. I. Snow cover fraction, albedo, grain size, and age. Clim Dyn 10:21–37
Meehl GA, Washington WM (1990) CO2 climate sensitivity and snow-sea-ice albedo parameterization in an atmospheric GCM coupled to a mixed-layer ocean model. Clim Change 16:2831–306
Mintz Y, Serafini YV (1992) A global monthly climatology of soil moisture and water balance. Clim Dyn 8:13–28
Namias J (1985) Some empirical evidence for the influence of snow cover on temperature and precipitation. Mon Weather Rev 113:1542–1553
Noilhan J, Lacarrère P (1995) GCM gridscale evaporation from mesoscale modelling. J Clim 8:206–223
Noilhan J, Planton S (1989) A simple parameterization of land surface processes for meteorological models. Mon Weather Rev 117:536–549
Noilhan J, Lacarrère P, Bougeault P (1991) An experiment with an advanced surface parameterization in a meso beta-scale model. Part III: comparison with the HAPEX-MOBILHY dataset. Mon Weather Rev 119:2393–2413
Oglesby RJ (1990) Sensitivity of glaciation to initial snow cover, CO2 snow albedo, and oceanic roughness in the NCAR CCM. Clim Dyn 4:219–235
Robinson DA, Kukla G (1984) Albedo of dissipating snow cover. J Clim Appl Meteorol 23:1626–1634
Robinson D, Kunzi K, Kukla G, Rott H (1984) Comparative utility of microwave and shortwave satellite data for all-weather charting of snow cover. Nature 312:434–435
Schutz C, Bregman LD (1987) Global annual snow accumulation by months. Rand Corporation, N-2551-AF (available from Rand Corporation, 1200 Main Street, Santa Monica, CA 90406)
Vernekar AD, Zhou J, Shukla J (1995) The effect of Eurasian snow cover on the Indian monsoon. J Clim 8:248–266
Verseghy DL (1991) CLASS — a Canadian Land Surface Scheme for GCMS. I. Soil model. Int J Climatol 11:111–133
Walsh JE, Tucek DR, Peterson MR (1982) Seasonal snow cover and short-term climatic fluctuations over the United States. Mon Weather Rev 110:1474–1485
Webb RS, Rosenzweig CE, Levine ER (1991) A global data set of soil particle size properties, Tech Rep 4286 NASA, GISS, New York
Wilson MF, Henderson-Sellers A (1985) A global archive of land cover and soils data for use in general circulation climate models. J Climatol 5:119–143
Yasunari T, Kitoh A, Tokioka T (1991) Local and remote responses to excessive snow mass over Eurasia appearing in the northern spring and summer climate — a study with the MRI GCM. J Meteorol Soc Japan 69:473–487
Yeh TC, Wetherald RT, Manabe S (1983) A model study of the short-term climatic and hydrologic effects of sudden snowcover removal. Mon Weather Rev 11:1013–1024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douville, H., Royer, J.F. & Mahfouf, J.F. A new snow parameterization for the Météo-France climate model. Climate Dynamics 12, 37–52 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208761
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00208761