Abstract
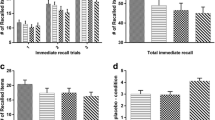
A combined visual (pictures) and auditory (word lists) memory test developed to trace the course of information processing under pharmacological or other influences was validated in a group of 20 subjects (control group) and then applied to determine the amnesic effects of lormetazepam and the reversal of these effects by the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. Three groups of n=10 subjects received either 0.02 mg/kg IV lormetazepam (groups B and C) or placebo (group A) followed 14 min later by 0.03 mg/kg IV Ro 15-1788 (groups A and C) or placebo (group B). The time course of memory performance in the three groups was investigated and compared across three consecutive 14-min phases: before (phase 1) and after (phase 2) the first intravenous administration, and after the second treatment (phase 3). Results were also compared with those of 20 subjects from a drug-free control group in order to verify the memory test. Lormetazepam clearly impaired immediate and delayed free recall as well as recognition in both visual and auditory tasks. These effects were completely reversed by Ro 15-1788, which alone had no clear effect on memory performance in this study. Psychometric scales indicated concomitant sedation and impaired concentration after lormetazepam alone. Interestingly, lormetazepam retrogradely enhanced performance in the visual test of delayed free recall. The impaired acquisition of new information after the administration of lormetazepam may be associated with an improvement of the consolidation process of information acquired before drug treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson RC, Shiffrin RM (1968) Human memory: A proposed system and its control processes. In: Spence KW, Spence JT (eds) The psychology of learning and motivation, Vol 2. Academic, New York, pp 89–95
Baddeley AD, Hitch G (1974) Working memory. In: Bower GH (ed) The psychology of learning and memory, Vol 8. Academic, New York, pp 47–89
Bixler EO, Scharf MB, Soldatos CR, Mitsky DJ, Kales E (1979) Effects of hypnotic drugs on memory. Life Sci 25:1379–1388
Braestrup C, Schmiechen R, Neef G, Nielsen M, Petersen EN (1982) Interaction of convulsive ligands with benzodiazepine receptors. Science 216:1241–1243
Clarke PRF, Eccersley PS, Frisby JP, Thornton JA (1970) The amnesic effect of diazepam (Valium). Br J Anaesth 42:690–697
Costa E, Guidotti A, Mao CC (1975) Evidence for the involvement of GABA in the action of benzodiazepines: studies on rat cerebellum. In: Costa E, Greengard P (eds) Mechanisms of action of benzodiazepines. Raven, New York, pp 113–130
Craik FIM (1983) On the transfer of information from temporary to permanent memory. Philos Trans R Soc Lond (Biol) 302:341–359
Curran HV (1986) Tranquilising memories: A review of the effects of benzodiazepines on human memory. Biol Psychol 23:179–213
Darragh A, Lambe R, Kenny M, Brick I, Taaffe W, O'Boyle C (1982) Ro 15–1788 antagonises the effects of diazepam in man without altering diazepam bioavailability. Br J Clin Pharmacol 14:677–682
Dorow R, Duka T (1986) Anxiety: Its generation by drugs and their withdrawal. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) GABAergic transmission and anxiety. Raven, New York, pp 221–225
Dorow R, Horowski R, Paschelke G, Amin M, Braestrup C (1983) Severe anxiety induced by FG 7142, a β-carboline ligand for benzodiazepine receptors. Lancet II:98–99
Duka T, Höller L, Obeng-Gyan R, Dorow R (1986) Initial human pharmacology of the neutral benzodiazepine receptor antagonist β-carboline ZK 93 426. Br J Clin Pharmacol 22:228P
Duka T, Edelmann V, Schütt B, Dorow R (1987) β-carbolines, as tools in memory research: human data with the β-carboline ZK 93 426 In: Hindmarch I, Ott H, Roth T (eds) Benzodiazepine receptor ligands: Memory and information processing. Psychopharmacology [Suppl] (in press)
File SE, Pellow S (1986) Intrinsic actions of the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Ro 15–1788. Psychopharmacology 88:1–11
George KA, Dundee JW (1977) Relative amnesic actions of diazepam, flunitrazepam and lorazepam in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 4:45–50
Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP (1975) Effects of diazepam and scopolamine on storage, retrieval and organizational processes in memory. Psychopharmacology 44:257–262
Haefely W, Kulcsár A, Möhler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Schaffner R (1975) Possible involvement of GABA in the central actions of benzodiazepines. In: Costa E, Greengard P (eds) Mechanisms of action of benzodiazepines. Raven, New York, pp 131–151
Hinrichs JV, Ghoneim MM, Mewaldt SP (1984) Diazepam and memory: retrograde facilitation produced by interference reduction. Psychopharmacology 84:158–162
Hommer DW, Breier A, Paul SM, Davis M, Weingartner H (1986) Ro 15-1788, a specific benzodiazepine antagonist, blocks the sedative, anxiolytic and attentional but not amnestic effects of diazepam in humans. Abstracts of the 25th ACNP Annual Meeting in Washington DC, 204
Hümpel M, Nieuweboer B, Milius W, Hanke H, Wendt H (1980) The pharmacokinetics of lormetazepam. II. Radioimmunological determinations in plasma and urine of young and elderly volunteers. First-pass effect. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28:673
Hunkeler W, Möhler H, Pieri L, Polc P, Bonetti EP, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1981) Selective antagonists of benzodiazepines. Nature 290:514–516
Jones BM (1973) Memory impairment on the ascending and descending limbs of the blood and alcohol curve. J Abnorm Psychol 82:24–32
Kubicki St, Ott H, Rohloff A, Fichte K (1985) Vigilanz und Amnesie nach Benzodiazepingabe: Neurophysiologische und pharmakopsychologische Aspekte. In: J Schulte am Esch (ed) Benzodiazepine in Anästhesie und Intensivmedizin. Editiones Roche, Basel, pp 57
Lister RG (1975) The amnesic action of benzodiazepines in man. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 9:87–94
Lister RG, File SE (1984) The nature of lorazepam-induced amnesia. Psychopharmacology 83:183–187
Mann RE, Cho-Young J, Vogel-Sprott M (1984) Retrograde enhancement by alcohol of delayed free recall performance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:639–642
Mewaldt SP, Hinrichs JV, Ghoneim MM (1983) Diazepam and memory: support for a duplex model of memory. Mem Cognit 11:557–564
Möhler H, Okada T (1977) Benzodiazepine receptors: demonstration in the central nervous system. Science 198:849–851
O'Boyle C, Lambe R, Darragh A, Taffe A, Brick I, Kenny M (1983) Ro 15–1788 antagonizes the effects of diazepam in man without affecting its bioavailability. Br J Anaesth 55:349–355
Ott H, Hemmerling K-G, Kugler J, Suttmann H, Doenicke A, Tesch C, Strä§ner G (1980). Amnestische Begleitwirkungen nach i.v.-Gabe von Lormetazepam and Flunitrazepam. In: Doenicke A, Ott H, (eds) Lormetazepam Noctamid, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 13.1–13.10
Pandit SK, Heisterkamp DV, Cohen PJ (1976) Further studies of the anti-recall effect of lorazepam: a dose-time-effect relationship. Anesthesiology 45:495–500
Parker ES, Birnbaum IM, Noble EP (1976) Alcohol and memory: storage and state-dependency. J Verb Learn Verb Behav 15:691–702
Parker ES, Birnbaum IM, Weingartner H, Hartley JT, Stillman RC, Wyatt RJ (1980) Retrograde enhancement of human memory with alcohol. Psychopharmacology 69:219–222
Parker ES, Morihisa JM, Wyatt RJ, Schwartz BL, Weingartner H, Stillman RC (1981) The alcohol facilitation effect on memory: a dose-response study. Psychopharmacology 74:88–92
Polc P, Bonetti EP, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1982) A three-state model of the benzodiazepine receptor explains the interactions between the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15–1788, benzodiazepine tranquilizers, β-carbolines, and phenobarbitone. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:260–264
Roehrs T, McLenaghan A, Koshorek G, Zorick F, Roth T (1984) Amnesic effects of lormetazepam. In: Hindmarch I, Ott H, Roth T (eds) Sleep, benzodiazepines and performance. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 165–172
Ryback RS (1971) The continuum and specificity of the effects of alcohol on memory: A review. Q J Stud Alcohol 32:995–1016
Schöpf J, Laurian S, Le PK, Gaillard J-M (1984) Intrinsic activity of the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15–1788 in man: an electrophysiological investigation. Pharmacopsychiatry 17:79–83
Squires RE, Braestrup JL (1977) Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature 266:732–734
Stephens DN, Kehr W (1985) β-Carbolines can enhance or antagonize the effects of punishment in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:143–147
Study RE, Barker JL (1981) Diazepam and (−)pentobarbital. Fluctuation analysis reveals different mechanisms for potentiation of GABA responses in cultured central neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7180–7184
Subhan Z (1984) The effects of benzodiazepines on short-term memory and information processing. In: Hindmarch I, Ott H, Roth T (eds) Sleep, benzodiazepines and performance. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 173–181
Venault P, Chapoutier G, de Carvalho LP, Simiand J, More M, Dodd RH, Rossier J (1986) Benzodiazepine impairs and β-carboline enhances performance in learning and memory. Nature 321:864–866
Weingartner H (1985) Models of memory dysfunction. Ann NY Acad Sci 444:359–369
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article is part of the doctoral thesis of Dagmar Berenberg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorow, R., Berenberg, D., Duka, T. et al. Amnestic effects of lormetazepam and their reversal by the benzodiazepine antagonist Ro 15-1788. Psychopharmacology 93, 507–514 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207244
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207244