Summary
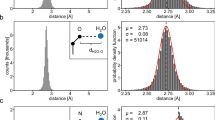
Water molecules are known to play an important rôle in mediating protein-ligand interactions. If water molecules are conserved at the ligand-binding sites of homologous proteins, such a finding may suggest the structural importance of water molecules in ligand binding. Structurally conserved water molecules change the conventional definition of ‘binding sites’ by changing the shape and complementarity of these sites. Such conserved water molecules can be important for site-directed ligand/drug design. Therefore, five different sets of homologous protein/protein-ligand complexes have been examined to identify the conserved water molecules at the ligand-binding sites. Our analysis reveals that there are as many as 16 conserved water molecules at the FAD binding site of glutathione reductase between the crystal structures obtained from human and E. coli. In the remaining four sets of high-resolution crystal structures, 2–4 water molecules have been found to be conserved at the ligand-binding sites. The majority of these conserved water molecules are either bound in deep grooves at the protein-ligand interface or completely buried in cavities between the protein and the ligand. All these water molecules, conserved between the protein/protein-ligand complexes from different species, have identical or similar apolar and polar interactions in a given set. The site residues interacting with the conserved water molecules at the ligand-binding sites have been found to be highly conserved among proteins from different species; they are more conserved compared to the other site residues interacting with the ligand. These water molecules, in general, make multiple polar contacts with protein-site residues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edsall, J. and McKenzie, H.A., Adv. Biophys., 16 (1983) 53.
Blake, C.C.F., Pulford, W.C.A. and Artymiuk, P.J., J. Mol. Biol., 167 (1983) 693.
Sreenivasan, U. and Axelsen, P.H., Biochemistry, 31 (1992) 12785.
Rashin, A.A., Iofin, M. and Honig, B., Biochemistry, 25 (1986) 3619.
Loris, R., Stas, P.P.G. and Wyns, L., J. Biol. Chem., 269 (1994) 26722.
Thanki, N., Umrania, Y., Thornton, J.M. and Goodfellow, J.M., J. Mol. Biol., 224 (1991) 669.
Finney, J.L., Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B, 278 (1977) 3.
Vyas, N.K., Vyas, M.N. and Quiocho, F.A., Science, 242 (1988) 1290.
Poornima, C.S. and Dean, P.M., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 9 (1995) 500.
Poornima, C.S. and Dean, P.M., J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Design, 9 (1995) 513.
Dean, P.M., Barakat, M.T. and Todorov, N.P., In Dean, P.M., Jolles, G. and Newton, C.G. (Eds.) New Perspectives in Drug Design, Academic Press, London, 1995, pp. 155–183.
LaLonde, J.M., Bernlohr, D.H. and Banaszak, L.J., Biochemistry, 33 (1994) 4885.
Zhang, X.-J. and Matthews, B.W., Protein Sci., 3 (1994) 1031.
Mittl, P.R.E. and Schulz, G.E., Protein Sci., 3 (1994) 799.
Karplus, P.A. and Schulz, G.E., J. Mol. Biol., 210 (1989) 163.
Zou, J.-Y., Flocco, M.M. and Mowbray, S.L., J. Mol. Biol., 233 (1993) 739.
Karpusas, M., Holland, D. and Remington, S.J., Biochemistry, 30 (1991) 6024.
Remington, S.J., Wiegand, G. and Huber, R., J. Mol. Biol., 158 (1982) 111.
Dunn, C.R. and Holbrook, J.J., Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London Ser. B, 332 (1991) 177.
Abad-Zapatero, C., Griffith, J.P., Sussman, J.L. and Rossmann, M.G., J. Mol. Biol., 198 (1987) 445.
Ji, X., Armstrong, R.N. and Gilliland, G.L., Biochemistry, 32 (1993) 12949.
Raghunathan, S., Chandross, R.J., Kretsinger, H.R., Allison, T.J., Penington, C.J. and Rule, G.S., J. Mol. Biol., 338 (1994) 815.
Connolly, M.L., Science, 221 (1983) 709.
Hubbard, S.J., Gross, K.-H. and Argos, P., Protein Eng., 7 (1994) 613.
Hubbard, S.J. and Argos, P., Protein Sci., 3 (1995) 2194.
Kuhn, L.A., Siani, M.A., Pique, M.E., Fisher, C.L., Getzoff, E.D. and Trainer, J.A., J. Mol. Biol., 228 (1992) 13.
Finer-Moore, J.S., Kossiakoff, A.A., Hurley, J.H., Earnest, T. and Stoud, R.M., Proteins, 12 (1992) 203.
Kossiakoff, A.A., Sintchak, M.D., Shpungin, J. and Presta, L.G., Proteins, 12 (1992) 223.
Williams, M.A., Goodfellow, J.M. and Thornton, J., Protein Sci., 3 (1994) 1224.
Meiering, E.M. and Wagner, G., J. Mol. Biol., 247 (1995) 294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poornima, C.S., Dean, P.M. Hydration in drug design. 3. Conserved water molecules at the ligand-binding sites of homologous proteins. J Computer-Aided Mol Des 9, 521–531 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00124323
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00124323