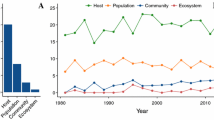
The influence of parasites in ecosystems, especially on biodiversity, is discussed. Various examples illustrate the role that parasites play in the outcome of interspecific competition, in the success of invading species, and in the separation of emerging species. Parasites can be stabilizers or destabilizers, depending on factors such as susceptibility of hosts and size of the ecosystem. Parasites play a major role each time ‘something’ disturbs living beings at the populational and/or specific level, as they do at the individual level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson R.C. (1972) The ecological relationships of meningeal worm and native cervids in North America. J. Wildlife Dis. 8, 304–10.
Bakker R.T. (1983) The deer flees, the wolf pursues: incongruencies in predator-prey coevolution. In Coevolution (D.J. Futuyma and M. Slatkin, eds) pp. 350–82. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer.
Barbehenn K.R. (1969) Host-parasite relationships and species diversity in mammals: an hypothesis. Biotropica 1, 29–35.
Bauer O.N. and Hoffman G.L. (1976) Helminth range extension by translocation of fish. In Wildlife Diseases (L.A. Page, ed.). pp. 163–72. New York: Plenum Press.
Black F.L. (1992) Why did they die? Science 258, 1730–8.
Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Gerasimov S., Orsini P. and Thaler L. (1983) Le complexe d'espèces du genre Mus en Europe centrale et orientale. Z Säugetierkunde 48, 78–85.
Boulétreau, M., Fouillet, P. and Allemand, R. (1991) Parasitoids affect competitive interactions between the sibling species, Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. In Insect Parasitoids, 4th European Workshop. Redia 84, 171–7.
Combes C. (1991) Ethological aspects of parasite transmission. Am. Naturalist 138, 866–80.
Combes C. (1995). Interactions durables. Ecologie et Evolution du Parasitisme. Paris: Masson.
Dawkins R. (1982) The Extended Phenotype. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Dawkins R. (1990) Parasites, desiderata lists and the paradox of the organism. Parasitology 100, 63–73.
Feener D.H.Jr (1981) Competition between ant species: outcome controlled by parasitic flies. Science 214, 815–6.
Freeland W.J. (1983) Parasites and the coexistence of animal species. Am Naturalist 121, 223–36.
Freeland W.J. and Boulton W.J. (1990) Coevolution of food webs: parasites, predators and plant secondary compounds. Biotropica 24. 309–17.
Golvan Y.J. and Rioux J.A. (1961) Ecologie des mérions du Kurdistan iranien. Relation avec l'épidémiologie de la peste rurale. Ann. Parasitol. Hum. Comp. 36, 449–558.
Golvan Y.J. and Rioux J.A. (1963) La peste, facteur de régulation des populations de mérions au Kurdistan iranien. La Terre et la Vie 1, 3–34.
Haldane, J.B.S. (1949) Disease and evolution. Ric. Sci. Suppl. 19, 68–76.
Holmes, J.C. (1996) Parasites as threats to biodiversity in shrinking ecosystems. Biodiv. Conserv. (this volume).
Holt R.D. and Pickering J. (1985) Infectious diseases and species coexistence: a model of Lotka-Volterra form. Am. Naturalist 126, 196–211.
Kelsall J.P. and Prescott W. (1971) Moose and deer behaviour in snow in Fundy National Park, New Brunswick. Can. Wildlife Service Rep. Series 15. Ottawa, Canada, 1–25.
Lindström E.R., Andren H., Angeltam P., Cederlund G., Hornfeldt B., Jaderberg L., Lemnell P.A., Martinsson B., Skold K. and Swenson G.E. (1994) Disease reveals the predator: sarcoptic mange, red fox predation, and prey populations. Ecology 75, 1042–9.
Malmberg G. (1993) Gyrodactylidae and gyrodactylosis of Salmonidae. Bull. français de la pêche et de la pisciculture 328, 5–46.
Margalef R. and Gutierez E. (1983) How to introduce connectance in the frame of an expression for diversity? Am. Naturalist 121, 601–7.
Mas-Coma S. and Montoliu I. (1987) The life-cycle of Dollfusinus frontalis a brachylaimid trematode of small mammals (Insectivora and Rodentia). Int. J. Parasitol. 17, 1063–79.
Mas-Coma S., Galan-Puchades M.T., Fuentes M.V., Valero M.M. and Jimenez A.M. (1988) Sobre la composición cuantitativa de las parasitofaunas insulares: posible efecto regulador de las especies parasitas sobre las poblaciones de sus hospedadores. In Mamiferos y Helmintos (V. Sans-Coma, S. Mas-Coma and J. Gosalbez, eds) pp. 217–51. Barcelona: Ketres Editora.
Moore J. (1984) Parasites that change the behavior of their host. Sci. Am. 250, 108–15.
Morand, S. (1996) Biodiversity of parasites in relation to their life cycle. In Aspects of the Genesis and Maintenance of Biodiversity (M. Hochberg, J. Clobert and R. Barbault, eds) pp. 243–260.
Moulia C., Aussel J.P., Bonhomme F., Boursot P., Nielsen J.T. and Renaud F. (1991) Wormy mice in a hybrid zone: a genetic control of susceptibility to parasite infection. J. Evol. Biol. 4. 679–87.
Moulia C., Le Brun N., Orth A., Dallas J. and Renaud F. (1993) Experimental evidence of genetic determinism in high susceptibility to pinworms infections in mice: a hybrid zone model. Parasitology 106, 387–93.
Nelson B.C. and Smith C.R. (1980) Ecology of sylvatic plague in lava caves at Lava Beds National Monument, California. In Fleas: Proceedings of the International Conference on Fleas (R. Traub and H. Starcke, eds) Rotterdam: Balkema: 273–5.
Prévost G., Boulétreau M. and Wajnberg E. (1989) Effets de la surpopulation larvaire sur l'évolution des larves de Drosophiles parasitées par les Hyménoptères Cynipides du genre Leptopilina. Bull. Soc. Ecophysio. 14, 109–13.
Price P.W., Westoby M., Rice B., Atsatt P.R., Fritz R.S., Thompson J.N. and Mobley K. (1986) Parasite mediation in ecological interactions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 17, 487–505.
Price P.W., Westoby M. and Rice B. (1988) Parasite-mediated competition: some predictions and results. Am. Naturalist 131 544–55.
Richner H., Oppliger A. and Christe P. (1993) Effect of an ectoparasite on the reproduction in great tits. J. Anim. Ecol. 62, 703–10.
Sage R.D., Heyneman D., Lim K.C. and Wilson A.C. (1986) Wormy mice in a hybrid zone. Nature 324, 60–3.
Toft C.A. and Aeschlimann A. (1991) Introduction: coexistence or conflict? In Parasite-Host Associations: Coexistence or Conflict? (C.A. Toft, A. Aeschlimann and L. Bolis, eds) pp. 1–12. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Whitham T.G. (1989) Plant hybrid zones as sinks for pests. Science 244, 1490–3.
Whitlaw H.A. and Lankester M.W. (1994a) A retrospective evaluation of the effects of partelaphostrongylosis on moose populations. Can. J. Zool. 72, 1–7.
Whitlaw H.A. and Lankester M.W. (1994b) The co-occurrence of moose, white-tailed deer and Parelaphostrongylus tenuis in Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 72, 819–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Combes, C. Parasites, biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Biodivers Conserv 5, 953–962 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00054413
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00054413