Abstract
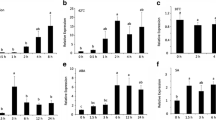
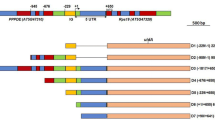
In Arabidopsis thaliana, the activation process of the A1 EF-1α gene depends on several elements. Using the GUS reporter gene, transient expression experiments have shown that mutations of upstream cis-acting elements of the A1 promoter, or the deletion of an intron located within the 5′ non-coding region, similarly affect expression in dicot or monocot protoplasts. The results reported here strongly suggest that this 5′ intron is properly spliced in Zea mays. We show that two trans-acting factors, specifically interacting with an upstream activating sequence (the TEF 1 box), are present in nuclear extracts prepared from A. thaliana, Brassica rapa, Nicotiana tabacum and Z. mays. In addition, a DNA sequence homologous to the TEF 1 box, found at approximately the same location within a Lycopersicon esculentum EF-1α promoter, interacts with the same trans-acting factors. Homologies found between the A. thaliana and L. esculentum TEF 1 box sequences have allowed us to define mutations of this upstream element which affect the interaction with the corresponding trans-acting factors. These results support the notion that the activation processes of A. thaliana EF-1α genes have been conserved among angiosperms and provide interesting data on the functional structure of the TEF 1 box.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelos, M, Bardet, C, Liboz, T, Le Van Thai, A, Curie, C, Lescure, B: The gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation elongation factor EF-1α: Molecular cloning, characterization and expression. Mol Gen Genet 219: 106–112 (1989).
Bouchez, D, Tokuhisa, JG, Llewellyn, DJ, Dennis, ES, Ellis, JG: The ocs-element is a component of the promoters of several T-DNA and plant viral genes. EMBO J 8: 4197–4204 (1989).
Brinkmann, H, Martinez, P, Quigley, F, Martin, W, Cerff, R: Endosymbiotic origin and codon bias of the nuclear gene for chloroplast glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase from maize. J Mol Evol 26: 320–328 (1987).
Bruhat, A, Tourmente, S, Chapel, S, Sobrier, ML, Coudere, JL, Dastugue, B: Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional regulation of β3 tubulin gene by 20-hydroxyecdysone in Drosophila Kc cells. Nucl Acids Res 18: 2861–2867 (1990).
Callis, J, Fromm, M, Walbot, V: Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Devel 1: 1183–1200 (1987).
Chung, S, Perry, R: Importance of introns for expression of mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol 9: 2075–2082 (1989).
Chupeau, Y, Bourgin, JP, Missonier, C, Dorion, N, Morel, G: Préparation et culture de protoplastes de divers Nicotiana. CR Acad Sci 278: 1565–1568 (1974).
Curie, C, Liboz, T, Bardet, C, Gander, E, Médale, C, Axelos, M, Lescure, B: Cis and trans-acting elements involved in the activation of Arabidopsis thaliana A1 gene encoding the translation elongation factor EF-1α. Nucl Acids Res 19: 1305–1310 (1991).
Fromm, M, Taylor, LP, Walbot, V: Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 5824–5828 (1985).
Giuliano, G, Pichersky, E, Malik, VS, Timko, MP, Scolnik, PA, Cashmore, AR: An evolutionarily conserved protein binding sequence upstream of a plant light-regulated gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 7089–7093 (1988).
Goodall, GJ, Filipowicz, W: Different effects of intron nucleotide composition and secondary structure on pre-mRNA splicing in monocot and dicot plants. EMBO J 10: 2635–2644 (1991).
Green, PJ, Kay, SA, Chua, N-H: Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J 6: 2543–2549 (1987).
Gruissem, W: Of fingers, zippers, and boxes. Plant Cell 2: 827–828 (1990).
Hovemann, B, Richter, S, Waldorf, U, Cziepluch, C: Two genes encode related cytoplasmic elongation factors (EF-1α) in Drosophila melanogaster with continuous and stage specific expression. Nucl Acids Res 16: 3175–3193 (1988).
Huet, J, Sentenac, A: TUF, the yeast DNA-binding factor specific for UAS rpg upstream activating sequences: Identification of the protein and its DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 3648–3652 (1987).
Jefferson, RA, Kavanagh, TA, Bevan, MW: GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6: 3901–3907 (1987).
Keith, B, Chua, N-H: Monocot and dicot pre-mRNAs are processed with different efficiencies in transgenic tobacco. EMBO J 5: 2419–2425 (1986).
Lendstra, JA, VanVliet, A, Arnberg, AC, VanHemert, FJ, Moller, W: Genes coding for the elongation factor EF-1α in Artemia. Eur J Biochem 155: 475–483 (1986).
Liboz, T, Bardet, C, Le Van Thai, A, Axelos, M, Lescure, B: The four members of the gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation factor EF-1α are actively transcribed. Plant Mol Biol 14: 107–110 (1989).
Monaci, P, Nicosia, A, Cortese, R: Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human α 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J 7: 2075–2087 (1988).
Pfeifer, K, Arcangioli, B, Guarente, L: Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of CYC1 gene. Cel 49: 9–18 (1987).
Pröls, M, Töpfer, R, Schell, J, Steinbiss, H-H: Transient gene expression in tobacco protoplasts. I. Time course of CAT appearance. Plant Cell Rep 7: 221–224 (1988).
Riis, B, Rattan, SIS, Clark, BFC, Merrick, WC: Eukaryotic protein elongation factors. Trends Biochem Sci 15: 420–424 (1991).
Ripe, RA, Lorenzen, SI, Brenner, DA, Breindl, M: Regulatory elements in 5′ flanking region and the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the mouse alpha 1 type collagen gene. Mol Cell Biol 9: 2224–2227 (1989).
Shewmaker, CK, Ridge, NP, Pokalsky, AR, Rose, RE, Hiatt, WR: Nucleotide sequence of an EF-1α genomic clone from tomato. Nucl Acids Res 18: 4276 (1990).
Singh, K, Dennis, ES, Ellis, JG, Llewellyn, DJ, Tokuhisa, JG, Wahleithner, JA, Peacock, WJ: OCSBF-1, a maize ocs enhancer binding factor: isolation and expression during development. Plant Cell 2: 891–903 (1990).
Uetsuki, T, Naito, A, Nagata, S, Kaziro, Y: Isolation and characterization of the human chromosomal gene for polypeptide chain elongation factor EF-1α. J. Biol Chem 264: 5791–5798 (1989).
Willmitzer, L: The use of transgenic plants to study plant gene expression. Trends Genet 4: 13–18 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curie, C., Liboz, T., Montané, MH. et al. The activation process of Arabidopsis thaliana A1 gene encoding the translation elongation factor EF-1α is conserved among angiosperms. Plant Mol Biol 18, 1083–1089 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047711
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047711