Abstract
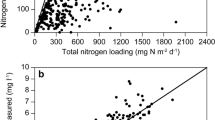
The mass balance for total nitrogen (N) was studied over a four-year period in 16 shallow mainly eutrophic 1st order Danish lakes. Water was sampled in the main inlet of each lake 18–26 times annually, and from the outlets and the lake 19 times annually. Water was also sampled from minor inlets, although less frequently. N input and output were calculated using daily data on discharge (Q), the latter being obtained either from the Q/H relationship based on automatic recordings of water level (H) for the main in- and outlet, or by means of Q/Q relationships for the minor inlets. Annual mean N retention in the lakes ranged from 47 to 234 mg N m−2 d−1, and was particularly high in lakes with high N loading. Annual percentage retention (N ret −y%) ranged from 11 to 72%. Non-linear regression analysis revealed that hydraulic retention time and mean depth accounted for 75% of the variation in annual mean N ret −y% and, in combination with inlet N concentration, accounted for 84% of the variation in the in-lake N concentration. N ret % varied according to season, being higher in the second and third quarter than in the first and fourth quarter (median 18–19%). A simple model was developed for predicting monthly nitrogen retention (N ret −m) on the basis of external N loading, the lake water pool of nitrogen N pool , hydraulic loading and lake water temperature. Calibration of only two parameters on data from the randomly selected 8 out of 16 lakes rendered the model capable of accurately simulating seasonal dynamics of the in-lake N concentration and N ret −m in all 16 lakes. We conclude that with regard to shallow, eutrophic lakes with a relatively low hydraulic retention time, it is now possible to determine not only annual mean nitrogen retention, but also the seasonal variation in N ret−m . Prediction of seasonal variation in N loading of downstream N-limited coastal areas is thereby rendered much more reliable.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmoneim MA, Olah J & Szabo P (1986) Denitrification in water bodies and sediments of Hungarian shallow waters. Aquacultura Hungarica 5: 133–146
Andersen JM (1974) Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets and the role of sediments in six shallow Danish lakes. Arch. Hydrobiol. 74: 528–550
Andersen JM (1977) Rates of denitrification of undisturbed sediment from six lakes as function of nitrate concentration, oxygen and temperature. Arch. Hydrobiol. 80: 147–159
Bachmann RW (1984) Calculation of phosphorus and nitrogen loadings to natural and artificial lakes. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol. 22: 239–243
Bengtsson L (1978) Effects of sewage diversion in lake Södra Bergundasjöen 1: N and phosphorus budgets. Vatten 1: 2–9
Christensen PB, Nielsen LP, Sørensen J & Revsbech NP (1990) Denitrification in nitrate-rich streams: diurnal and seasonal variation related to benthic oxygen metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 35: 640–651
Dudel G & Kohl JG (1992) The nitrogen budget of a shallow lake (Grosser Müggelsee, Berlin). Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 77: 43–72
Gibson CE, Smith RV & Stewart DA (1992) The nitrogen cycle in Lough Neagh, N. Ireland 1975 to 1987. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 77: 73–83
Hovmand MF, Grundahl L, Runge EM, Kemp KK & Aistrup W (1993) Atmosfærisk deposition af kvælstof og fosfor. Faglig rapport fra DMU nr. 91. Danmarks Miljøundersøgelser, pp [In Danish]
Howarth RW, Marino R & Lane J (1988) Nitrogen fixation in freshwater, estuarine, and marine ecosystems. 1. Rates and importance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 669–687
Jenkins MC & Kemp WM (1984) The coupling of nitrification and denitrification in two estuarine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29(3): 609–619
Jensen JP, Kristensen P & Jeppesen E (1991) Relationships between N loading and in-lake N concentrations in shallow Danish lakes. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol. 24: 201–204
Jensen JP, Jeppesen E, Kristensen P, Christensen PB & Søndergaard M (1992) Nitrogen loss and denitrification as studied in relation to reductions in nitrogen loading in a shallow, hypertrophic lake (Lake Søbygård, Denmark). Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 77: 29–42
Jensen JP, Jeppesen E, Olrik K & Kristensen P (1994) Impact of nutrients and physical factors on the shift from cyanobacterial to chlorococcal green algal dominance in shallow Danish lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 51: 1692–1699
Jeppesen E, Kristensen P, Jensen JP, Søndergaard M, Mortensen E & Lauridsen T (1991) Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Mem. Ist. Ital. Idrobiol. 48: 127–148
Kelly CA, Rudd JWM, Hesslein RH, Schindler DW, Dillon PJ, Driscoll CT, Gherini SA & Hecky RE (1987) Prediction of biological acid neutralization in acid-sensitive lakes. Biogeochemistry 3: 129–140
Kristensen P, Kronvang B, Jeppesen E, Græsbøll P, Erlandsen M, Rebsdorf AA, Bruhn A & Søndergaard M (1990) Ferske vandområder - vandløb, kilder og søer. Vandmiljøplanens Overvågningsprogram 1989. Danmarks Miljøundersøgelser, 1990: 130 pp (In Danish)
Kronvang B, Ærtebjerg G, Grant R, Kristensen P, Hovmand M & Kirkegaard J (1993): Nationwide monitoring of nutrients and their ecological effects: state of the Danish aquatic environment. Ambio 22: 176–187
Leonardson L (1984) Does N2 fixation meet the nitrogen requirements of heterocystous bluegreen algae in shallow eutrophic lakes? Oecologia 63: 398–404
Levine SN & Schindler DW (1992) Modification of the N:P ratio in lakes by in situ processes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 37: 917–935
Lewandowski Z (1982) Temperature dependence of biological denitrification with organic materials addition. Water Res. 16: 19–22
Lijklema L, Jansen H & Roijackers RMM (1989) Eutrophication in the Netherlands. Wat. Sci. Tech. 21: 1899–1902
Messer JJ & Brezonik PL (1978) Denitrification in the sediments of lake Okeechobee. Verh. int. Verein. Limnol. 20: 2207–2216
Molot LA & Dillon PJ (1993) Nitrogen mass balances and denitrification rates in central Ontario Lakes. Biogeochemistry 20: 195–212
Nielsen LP (1992) Denitrification in sediments determined from nitrogen isotope paring. FEMS Microbial. Ecol. 86: 357–362
OECD (1982) Eutrophication of Waters. Monitoring, Assessments and Control. OECD, Paris. 210 pp
Oláh J & Szabó P (1986) Nitrogen cycle in a macrophyte covered fish pond. Aquacultura Hungarica 5: 165–177
Ripl W & Feibicke M (1992) Nitrogen metabolism in ecosystems — a new approach. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 77: 15–27
Risgaard-Petersen N, Rysgaard S & Revsbech NP (1993) A sensitive assay for determination of the isotope distribution in NO3-. J. Microbiol. Meth. 17: 155–164
Rysgaard S, Risgaard-Petersen N, Nielsen LP & Revsbech NP (1993) Nitrification and denitrification in lake and estuarine sediments measured by15N dilution technique and isotope pairing. Appl. Ecol. Microbiol. 59: 2093–2098
SAS (1989) SAS/STAT User's Guide, vers. 6, 4th edition
Seitzinger SP (1988) Denitrification in freshwater and coastal marine ecosystems: Ecological and geochemical significance. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 702–724
Seitzinger SP, Nielsen LP, Caffrey J & Bondo Christensen P (1993) Denitrification measurements in aquatic sediments: A comparison of three methods. Biogeochemistry 23: 147–167
Skaarup S & Nielsen LP (1994) Denitrification in a hypereutrophic shallow lake, Lake Søbygård, Denmark. In: Skaarup S (Ed) Denitrifikation i sedimenter belyst med15N teknik. MSc-thesis, University of Aarhus. [In Danish]
Solórzano L & Sharp JH (1980) Determination of total dissolved nitrogen in natural waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 751–754
Van Donk E, Grimm MP, Gulati RD & Klein Breteler JPG (1990) Whole-lake food-web manipulation as a means to study community interactions in a small ecosystem. Hydrobiologia 200/201: 275–289
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Windolf, J., Jeppesen, E., Jensen, J.P. et al. Modelling of seasonal variation in nitrogen retention and in-lake concentration: A four-year mass balance study in 16 shallow Danish lakes. Biogeochemistry 33, 25–44 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00000968