Summary
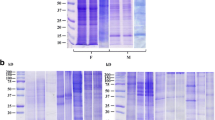
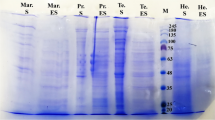
In conventional mice colonies, mouse pinworm, Syphacia obvelata is found very often. Several studies indicate that infection with this parasite can modulate the immune system of the host and can affect experimental final results. The aim of our study was to investigate the most immunogenic proteins of S. obvelata inducing both local and systemic immune response in naturally infected laboratory mice. Protein extracts of S. obvelata were analysed by Western blotting to examine their antigenic character. The antigens were probed with serum and mucosa of S. obvelata naturally infected mice. Surface and somatic antigens were recognized by serum and mucosal IgG, IgA and IgM antibodies. The most immunogenic and dominant proteins were observed. Proteins of Mw ∼ 70, 65 and 48 kDa showed the most evident reaction with serum and mucosa antibodies of infected animals. Surface and somatic antigens of nematode S. obvelata eliciting immune response in laboratory mice may be useful in development of a diagnostic test which could be applied for the infection control prior the experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumans, V. (1988): Environmental enrichment: practical applications. Proceedings of the 2 nd World Congress on Alternatives, Ultrecht 1988, 187–191
Bazzano, T., Restel, T. I., Pinto, R. M., Gomes, D. C. (2002): Patterns of infection with the nematodes Syphacia obvelata and Aspicularis tetraptera in conventionaly maintained laboratory mice. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, 97:1–5
Beattie, G. M., Baird, S. M., Lipsick, R. A., Lannon, R. A., Kaplon, N. O. (1981): Induction of T-and B-lymphocyte responses in antigenically stimulated athymic mice. Cancer Res., 41: 2322–2327
Brett, S. J. (1983): Immunodepression in Giardia muris and Spironucleus muris infections in mice. Parasitology, 87: 507–515
De Graaf, D. C., Berghen, P., Moens, L., De Marez, T. M., Raes, S., Blaxter, M. L., Vercruysse, J. (1996): Isolation, characterization and immunolocalization of a globin-like antigen from Ostertagia ostertagi adults. Parasitology, 113: 63–69
De Vos, T., Danell, G., Dick, T. A. (1992): Trichinella spiralis: dose dependence and kinetics of the mucosal immune responses in mice. Exp. Parasitol., 75: 99–111
Dick, T. A., Wright, K. A. (1973): The ultrastructure of cuticle of the nematode Syphacia obvelata (Rudolphi, 1802). I. The body cuticle of larvae males, and females, and observation on its development. Can. J. Zool., 51: 187–196
Gilioli, R., Andrade, L. A. G., Passos, L. A. C., Silva, F. A., Rodrigues, D. M., Guaraldo, A. M. A. (2000): Parasite survey in mouse and rat colonies of Brazilian laboratory animal houses kept under different sanitary barrier conditions. Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., 52: 33–37
Jacobson, R. H., Reed, N. D. (1974): The thymus dependence of resistance to pinworm infection in mice. J. Parasitol., 60: 976–979
Keith, K. A., Dunkan, M. C., Murray, M., Bairden, K., Tait, A. (1990): Stage-specific cuticular proteins of Ostertagia circumcincta and Ostertagia ostertagi. Int. J. Parasitol., 20: 1037–1045
Kolodyński, J., Okulewicz, A. (1998): Immunoprophylaxis in parasitology. Wiad. Parazytol., 44: 203–215
Laemmli, U. K. (1970): Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227: 680–685
Lübcke, R., Hutchenson, F. A. R., Barbezat, G. O. (1992): Impaired intestinal electrolyte transport in rats infested with the common parasite Syphacia muris. Dig. Dis. Sci., 37: 60–64
McNair, D. M., Timmons, E. H. (1977): Effects of Aspiculuris tetraptera and Syphacia obvelata on exploratory behavior of an inbred mouse strain. Lab. Anim. Sci., 27: 38–42
Okulewicz, A., Perec, A. (2003): Parasite infections in laboratory mice colonies. Polish J. Vet. Sci, 6: 51–53
Pacon, J., Piekarska, J. (2004): Mice parasites in selected colonies of laboratory animal houses. Wiad. Parazytol., 50: 93–94
Panter, H. C. (1969): Studies on host-parasite relationships: Syphacia obvelata in the mouse. J. Parasitol., 55: 74–78
Pinto, R. M., Vicente, J. J., Noronha, D., Goncalves, L., Gomes, D. C. (1994): Helminth parasites of conventionally maintained laboratory mice. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, 89: 33–40
Pinto, R. M., Gonclaves, L., Noronha, D., Gomes, D. C. (2001): Worm burdens in outbred and inbred laboratory rats with morphometric data on Syphacia muris (Yamaguti 1935) Yamaguti, 1941 (Nematoda, Oxyuroidea). Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, 96: 133–136
Sato, Y., Ooi Monaka, O. K., Nonaka, N., Oku, Y., Kamiya, M. (1995): Antibody production in Syphacia obvelata infected mice. J. Parasitol., 81: 559–562
Schallig, H. D. F. H., Van Leeuwen, M. A. W. (1994): Immune responses of Texel sheep to excretory/secretory products of helminth parasites: effects on host immune responses. Parasitology, 96: 123–166
Shibahara, T. (1999): Necessity of reexamining the pathogenicity and elimination of parasites in rats and mice. Microbial status and genetic evaluation of mice and rats. Proc. 1999 US/Japan Conference
Taffs, L. F. (1976): Pinworms infections in laboratory rodents: A review. Lab. Anim., 10: 1–13
Towbin, H., Stacklin, T., Gordon, J. (1979): Electrophoretic transfer of protein from polyacrylamide gels to nitro-cellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 76: 4350–4354
Wagner, M. (1988): The effect of infection with the pinworm (Syphacia muris) on rat growth. Lab. Anim. Sci., 38: 476–478
Wedrychowicz, H., Homles, P. H., Tait, A. (1994): Surface antigens of exsheated infective larvae of Ostertagia circumcincta. Acta Parasitol., 39: 162–169
Wedrychowicz, H. (1997): Surface proteins of nematodes and thier role in host-parasite relationship. Med. Wet., 53: 566–569
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Perec, A., Okulewicz, A. The presence of Syphacia obvelata in laboratory mice (BALB/c) — parasite antigens in immune response. Helminthologia 43, 203–207 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11687-006-0038-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11687-006-0038-5