Abstract
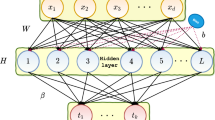
Compared with traditional learning methods such as the back propagation (BP) method, extreme learning machine provides much faster learning speed and needs less human intervention, and thus has been widely used. In this paper we combine the L 1/2 regularization method with extreme learning machine to prune extreme learning machine. A variable learning coefficient is employed to prevent too large a learning increment. A numerical experiment demonstrates that a network pruned L 1/2 regularization has fewer hidden nodes but provides better performance than both the original network and the network pruned by L 2 regularization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop, C.M., 1995. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. Oxford University Press, UK.
Chen, S., Donoho, D.L., Saunders, M.A., 2001. Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM Rev., 43(1):129–159. [doi:10.1137/S003614450037906X]
Donoho, D.L., Huo, X., 2001. Uncertainty principles and ideal atomic decomposition. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 47(7):2845–2862. [doi:10.1109/18.959265]
Horata, P., Chiewchanwattana, S., Sunat, K., 2013. Robust extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing, 102:31–44. [doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2011.12.045]
Hornik, K., Stinchcombe, M., White, H., 1989. Multilayer feedforward networks are universal approximators. Neur. Networks, 2(5):359–366. [doi:10.1016/0893-6080(89)90020-8]
Huang, G.B., Siew, C.K., 2004. Extreme learning machine: RBF network case. Proc. 8th Int. Conf. on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision, p.1029–1036. [doi:10.1109/ICARCV.2004.1468985]
Huang, G.B., Zhu, Q.Y., Siew, C.K., 2004. Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. Proc. IEEE Int. Joint Conf. on Neural Networks, p.985–990. [doi:10.1109/IJCNN.2004.1380068]
Huang, G.B., Zhu, Q.Y., Siew, C.K., 2006. Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 70(1–3):489–501. [doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126]
Huang, G.B., Wang, D.H., Lan, Y., 2011. Extreme learning machines: a survey. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern., 2(2):107–122. [doi:10.1007/s13042-011-0019-y]
Miche, Y., Sorjamaa, A., Bas, P., et al., 2010. OP-ELM: optimally pruned extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans. Neur. Networks, 21(1):158–162. [doi:10.1109/TNN.2009.2036259]
Miche, Y., van Heeswijk, M., Bas, P., et al., 2011. TROPELM: a double-regularized ELM using LARS and Tikhonov regularization. Neurocomputing, 74(16):2413–2421. [doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2010.12.042]
Rasmussen, C.E., Williams, C.K.I., 2006. Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA.
Soria-Olivas, E., Gomez-Sanchis, J., Jarman, I.H., et al., 2011. BELM: Bayesian extreme learning machine. IEEE Trans. Neur. Networks, 22(3):505–509. [doi:10.1109/TNN.2010.2103956]
Tibshirani, R., 1996. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B, 58(1):267–288.
Wu, W., 2003. Computation of Neural Networks. Higher Education Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Xu, G.B., Zhou, D.H., 2010. Fault prediction for statedependent fault based on online learning neural network. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Eng. Sci.), 44(7):1251–1254 (in Chinese).
Xu, Z.B., 2010. Data modeling: visual psychology approach and L 1/2 regularization theory. Proc. Int. Congress of Mathmaticians, p.3151–3184.
Xu, Z.B., Zhang, H., Wang, Y., et al., 2010. L 1/2 regularization. Sci. China Inform. Sci., 53(6):1159–1169. [doi:10.1007/s11432-010-0090-0]
Yan, G.F., Zhang, S.L., Liu, M.Q., 2004. Standard neural network model and its application. J. Zhejiang Univ. (Eng. Sci.), 38(3):297–301 (in Chinese).
Zhang, W.B., Ji, H.B., 2013. Fuzzy extreme learning machine for classification. Electron. Lett., 49(7):448–450. [doi:10.1049/el.2012.3642]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11171367) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Yt., Wu, W., Yang, Wy. et al. A pruning algorithm with L 1/2 regularizer for extreme learning machine. J. Zhejiang Univ. - Sci. C 15, 119–125 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300197
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.C1300197