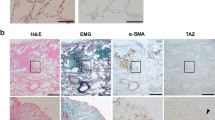
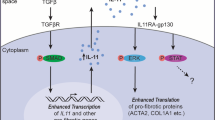
Abstract
The transforming growth factor (TGF) superfamily encompasses about 30 members in mammals. The effect of TGF-β subfamily members is exerted and regulated via selective pathways of synthesis and signaling that involve activation of latent TGF-β, specific and high-affinity binding to cell membrane serine/threonine kinase receptors, activation of intracellular cascades that include Smad molecules and mitogen-activated protein kinases, and regulated termination of the effect by diverse mechanisms including protein degradation and transcriptional activation. Several comprehensive reviews on TGF-β biology in general and on the role of this cytokine in other diseases have been published recently. In recent years an unexpected role of TGF-β on lung homeostasis has been revealed. Here, we discuss the contribution of TGF-β to the pathogenesis of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, two common illnesses of the lung, as well as of lymphangioleiomyomatosis, a rare disease in women. The information we collate and integrate places TGF-β at a pivotal point within complex networks that control lung physiology as well as the physiopathology of these lung diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annes, J. P., Munger, J. S., and Rifkin, D. B. (2003) Making sense of latent TGF beta activation. J. Cell Sci. 116, 217–224.
Attisano, L. and Wrana, J. L. (2002) Signal transduction by the TGF-beta superfamily. Science 296, 1646–1647.
Benson, J. R. (2004) Role of transforming growth factor beta in breast carcinogenesis. Lancet Oncol. 5, 229–239.
Marek, A., Brodzicki, J., Liberek, A., and Korzon, M. (2002) TGF-beta (transforming growth factor-beta) in chronic inflammatory conditions—a new diagnostic and prognostic marker? Med. Sci. Monit., 8, RA145-RA151.
Derynck, R., Jarrett, J. A., Chen, E. Y., et al. (1985) Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature 316, 701–705.
Martin, R., Haendler, B., Hofer-Warbinek, R., et al. (1987) Complementary DNA for human glioblastoma-derived T cell suppressor factor, a novel member of the transforming growth factor-beta gene family. EMBO J. 6, 3673–3677.
ten Dijke, P., Geurts van Kessel, A. H., Foulkes, J. G., and Le Beau, M. M. (1988) Transforming growth factor type beta-3 maps to human chromosome 14, region q23–q24. Oncogene 3, 721–724.
Kwong, K. Y., Literat, A., Zhu, N. L., et al. (2004) Expression of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta1) in human epithelial alveolar cells: a pro-inflammatory mediator independent pathway. Life Sci. 74, 2941–2957.
Koli, K., Saharinen, J., Hyytiainen, M., Penttinen, C., and Keski-Oja, J. (2001) Latency, activation, and binding proteins of TGF-beta. Microsc. Res. Tech. 52, 354–362.
Munger, J. S., Huang, X., Kawakatsu, H., et al. (1999) The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta 1: a mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell 96, 319–328.
Goumans, M. J. and Mummery, C. (2000) Functional analysis of the TGF beta receptor/Smad pathway through gene ablation in mice. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 44, 253–265.
Kaartinen, V., Voncken, J. W., Shuler, C., et al. (1995) Abnormal lung development and cleft palate in mice lacking TGF-beta 3 indicates defects of epithelial-mesenchymal interaction. Nat. Genet. 11, 415–421.
Franzen, P., ten Dijke, P., Ichijo, H., et al. (1993) Cloning of a TGF beta type I receptor that forms a heteromeric complex with the TGF beta type II receptor. Cell 75, 681–692.
Zhao, Y., Young, S. L., McIntosh, J. C., Steele, M. P., and Silbajoris, R. (2000) Ontogeny and localization of TGF-beta type I receptor expression during lung development. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 278, L1231-L1239.
Bottinger, E. P., Jakubczak, J. L., Haines, D. C., Bagnall, K., and Wakefield, L. M. (1997) Transgenic mice overexpressing a dominant-negative mutant type II transforming growth factor β receptor show enhanced tumorigenesis in the mammary gland and lung in response to the carcinogen 7,12-dimethylbene-α-anthracene. Cancer Res. 57, 5564–5570.
Larsson, J., Goumans, M. J., Sjostrand, L. J., et al. (2001) Abnormal angiogenesis but intact hematopoietic potential in TGF-beta type I receptor-deficient mice. EMBO J. 20, 1663–1673.
Oshima, M., Oshima, H., and Taketo, M. M. (1996) TGF β receptor type II deficiency results in defects of yolk sac hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis. Dev. Biol. 179, 297–302.
Datto, M. and Wang, X. F. (2000) The Smads: transcriptional regulation and mouse models. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 11, 37–48.
Sirard, C., Kim, S., Mirtsos, C., et al. (2000) Targeted disruption in murine cells reveals variable requirement for Smad4 in transforming growth factor b-related signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2063–2070.
Massague, J. (2000) How cells read TGF-β signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 169–178.
Kavsak, P., Rasmussen, R. K., Causing, C. G., et al. (2000) Smad7 binds to Smurf2 to form an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets the TGF-β receptor for degradation. Mol. Cell 6, 1365–1375.
Koinuma, D., Shinozaki, M., Komuro, A. et al. (2003) Arkadia amplifies TGF-beta superfamily signalling through degradation of Smad7. EMBO J. 22, 6458–6470.
Hanyu, A., Ishidou, Y., Ebisawa, T., Shimanuki, T., Imamura, T., and Miyazono, K. (2001) The N domain of Smad7 is essential for specific inhibition of transforming growth factor-β signaling. J. Cell Biol. 155, 1017–1027.
Pulaski, L., Landstrom, M., Heldin, C. H., and Souchelnytskyi, S. (2001) Phosphorylation of Smad7 at Ser-249 does not interfere with its inhibitory role in transforming growth factor-β-dependent signaling but affects Smad7-dependent transcriptional activation. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 14,344–14,349.
Reguly, T. and Wrana, J. L. (2003) In or out? The dynamics of Smad nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 216–220.
Funaba, M., Zimmerman, C. M., and Mathews, L. S. (2002) Modulation of Smad2-mediated signaling by extracellular signal-regulated kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41,361–41,368.
Engel, M. E., McDonnell, M. A., Law, B. K., and Moses, H. L. (1999) Interdependent SMAD and JNK signaling in transforming growth factor β-mediated transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37,413–37,420.
Wicks, S. J., Lui, S., Abdel-Wahab, N., Mason, R. M., and Chantry, A. (2000) Inactivation of smad-transforming growth factor β signaling by Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 8103–8111.
Yakymovych, I., ten Dijke, P., Heldin, C. H., and Souchelnytskyi, S. (2001) Regulation of Smad signaling by protein kinase C. FASEB J. 15, 553–555.
Birchenall-Roberts, M. C., Fu, T., Bang, O. S., et al. (2004) Tuberous sclerosis complex 2 gene product interacts with human SMAD proteins: a molecular link of two tumor suppressor pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25,605–25,613.
Zavadil, J., Bitzer, M., Liang, D., et al. (2001) Genetic programs of epithelial cell plasticity directed by transforming growth factor-β. PNAS 98, 6686–6691.
Brown, K. and Bhowmick, N. A. (2004) Linking TGF-beta-mediated Cdc25A inhibition and cytoskeletal regulation through RhoA/p160(ROCK) signaling. Cell Cycle 3, 408–410.
Vinals, F. and Pouyssegur, J. (2001) Transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) promotes endothelial cell survival during in vitro angiogenesis via an autocrine mechanism implicating TGF-α signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 7218–7230.
Griswold-Prenner, I., Kamibayashi, C., Maruoka, E. M., Mumby, M. C., and Derynck, R. (1998) Physical and functional interactions between type I transforming growth factor β receptors and Bα, a WD-40 repeat subunit of phosphatase 2A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 6595–6604.
Frederick, J. P. and Wang, X. F. (2002) Smads “freeze” when they ski. Structure (Camb.) 10, 1607–1611.
Barbato, A., Turato, G., Baraldo, S., et al. (2003) Airway inflammation in childhood asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 168, 798–803.
Knight, D. (2001) Epithelium-fibroblast interactions in response to airway inflammation. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 79, 160–164.
Verrecchia, F., Chu, M. L., and Mauviel, A. (2001) Identification of novel TGF-beta/Smad gene targets in dermal fibroblasts using a combined cDNA microarray/promoter transactivation approach. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 17,058–17,062.
McKarns, S. C., Letterio, J. J., and Kaminski, N. E. (2003) Concentration-dependent bifunctional effect of TGF-beta 1 on immunoglobulin production: a role for Smad3 in IgA production in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 3, 1761–1774.
Pepper, M. S., Vassalli, J. D., Orci, L., and Montesano, R. (1993) Biphasic effect of transforming growth factor-beta 1 on in vitro angiogenesis. Exp. Cell. Res. 204, 356–363.
Dunker, N. and Krieglstein, K. (2000) Targeted mutations of transforming growth factor-beta genes reveal important roles in mouse development and adult homeostasis. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 6982–6988.
Zhou, L., Dey, C. R., Wert, S. E., and Whitsett, J. A. (1996) Arrested lung morphogenesis in transgenic mice bearing an SP-C-TGF-beta 1 chimeric gene. Dev. Biol. 175, 227–238.
Zhao, J., Crowe, D. L., Castillo, C., Wuenschell, C., Chai, Y., and Warburton, D. (2000) Smad7 is a TGF-beta-inducible attenuator of Smad2/3-mediated inhibition of embryonic lung morphogenesis. Mech. Dev. 93, 71–81.
Luukko, K., Ylikorkala, A., and Makela, T. P. (2001) Developmentally regulated expression of Smad3, Smad4, Smad6, and Smad7 involved in TGF-beta signaling. Mech. Dev. 101, 209–212.
Sirard, C., de la Pompa J. L., Elia, A., et al. (1998) The tumor suppressor gene Smad4/Dpc4 is required for gastrulation and later for anterior development of the mouse embryo. Genes Dev. 12, 107–119.
Yang, X., Letterio, J. J., Lechleider, R. J., et al. (1999) Targeted disruption of SMAD3 results in impaired mucosal immunity and diminished T cell responsiveness to TGF β. EMBO J. 18, 1280–1291.
Duvernelle, C., Freund, V., and Frossard, N. (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta and its role in asthma. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 16, 181–196.
Bartram, U. and Speer, C. P. (2004) The role of transforming growth factor beta in lung development and disease. Chest 125, 754–765.
Wojnarowski, C., Frischer, T., Hofbauer, E., et al. (1999) Cytokine expression in bronchial biopsies of cystic fibrosis patients with and without acute exacerbation. Eur. Respir. J. 14, 1136–1144.
Kokturk, N., Tatlicioglu, T., Memis, L., Akyurek, N., and Akyol, G. (2003) Expression of transforming growth factor beta1 in bronchial biopsies in asthma and COPD. J. Asthma 40, 887–893.
Cohn, L., Elias, J. A., and Chupp, G. L. (2004) Asthma: mechanisms of disease persistence and progression. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22, 789–815.
Ndukwu, I. M., Naureckas, E. T., Maxwell, C., Waldman, M., and Leff, A. R. (1999) Relationship of cellular transmigration and airway response after allergen challenge. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 160, 1516–1524.
Hara, K., Hasegawa, T., Ooi, H., et al. (2001) Inhibitory role of eosinophils on cell surface plasmin generation by bronchial epithelial cells: inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor beta. Lung 179, 9–20.
Cho, J. Y., Miller, M., Baek, K. J., et al. (2004) Inhibition of airway remodeling in IL-5-deficient mice. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 551–560.
Isenberg-Feig, H., Justice, J. P., and Keane-Myers, A. (2003) Animal models of allergic asthma. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 3, 70–78.
Zemann, B., Schwaerzler, C., Griot-Wenk, M., et al. (2003) Oral administration of specific antigens to allergy-prone infant dogs induces IL-10 and TGF-beta expression and prevents allergy in adult life. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 111, 1069–1075.
Schramm, C., Herz, U., Podlech, J., et al. (2003) TGF-beta regulates airway responses via T cells. J. Immunol. 170, 1313–1319.
Kumar, R. K., Herbert, C., Thomas, P. S., et al. (2003) Inhibition of inflammation and remodeling by roflumilast and dexamethasone in murine chronic asthma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 307, 349–355.
Jain, V. V., Kitagaki, K., Businga, T., et al. (2002) CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides inhibit airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 110, 867–872
Silverman, E. S., Palmer, L. J., Subramaniam, V., et al. (2004) Transforming growth factor-beta1 promoter polymorphism C-509T is associated with asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 169, 214–219.
Paraskakis, E., Sourvinos, G., Passam, F., et al. (2003) Microsatellite DNA instability and loss of heterozygosity in bronchial asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 22, 951–955.
Yuyama, N., Davies, D. E., Akaiwa, M., et al. (2002) Analysis of novel disease-related genes in bronchial asthma. Cytokine 19, 287–296.
Zou, J., Young, S., Zhu, F., et al. (2002) Microarray profile of differentially expressed genes in a monkey model of allergic asthma. Genome Biol., 3, research0020.
Takizawa, H., Tanaka, M., Takami, K., et al. (2001) Increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta1 in small airway epithelium from tobacco smokers and patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 163, 1476–1483.
Hodge, S., Hodge, G., Holmes, M., Flower, R., and Scicchitano, R. (2001) Interleukin-4 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha inhibit transforming growth factor-beta, production in a human bronchial epithelial cell line: possible relevance to inflammatory mechanisms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respirology 6, 205–211.
Luethviksson, B. R. and Gunnlaugsdottir, B. (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta as a regulator of site-specific T-cell inflammatory response. Scand. J. Immunol. 58, 129–138.
Hodge, S. J., Hodge, G. L., Reynolds, P. N., Scicchitano, R., and Holmes, M. (2003) Increased production of TGF-beta and apoptosis of T lymphocytes isolated from peripheral blood in COPD. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 285, L492-L499.
Silverman, E. K., Speizer, F. E., Weiss, S. T., et al. (2000) Familial aggregation of severe, earlyonset COPD: candidate gene approaches. Chest 117, 273S-274S.
Wu, L., Chau, J., Young, R. P., et al. (2004) Transforming growth factor-beta1 genotype and susceptibility to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 59, 126–129.
Li, H., Cui, D., Ma, N., et al. (2002) The effect of extracellular matrix remodeling on airflow obstruction in a rat model of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 25, 403–407.
Morris, D. G., Huang, X., Kaminski, N., et al. (2003) Loss of integrin alpha(v)beta6-mediated TGF-beta activation causes Mmp12-dependent emphysema. Nature 422, 169–173.
Pittet, J. F., Griffiths, M. J., Geiser, T., et al. (2001) TGF-beta is a critical mediator of acute lung injury. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 1537–1544.
Neptune, E. R., Frischmeyer, P. A., Arking, D. E., et al. (2003) Dysregulation of TGF-beta activation contributes to pathogenesis in Marfan syndrome. Nat. Genet. 33, 407–411.
Stemer-Kock, A., Thorey, I. S., Koli, K., et al. (2002) Disruption of the gene encoding the latent transforming growth factor-beta binding protein 4 (LTBP-4) causes abnormal lung development, cardiomyopathy, and colorectal cancer. Genes Dev. 16, 2264–2273.
Zheng, T., Zhu, Z., Wang, Z., et al. (2000) Inducible targeting of IL-13 to the adult lung causes matrix metalloproteinase- and cathepsin-dependent emphysema. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 1081–1093.
Lee, C. G., Homer, R. J., Zhu, Z., et al. (2001) Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating transforming growth factor beta(1). J. Exp. Med. 194, 809–821.
Yanagisawa, J., Yanagi, Y., Masuhiro, Y., et al. (1999) Convergence of transforming growth factor-beta and vitamin D signaling pathways on SMAD transcriptional coactivators. Science 283, 1317–1321.
Massaro, G. D. and Massaro, D. (1997) Retinoic acid treatment abrogates elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema in rats. Nat. Med. 3, 675–677.
Fujita, M., Ye, Q., Ouchi, H., et al. (2004) Retinoic acid fails to reverse emphysema in adult mouse models. Thorax 59, 224–230.
Wang, H., Liu, X., Umino, T., et al. (2001) Cigarette smoke inhibits human bronchial epithelial cell repair processes. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 25, 772–779.
Ogawa, E., Elliott, W. M., Hughes, F., Eichholtz, T. J., Hogg, J. C., and Hayashi, S. (2004) Latent adenoviral infection induces production of growth factors relevant to airway remodeling in COPD. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 286, L189-L197.
Solway, J., Forsythe, S. M., Halayko, A. J., Vieira, J. E., Hershenson, M. B., and Camoretti-Mercado, B. (1998) Transcriptional regulation of smooth muscle contractile apparatus expression. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 158, S100-S108.
Camoretti-Mercado, B., Liu, H. W., Halayko, A. J., et al. (2000) Physiological control of smooth muscle-specific gene expression through regulated nuclear translocation of serum response factor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 30,387–30,393.
Parmacek, M. S. (2001) Transcriptional programs regulating vascular smooth muscle cell development and differentiation. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 51, 69–89.
Kumar, M. S. and Owens, G. K. (2003) Combinatorial control of smooth muscle-specific gene expression. Arterioscl. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 23, 737–747.
Camoretti-Mercado, B., Dulin, N. O., and Solway, J. (2003) Serum response factor function and dysfunction in smooth muscle. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 137, 223–235.
Zhe, X., Yang, Y., Jakkaraju, S., and Schuger, L. (2003) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 downregulation in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: potential consequence of abnormal serum response factor expression. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 28, 504–511.
Qiu, P., Feng, X. H., and Li, L. (2003) Interaction of Smad3 and SRF-associated complex mediates TGF-beta1 signals to regulate SM22 transcription during myofibroblast differentiation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 35, 1407–1420.
Evans, S. E., Colby, T. V., Ryu, J. H., and Limper, A. H. (2004) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 and extracellular matrix-associated fibronectin expression in pulmonary lymphangioleiomyo-matosis. Chest 125, 1063–1070.
Matsui, K., Takeda, K., Yu, Z. X., Travis, W. D., Moss, J., and Ferrans, V. J. (2000) Role for activation of matrix metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 124, 267–275.
Yu, Q. and Stamenkovic, I. (2000) Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 14, 163–176.
Carsillo, T., Astrinidis, A., and Henske, E. P. (2000) Mutations in the tuberous sclerosis complex gene TSC2 are a cause of sporadic pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. PNAS 97, 6085–6090.
Roberts, A. B. and Wakefield, L. M. (2003) The two faces of transforming growth factor β in carcinogenesis. PNAS 100, 8621–8623.
Karbowniczek, M., Astrinidis, A., Balsara, B. R., et al. (2003) Recurrent lymphangiomyomatosis after transplantation: genetic analyses reveal a metastatic mechanism. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 167, 976–982.
Yang, Y. A., Dukhanina, O., Tang, B., et al. (2002) Lifetime exposure to a soluble TGF-beta antagonist protects mice against metastasis without adverse side effects. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1607–1615.
Muraoka, R. S., Dumont, N., Ritter, C. A., et al. (2002) Blockade of TGF-beta inhibits mammary tumor cell viability, migration, and metastases. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1551–1559.
Lee, B. S. and Nowak, R. A. (2001) Human leiomyoma smooth muscle cells show increased expression of transforming growth factor-beta-3 (TGF-beta-3) and altered responses to the antiproliferative effects of TGF-beta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 913–920.
Kobayashi, T., Minowa, O., Sugitani, Y., et al. (2001) A germ-line Tsc1 mutation causes tumor development and embryonic lethality that are similar but not identical to those caused by Tsc2 mutation in mice. PNAS 98, 8762–8767.
Onda, H., Lueck, A., Marks, P. W., Warren, H. B., and Kwiatkowski, D. J. (1999) Tsc2(+/−) mice develop tumors in multiple sites that express gelsolin and are influenced by genetic background. J. Clin. Invest. 104, 687–695.
Churchill, J., Cheng, B., Ma, L., et al. (2003) Immunohistochemical characterization of lymphangioleio-myomatosis (LAM) derived smooth muscle cells (SMC) [abstract]. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 167, A330.
Chen, W., Jin, W., Hardegen, N., et al. (2003) Conversion of peripheral CD4+CD25-naive T cells to CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells by TGF-beta induction of transcription factor Foxp 3. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1875–1886.
Zuany-Amorim, C., Sawicka, E., Manlius, C., et al. (2002) Suppression of airway eosinophilia by killed Mycobacterium vaccae-induced allergen-specific regulatory T-cells. Nat. Med. 8, 625–629.
Wen, F. Q., Kohyama, T., Skold, C. M., et al. (2003) Glucocorticoids modulate TGF-beta production by human fetal lung fibroblasts. Inflammation 27, 9–19.
Chakir, J., Shannon, J., Molet, S., et al. (2003) Airway remodeling-associated mediators in moderate to severe asthma: effect of steroids on TGF-beta, IL-11, IL-17, and type I and type III collagen expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 111, 1293–1298.
Arutiunov, G. P., Korsunskaia, M. I., Cherniavskaia, T. K., Vershinin, A. A., Rozanov, A. V., and Balanina, N. O. (2000) Safety and clinical efficiency of long-term complete blockade of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. Ter. Arkh. 72, 52–56.
Li, X., Rayford, H., and Uhal, B. D. (2003) Essential roles for angiotensin receptor AT1a in bleomycin-induced apoptosis and lung fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Pathol. 163, 2523–2530.
Myou, S., Fujimura, M., Kamio, Y., et al. (2000) Effect of losartan, a type 1 angiotensin II receptor antagonist, on bronchial hyperresponsiveness to methacholine in patients with bronchial asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 162, 40–44.
el-Agroudy, A. E., Hassan, N. A., Foda, M. A., et al. (2003) Effect of angiotensin II receptor blocker on plasma levels of TGF-beta 1 and interstitial fibrosis in hypertensive kidney transplant patients. Am. J. Nephrol. 23, 300–306.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Camoretti-Mercado, B., Solway, J. Transforming growth factor-β1 and disorders of the lung. Cell Biochem Biophys 43, 131–148 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:43:1:131
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:43:1:131