Abstract
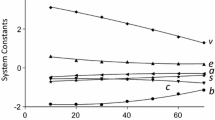
Cyano (CN), butyl (C4), phenyl and octadecyl (C18) phases prepared from the same base silica gel were chromatographically characterized in order to assess the relative importance of lipophilic, π–π and dipole–dipole interactions in governing retention on these differing phases. Dipole interactions of analytes (possessing dipole moments and low lipophilicity) with CN phases were primarily responsible for the elution order. However, as the analytes’ lipophilicity increased, the lipophilic interaction predominated over the dipole interaction. In comparison, retention on the phenyl phase appeared to be complex, being controlled by a mixture of lipophilic, π–π and dipole–dipole interactions. Retention on the C4 and C18 phases was dictated by the analyte’s lipophilicity and its accessibility into the phase.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldberg AP (1982) J Anal Chem 54:342–345. doi:10.1021/ac00239a051
Euerby MR, Petersson P (2003) J Chromatogr A 994:13–36. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00393-5
Kimata K, Iwaguchi K, Onishi S, Jinno K, Eksteen R, Hosoya K, Araki M, Tanaka N (1989) J Chromatogr Sci 27:721–729
Gonnet C, Bory C, Lachatre G (1982) Chromatographia 16:242–246. doi:10.1007/BF02258911
Engelhardt H, Jungheim M (1990) Chromatographia 29:59–68. doi:10.1007/BF02261141
Akapo SO, Simpson CF (1990) J Chromatogr Sci 28:186–193
Neue UD, Serowik E, Iraneta PC, Alden BA, Walter TH (1999) J Chromatogr A 849:87–100. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00435-5
McCalley DV (1997) J Chromatogr A 769:169–178. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(96)01079-5
McCalley DV (1996) J Chromatogr A 738:169–179. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(96)00136-7
Neue UD, Van Tran K, Iraneta PC, Alden BA (2003) J Sep Sci 26:174–186. doi:10.1002/jssc.200390025
Claessens HA, van Straten MA, Cramers CA, Jezierska M, Buszewski B (1998) J Chromatogr A 826:135–156. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00749-3
Majors RE (1980) J Chromatogr Sci 18:488–511
Snyder LR, Dolan JW, Carr PW (2004) J Chromatogr A 1060:77–116
Marchand DH, Croes K, Dolan JW, Snyder LR (2005) J Chromatogr A 1062:57–64. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2004.11.015
Croes K, Steffens A, Marchand DH, Snyder LR (2005) J Chromatogr A 1098:123–130. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.08.090
Stenlake JB (1979) Foundations of molecular pharmacology vol 2. Athlone Press, University of London, London, UK
Foster R (1969) Organic charge-transfer complexes. Academic Press, New York
Wijnja H, Pignatallo JJ, Malekani K (2004) J Environ Qual 33:265–275
Dill KA, Bromberg S (2003) Molecular driving forces. Garland Science, New York
Euerby MR, Petersson P, Campbell W, Roe W (2007) J Chromatogr A 1154:138–151. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.03.119
Beredensen GE, de Galan L (1978) J Liq Chromatogr 1:561–586. doi:10.1080/01483917808060019
Beredensen GE, Pikaart KA, de Galan L (1980) J Liq Chromatogr 3:1437–1464. doi:10.1080/01483918008062788
Petersson P, Euerby MR (2007) J Sep Sci 30:2012–2024. doi:10.1002/jssc.200700086
O’Gara JE, Alden BA, Gendreau CA, Iraneta PC, Walter TM (2000) J Chromatogr A 893:245–251. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00696-8
McCalley DV (1999) J Chromatogr A 844:23–28. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(99)00250-2
Yang M, Fazio S, Munch D, Drumm P (2005) J Chromatogr A 1097:124–129. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.08.028
Neue UD, O’Gara JE, Méndez A (2006) J Chromatogr A 1127:174–1614. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.06.006
Yamagai C, Katashiba N (1996) Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 44:1338–1343
Sangster J (1997) Fundamentals and physical chemistry. Wiley, New York, pp 79–112
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Drs A Brooks, D. Martin, A. Ray (AstraZeneca R & D Charnwood, Loughborough, UK) and Mr N. Riasat (University of Nottingham, Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Nottingham, UK) for assisting in the elucidation of the degradative stability of cyano phases at intermediate pH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markopoulou, C., Tweedlie, T., Watson, D. et al. A Study of the Relative Importance of Lipophilic, π–π and Dipole–Dipole Interactions on Cyanopropyl, Phenyl and Alkyl LC Phases Bonded onto the Same Base Silica. Chroma 70, 705–715 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1224-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-009-1224-7