Abstract
Background
The prognostic significance of low-volume residual nodal disease following neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) is unknown.
Methods
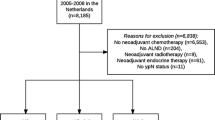
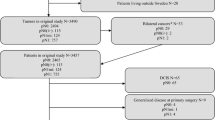
Women with cT1–4N0–1 breast cancer treated with NAC were identified from Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center (DFBWCC) and the National Cancer Database (NCDB). Disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) estimates according to pathologic nodal status were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method, with Cox proportional hazards regression used to assess the effect of clinical variables on survival outcomes.
Results
Among 967 DFBWCC patients, 27 (2.8%) had residual isolated tumor cells (ITCs) and 61 (6.3%) had micrometastases. Five-year DFS was significantly worse in those with residual ITCs (73.5%) and micrometastases (74.7%) relative to those who were ypN0 following NAC (88.4%, p < 0.001). On adjusted analysis, those with residual ITCs (hazard ratio [HR] 2.4, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.20–3.81) and micrometastases (HR 2.14, 95% CI 1.20–3.81) had increased risk of recurrence relative to ypN0 patients. Among 35,536 NCDB patients, 543 (1.5%) had ITCs and 1132 (3.2%) had micrometastases. Five-year OS estimates were significantly worse with increasing residual nodal burden: ypN0, 88.9%; ypN0[i+], 82.8%; ypN1mi, 79.5%; ypN1, 77.6% (p < 0.001). Compared with patients with ypN0 disease, NCDB patients with ITCs and micrometastases had 1.9- and 2.2-fold risk of death (p < 0.001). On subgroup analysis, the effect of low-volume residual disease on mortality was most pronounced in patients with triple-negative and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive disease.
Conclusions
Low-volume residual nodal disease following NAC is associated with poorer DFS and OS relative to those who are node negative.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galimberti V, Cole BF, Zurrida S, et al. Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(4):297–305.
Giuliano AE, Ballman K, McCall L, et al. Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: long-term follow-up from the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group (Alliance) ACOSOG Z0011 randomized trial. Ann Surg. 2016;264(3):413–420.
Fisher ER, Wang J, Bryant J, Fisher B, Mamounas E, Wolmark N. Pathobiology of preoperative chemotherapy: findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel (NSABP) protocol B-18. Cancer. 2002;95(4):681–695.
Klauber-DeMore N, Ollila DW, Moore DT, et al. Size of residual lymph node metastasis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer patients is prognostic. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(5):685–691.
Maaskant-Braat AJ, van de Poll-Franse LV, Voogd AC, et al. Sentinel node micrometastases in breast cancer do not affect prognosis: a population-based study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;127(1):195–203.
van Nijnatten TJ, Simons JM, Moossdorff M, et al. Prognosis of residual axillary disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in clinically node-positive breast cancer patients: isolated tumor cells and micrometastases carry a better prognosis than macrometastases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017;163(1):159–166.
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987;40(5):373–383.
Klabunde CN, Potosky AL, Legler JM, Warren JL. Development of a comorbidity index using physician claims data. J Clin Epidemiol. 2000;53(12):1258–1267.
Mougalian SS, Hernandez M, Lei X, et al. Ten-year outcomes of patients with breast cancer with cytologically confirmed axillary lymph node metastases and pathologic complete response after primary systemic chemotherapy. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(4):508–516.
Mamounas EP, Anderson SJ, Dignam JJ, et al. Predictors of locoregional recurrence after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results from combined analysis of National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-18 and B-27. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(32):3960–3966.
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;384(9938):164–172.
Fayanju OM, Ren Y, Thomas SM, et al. The clinical significance of breast-only and node-only pathologic complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT): a review of 20,000 breast cancer patients in the National Cancer Data Base (NCDB). Ann Surg. 2018;268(4):591–601.
Boughey JC, McCall LM, Ballman KV, et al. Tumor biology correlates with rates of breast-conserving surgery and pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: findings from the ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial. Ann Surg. 2014;260(4):608–614. (discussion 614-606).
Symmans WF, Wei C, Gould R, et al. Long-term prognostic risk after neoadjuvant chemotherapy associated with residual cancer burden and breast cancer subtype. J Clin Oncol. 2017;35(10):1049–1060.
Mittendorf EA, Vila J, Tucker SL, et al. The neo-bioscore update for staging breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: incorporation of prognostic biologic factors into staging after treatment. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2(7):929–936.
von Minckwitz G, Huang CS, Mano MS, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine for residual invasive HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(7):617–628.
Masuda N, Lee SJ, Ohtani S, et al. Adjuvant capecitabine for breast cancer after preoperative chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(22):2147–2159.
Boileau JF, Poirier B, Basik M, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: the SN FNAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(3):258–264.
Moo TA, Edelweiss M, Hajiyeva S, et al. Is low-volume disease in the sentinel node after neoadjuvant chemotherapy an indication for axillary dissection? Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25(6):1488–1494.
Curigliano G, Burstein HJ, P Winner E, et al. De-escalating and escalating treatments for early-stage breast cancer: the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus Conference on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2017. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(8):1700–1712.
Mamounas EP, White JR, Bandos H, et al. NSABP B-51/RTOG 1304: randomized phase III clinical trial evaluating the role of postmastectomy chest wall and regional nodal XRT (CWRNRT) and post-lumpectomy RNRT in patients (pts) with documented positive axillary (Ax) nodes before neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NC) who convert to pathologically negative Ax nodes after NC. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15_suppl):TPS1141-TPS1141.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the Breast Cancer Translational Research Fund at Dana-Farber/Brigham and Women’s Cancer Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
T.A.K. reports speaker fees from Genomic Health.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wong, S.M., Almana, N., Choi, J. et al. Prognostic Significance of Residual Axillary Nodal Micrometastases and Isolated Tumor Cells After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 26, 3502–3509 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07517-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-019-07517-2