Abstract
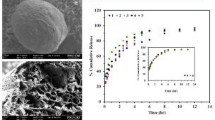
The purpose of this study was to prepare wax-incorporated pectin-based emulsion gel beads using a modified emulsion-gelation method. The waxes in pectin–olive oil mixtures containing a model drug, metronidazole, were hot-melted, homogenized and then extruded into calcium chloride solution. The beads formed were separated, washed with distilled water and dried for 12 h. The influence of various types and amounts of wax on floating and drug release behavior of emulsion gel beads of calcium pectinate was investigated. The drug-loaded gel beads were found to float on simulated gastric fluid if the sufficient amount of oil was used. Incorporation of wax into the emulsion gel beads affected the drug release. Water-soluble wax (i.e. polyethylene glycol) increased the drug release while other water-insoluble waxes (i.e. glyceryl monostearate, stearyl alcohol, carnauba wax, spermaceti wax and white wax) significantly retarded the drug release. Different waxes had a slight effect on the drug release. However, the increased amount of incorporated wax in the formulations significantly sustained the drug release while the beads remained floating. The results suggest that wax-incorporated emulsion gel beads could be used as a carrier for intragastric floating drug delivery.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Streubel, J. Siepmann, and R. Bodmeier. Drug delivery to the upper small intestine window using gastroretention technologies. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 6:501–508 (2006).
A. J. Moes. Gastroretentive dosage forms. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 10:143–195 (1993).
M. P. Cooreman, P. Krausgrill, and K. J. Hengels. Local gastric and serum amoxycilline concentrations after different oral application forms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 37:1506–1509 (1993).
S. S. Davis. Formulation strategies for absorption windows. Drug Discov Today. 10:249–257 (2005).
I. Krogel, and R. Bodmeier. Development of a multifunctional matrix drug delivery system surrounded by an impermeable cylinder. J Control Release. 61:43–50 (1999).
S. Desai, and S. Bolton. A floating controlled release drug delivery system: in-vitro – in-vivo evaluation. Pharm Res. 10:1321–1325 (1993).
A. Streubel, J. Siepmann, and R. Bodmeier. Floating microparticles based on low density foam powder. Int J Pharm. 241:279–292 (2002).
G. T. Grant, E. R. Morris, D. A. Rees, P. J. A. Smith, and D. Thom. Biological interactions between polysaccharides and divalent cations: The egg-box model. FEBS Lett. 32:195–198 (1973).
P. Sriamornsak, and J. Nunthanid. Calcium pectinate gel beads for controlled release drug delivery: I. Preparation and in-vitro release studies. Int J Pharm. 160:207–212 (1998).
P. Sriamornsak, and J. Nunthanid. Calcium pectinate gel beads for controlled release drug delivery: II. Effect of formulation and processing variables on drug release. J Microencapsul. 16:303–313 (1999).
P. Sriamornsak. Investigation of pectin as a carrier for oral delivery of proteins: using calcium pectinate gel beads. Int J Pharm. 169:213–220 (1998).
P. Sriamornsak. Effect of calcium concentration, hardening agent and drying condition on release characteristics of oral proteins from calcium pectinate gel beads. Eur J Pharm Sci. 8:221–227 (1999).
O. Chambin, G. Dupuis, D. Champion, A. Voilley, and Y. Pourcelot. Colon-specific drug delivery: Influence of solution reticulation properties upon pectin beads performance. Int J Pharm. 321:86–93 (2006).
P. Sriamornsak. Chemistry of pectin and its pharmaceutical uses: A review. Silpakorn Univ Int J. 3:206–228 (2003).
P. Sriamornsak, N. Thirawong, and S. Puttipipatkhachorn. Morphology and buoyancy of oil-entrapped calcium pectinate gel beads. AAPS J. 2004;6(3):article 24. (http://www.aapsj.org)
P. Sriamornsak, N. Thirawong, and S. Puttipipatkhachorn. Emulsion gel beads of calcium pectinate capable of floating on the gastric fluid: effect of some additives, hardening agent or coating on release behavior of metronidazole. Eur J Pharm Sci. 24:363–373 (2005).
S. S. Badve, P. Sher, A. Korde, and A. P. Pawar. Development of hollow/porous calcium pectinate beads for floating-pulsatile drug delivery. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 65:85–93 (2007).
P. Sriamornsak, S. Sungthogjeen, and S. Puttipipatkhachorn. Use of pectin as a carrier for intragastric floating drug delivery: Carbonate salt contained beads. Carbohydr Polym. 67:436–445 (2007).
J. Leroux, V. Langendorff, G. Schick, V. Vaishnav, and J. Mazoyer. Emulsion stabilizing properties of pectin. Food Hydrocolloids. 17:455–462 (2003).
N. Garti, and D. Reichman. Hydrocolloids as food emulsifiers and stabilizers. Food Structure. 12:411–426 (1993).
D. Poncelet, V. G. Babak, R. J. Neufeld, M. F. A. Goosen, and B. Burgarski. Theory of electrostatic dispersion of polymer solutions in the production of microgel beads containing biocatalyst. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 79:213–228 (1999).
M. K. Kumar, M. H. Shah, A. Ketkar, K. R. Mahadik, and A. Paradkar. Effect of drug solubility and different excipients on floating behaviour and release from glyceryl monooleate matrices. Int J Pharm. 272:151–160 (2004).
L. Rodriguez, N. Passerinim, C. Cavallari, M. Cini, P. Sancin, and A. Fini. Description and preliminary evaluation of a new ultrasonic atomizer for spray-congealing processes. Int J Pharm. 183:133–143 (1999).
M. Ozyazici, E. H. Gokce, and G. Ertan. Release and diffusional modelling of metronidazole lipid matrices. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 63:331–339 (2006).
F. Zhou, C. Vervaet, and J. P. Remon. Matrix pellets based on the combination of waxes, starches and maltodextrins. Int J Pharm. 133:155–160 (1996).
Q. R. Cao, T. W. Kim, and B. J. Lee. Photoimages and the release characteristics of lipophilic matrix tablets containing highly water-soluble potassium citrate with high drug loadings. Int J Pharm. 339:19–24 (2007).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank K. Kuakoon for laboratory assistance and Food & Cosmetic System Co., Ltd. (Thailand) for supplying pectin samples manufactured by CP Kelco (Denmark). Financial support from Faculty of Pharmacy, Silpakorn University is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sriamornsak, P., Asavapichayont, P., Nunthanid, J. et al. Wax-incorporated Emulsion Gel Beads of Calcium Pectinate for Intragastric Floating Drug Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 9, 571–576 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9082-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-008-9082-4