Abstract
In this paper, we propose a modified proximal point algorithm based on the Thakur iteration process to approximate the common element of the set of solutions of convex minimization problems and the fixed points of two nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings in the framework of \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. We also prove the Δ-convergence of the proposed algorithm. We also provide an application and numerical result based on our proposed algorithm as well as the computational result by comparing our modified iteration with previously known Sahu’s modified iteration.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
In this article, we assume that denotes the set of all positive integers and stands for the set of all real numbers. Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty subset of a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space, \((\mathcal{X}, d)\) and \(\mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\) denote the set all fixed points of a mapping \(\mathcal{T}:\mathcal{C}\rightarrow \mathcal{C}\).
Fixed point theory in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces was introduced by Kirk, afterward it attracted so many researchers of this field and has become a delightful topic of research for the past few years. Kirk proved the existence of a fixed point for a nonexpansive mapping defined on a bounded convex closed subset of a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space (see [23]).
Let \(\zeta :\mathcal{X}\rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be a proper convex function defined on \((\mathcal{X}, d)\). One of the vital problems of optimization is to find the minimizers of convex functional ζ over \(\mathcal{X}\), i.e., find \(\chi ^{*}\in \mathcal{X}\) such that
We denote by \(\mathop{\operatorname{argmin}}_{\varphi \in \mathcal{X }}\zeta (\varphi )\) the set of minimizers of ζ.
In 1970, Martinet [27] initiated the proximal point algorithm (shortly PPA) which is a capable tool for solving this minimization problem, and after that Rockafellar [32] developed the PPA in a Hilbert space and proved that this method converges to a solution of the convex minimization problem. Recently, it has become a fascinating topic to extend the PPA for solving an optimization problem in the setting of manifolds which are an extension of Hilbert, Banach, and linear spaces. For more details on convex optimization and proximal point algorithms, see ([7–9, 13, 15, 35, 38, 41–46]).
In 2013, Bačák [6] introduced the concept of PPA in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces, where the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) is generated as follows:
where \(\nu _{n}>0\). Later, it was proved by Ariza-Ruiz et al. [5] that if ζ has a minimizer and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }\nu _{n}=\infty \), then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) converges to the minimizer of ζ. This tremendous result became the reason for the success of convex analysis in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces during past two decades by fascinating research in this direction.
In 2015, Cholamjiak [11] proposed a modified PPA by using the Halpern iteration procedure in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces, where the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) is generated as follows:
where \(\nu _{n}> 0\), \(\lim_{n\to \infty }\rho _{n}=0\), and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }\rho _{n}=\infty \), and proved that \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) converges to the minimizer.
In the same year, Cholamjiak et al. [12] proposed a modified PPA by adopting the S-iteration procedure in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces, where the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) is generated as follows:
They proved some convergence theorems and showed that the above algorithm converges to the common fixed points of \(\mathcal{T}_{1}\) and \(\mathcal{T}_{2}\) and to the minimizers of a convex function ζ.
In the background of iteration processes, Mann [26], Ishikawa [21], and Halpern [20] are the three basic iterations utilized to approximate the fixed points of a nonexpansive mapping.
After these three basic iterative schemes, several researchers came up with the idea of generalized iterative schemes for the approximation of fixed points of nonlinear mappings. Here, we have a few iterations among the number of new iterative schemes: Noor iteration [28], Agarwal et al. iteration (S-iteration) [3], Abbas and Nazir iteration [2], Thakur’s iteration [39, 40], SP-iteartion [31], M-iteration [26], and so on.
In 2016, Chang et al. [10] established some strong convergence theorems for the PPA with S-iteration process to the common fixed points of asymptotically nonexpansive mappings and to the minimizer of a convex function in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces.
In 2018, Pakkaranang et al. [30] proposed a modified PPA with SP iteration process for three asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces and proved some convergence theorems.
Recently, Sahu et al. [34] introduced a modified PPA based on the S-iterative scheme to approximate a common element of the set of solutions of convex minimization problems and the set of fixed points of nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings in the setting of \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces, where the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) is generated as follows:
Motivated by the above work, we propose a modified PPA based on the Thakur iterative scheme, where the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) is generated as follows:
for all \(n \geq 1\), where \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) are appropriate real sequences in the interval \((0,1)\), and \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) are sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) are proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions. We also prove that the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) Δ-converges to a common element of the set of solutions of convex minimization problems and the set of fixed points of two nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings in the framework of \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. We also provide a numerical example and application to show the efficiency of our main result, and by using MATLAB R2018a, we also add the comparison tables for our proposed iteration and previously known Sahu’s modified iteration process.
2 Preliminaries
In this section, we recall some frequently used lemmas and concepts in our main results. A self-mapping \(\mathcal{T}\) defined on \(\mathcal{C}\) is said to be
-
(i)
nonexpansive if
$$ d(\mathcal{T}\chi , \mathcal{T}\varphi )\leq d(\chi , \varphi ) \quad \text{for all } \chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{C}; $$ -
(ii)
asymptotically nonexpansive [19] if there exists a sequence of real numbers \(\{\Upsilon _{n}\}\) in \([1,\infty )\) with \(\lim_{n\to \infty } \Upsilon _{n} = 1\) such that
$$ d\bigl(\mathcal{T}^{n}\chi , \mathcal{T}^{n}\varphi \bigr)\leq \Upsilon _{n} d( \chi , \varphi ) \quad \text{for all } \chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{C} \text{ and } n\in \mathbb{N}; $$ -
(iii)
nearly uniformly ϒ-Lipschitzian [33] if there exist a fix sequence \(\{a_{n}\}\) in \([0,\infty )\) with \(\lim_{n\to \infty } a_{n} = 0\) and a constant \(\Upsilon _{n} \geq 0\) with \(\Upsilon _{n} \leq \Upsilon \) for some \(\Upsilon \in [0, \infty )\) such that
$$ d\bigl(\mathcal{T}^{n}\chi , \mathcal{T}^{n}\varphi \bigr)\leq \Upsilon d(\chi , \varphi )+a_{n} \quad \text{for all } \chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{C} \text{ and } n\in \mathbb{N}; $$ -
(iv)
nearly asymptotically nonexpansive [33] if there exist \(\Upsilon _{n}\geq 1\) for all \(n\in \mathbb{N}\), \(\lim_{n\to \infty } \Upsilon _{n} = 1\), and a fix sequence \(\{a_{n}\}\) in \([0,\infty )\) with \(\lim_{n\to \infty } a_{n} = 0\) such that
$$ d\bigl(\mathcal{T}^{n}\chi , \mathcal{T}^{n}\varphi \bigr)\leq \Upsilon _{n} d( \chi , \varphi )+a_{n} \quad \text{for all } \chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{C} \text{ and } n \in \mathbb{N}; $$ -
(v)
nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive [1, 36] if there exist \(\Upsilon _{n}\geq 1\) for all \(n\in \mathbb{N}\), \(\lim_{n\to \infty } \Upsilon _{n} = 1\), and a fix sequence \(\{a_{n}\}\) in \([0,\infty )\) with \(\lim_{n\to \infty } a_{n} = 0\) and \(F(\mathcal{T})\neq \emptyset \) such that
$$ d\bigl(\mathcal{T}^{n}\chi , p\bigr)\leq \Upsilon _{n} d(\chi , p)+a_{n} \quad \text{for all } \chi \in \mathcal{C}, p\in F(\mathcal{T}) \text{ and } n\in \mathbb{N}. $$
A metric space \((\mathcal{X}, d)\) is called a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space if it is geodesically connected, and every geodesic triangle in \(\mathcal{X}\) is at least as “thin” as its comparison triangle in the Euclidean plane.
Lemma 2.1
([17])
Let \(\mathcal{X}\) be a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space, \(\chi , \varphi , \varrho \in \mathcal{X}\), and \(t\in [0, 1]\). Then
A geodesic space \(\mathcal{X}\) is a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space if and only if it satisfies the following inequality:
for all \(\chi , \varphi , \varrho \in \mathcal{X}\) and \(t \in [0, 1]\).
Let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a bounded sequence in \(\mathcal{X}\), a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space. For \(\chi \in \mathcal{X}\), set
The asymptotic radius \(r(\{\chi _{n}\})\) is given by
and the asymptotic center \(A(\{\chi _{n}\})\) of \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) is defined as follows:
It is known that if \(\mathcal{C}\) is a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space \(\mathcal{X}\), then \(A(\{\chi _{n}\})\) consists of exactly one point see [16].
In 2008, Kirk and Panyanak [24] gave a concept of convergence in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces which is an analogue of weak convergence in Banach spaces and restriction of Lim’s concepts of convergence [25] to \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces.
A sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) in \(\mathcal{X}\) is said to Δ-converge to \(\chi \in \mathcal{X}\) if χ is the unique asymptotic center for every subsequence \(\{\upsilon _{n}\}\) of \(\{\chi _{n}\}\). In this case, we write \(\Delta -\lim_{n} {\chi _{n}}=\chi \) and read as χ is the Δ-limit of \(\{\chi _{n}\}\).
Lemma 2.2
([16])
Suppose that \((\mathcal{X}, d)\) is a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space. Let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a bounded sequence in \(\mathcal{X}\). If \(A(\{\chi _{n}\}) = \{p\}\), \(\{\upsilon _{n}\}\) is a subsequence of \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) such that \(A(\{\upsilon _{n}\}) = \{\upsilon \}\) and \(d(\chi _{n}, \upsilon )\) converges, then \(p=\upsilon \).
Lemma 2.3
([24])
In a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space, every bounded sequence admits a Δ-convergent subsequence.
Definition 2.1
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space \(\mathcal{X}\) and \(\mathcal{T} : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be a mapping. We say that the mapping \(\mathcal{T}\) satisfies the demiclosedness principle if for any bounded sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) in \(\mathcal{C}\) with \(d(\chi _{n}, \mathcal{T}\chi _{n}) \rightarrow 0\) and for any its Δ-limit, \(\varrho \in \mathcal{C}\), it holds that \(\mathcal{T} \varrho =\varrho \).
Lemma 2.4
([1])
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space \(\mathcal{X}\) and \(\mathcal{T} : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be a uniformly continuous nearly asymptotically nonexpansive mapping. Then \(\mathcal{T}\) satisfies the demiclosedness principle.
Lemma 2.5
([37])
Let \(\mathcal{X}\) be a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space and \(\upsilon \in \mathcal{X}\). Suppose that \(\{t_{n}\}\) is a sequence in \([b, c]\) for some \(b, c \in (0,1)\) and \(\{\chi _{n}\}\), \(\{\varphi _{n}\}\) are sequences in \(\mathcal{X}\) such that \(\limsup_{n\to \infty } d(\chi _{n}, \upsilon )\leq r\), \(\limsup_{n\to \infty } d(\varphi _{n}, \upsilon ) \leq r\), and \(\lim_{n\to \infty } d((1- t_{n})\chi _{n} \oplus t_{n} \varphi _{n}, \upsilon )=r\) for some \(r\geq 0\). Then
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a convex subset of a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space, \(\mathcal{X}\). A function \(\zeta :\mathcal{C}\rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) is said to be convex if, for any geodesic \([\chi , \varphi ]:=\{\varsigma _{\chi , \varphi }(\nu ):0\leq \nu \leq 1\}:=\{\nu \chi \oplus (1-\nu )\varphi :0\leq \nu \leq 1\}\) joining \(\chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{C}\), the function \((\zeta \circ \varsigma )\) is convex, i.e.,
A function ζ defined on \(\mathcal{C}\) is said to be lower continuous at \(\varphi \in \mathcal{C}\) if
and lower semi-continuous on \(\mathcal{C}\) if it is lower semi-continuous at each point of \(\mathcal{C}\).
Let \(\mathcal{X}\) be a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space and \(\zeta : \mathcal{X} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be a proper convex and lower semi-continuous function. The Moreau–Yosida resolvent of ζ in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces is defined as follows:
for all \(\chi \in \mathcal{X}\) and \(\nu > 0\). The mapping \(\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }\) defined above is well defined for all \(\nu > 0\) which is called the proximal operator of ζ with parameter \(\nu > 0\) (see [22]).
Lemma 2.6
([4])
Let \((\mathcal{X}, d)\) be a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space and \(\zeta :\mathcal{C}\rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be a proper convex and lower semi-continuous function. Then, for all \(\chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{X}\) and \(\nu > 0\), the following identity holds:
Lemma 2.7
([22])
Let \((\mathcal{X}, d)\) be a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space and \(\zeta :\mathcal{C}\rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be a proper convex and lower semi-continuous function. Then the following identity holds:
for all \(\chi \in \mathcal{X}\) and \(0<\mu <\nu \).
Lemma 2.8
([5])
Let \((\mathcal{X}, d)\) be a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space and \(\zeta :\mathcal{C}\rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous. Then, for any \(\nu > 0\),
-
(a)
the proximal operator \(\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }\) of ζ is firmly nonexpansive, i.e.,
$$ d\bigl(\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }(\chi ),\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }( \varphi )\bigr) \leq d\bigl((1-t)\chi \oplus t \operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }( \chi ), (1-t) \varphi \oplus t \operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }(\varphi ) \bigr) $$for all \(\chi , \varphi \in \mathcal{X}\) and \(t \in (0, 1)\);
-
(b)
the set \(\mathcal{F}(\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta })\) of fixed points of \(\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta }\) coincides with the set \(\mathop{\operatorname{argmin}}_{\varphi \in \mathcal{X}} \zeta (\varphi )\) of minimizers of ζ.
Remark 1
Every firmly nonexpansive mapping is nonexpansive mapping.
Lemma 2.9
([29])
Let \(\{s_{n}\}\) be the sequences of nonnegative numbers such that
where \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) and \(\{\xi _{n}\}\) are sequences of nonnegative numbers such that \(\varsigma _{n}\subseteq [1, \infty )\) and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(\varsigma _{n}-1)<\infty \) and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(\xi _{n})<\infty \). Then \(\lim_{n\to \infty }s_{n}=0\) exists.
3 Main results
We begin with the following proposition.
Proposition 3.1
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete CAT (0) space \((\mathcal{X},d)\). Let \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, and \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be two uniformly continuous mappings satisfying the following:
-
(a)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings with sequence \(\{(a_{n}, \Upsilon _{n})\}\) such that \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty } a_{n}<\infty \) and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(\Upsilon _{n}-1)<\infty \);
-
(b)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mappings with sequence \(\{(q_{n}, \Gamma )\}\).
Let \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S})\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in \mathcal{C}} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in \mathcal{C}} \tau (\varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in \mathcal{C}\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in \(\mathcal{C}\) defined by (1.1). Then we have the following:
-
(D1)
\(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)\) exists for each \(p \in P\);
-
(D2)
\(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, \mathcal{T}\chi _{n}) =\lim_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, \mathcal{S}\chi _{n})=0\).
Proof
Let \(p\in P\). Then \(p=\mathcal{T}p\) and \(\zeta (p)\leq \zeta (\varphi )\) and \(\tau (p)\leq \tau (\varrho )\) for all \(\varphi , \varrho \in C\). Since, \(\zeta (p)\leq \zeta (\varphi )\), it follows that
for all \(\varphi \in C\) and hence \(p =\operatorname{prox}_{\nu _{n} \zeta } (p)\) for all . Similarly, we have \(p =\operatorname{prox}_{\delta _{n} \tau } (p)\) for all .
First, we prove that \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)\) exists. Note that \(\upsilon _{n} =\operatorname{prox}_{\nu _{n} \zeta } (\omega _{n})\) and \(\omega _{n} =\operatorname{prox}_{\delta _{n} \tau } (\chi _{n})\) for all . By Lemma 2.8, it follows that
and
Hence,
By using the definition of nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mapping and (1.1), we have
Also we have
where . By Lemma 2.9, \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n},p)\) exists.
(ii) Next we will prove that \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, \omega _{n}) = 0\) and \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n},\upsilon _{n}) = 0\). Assume that
for some \(r>0\). By Lemma 2.6, we have
Since \(\tau (p)\leq \tau (\chi _{n})\) for all , it follows that
and
Since \(\zeta (p)\leq \zeta (\omega _{n})\) for all , it follows that
From (3.4), we have
This implies that
By our assumption and taking \(\liminf_{n\rightarrow \infty }\) on both sides, we have
From (3.3), we have \(\limsup_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\varphi _{n}, p)\leq \limsup_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)= r\). Thus,
From (3.3), we also have
By taking \(\liminf_{n\rightarrow \infty }\) on both sides, we have
From (3.2), we have \(\limsup_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\varrho _{n}, p)\leq \limsup_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)= r\). Thus,
From (3.2), this implies that
Using (3.5), (3.9) and our assumptions, we get \(r =\liminf_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)\leq \liminf_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\omega _{n}, p)\), which together with \(\limsup_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\omega _{n}, p)\leq \limsup_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)=r\) gives us that
Hence, from (3.6), we have
From (3.2), we have
Using (3.5) and (3.9), we get \(r =\liminf_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)\leq \liminf_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\upsilon _{n}, p)\), which together with \(\limsup_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\upsilon _{n}, p)\leq \limsup_{n \rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n}, p)=r\) gives us that
Hence, from (3.7), (3.11), and (3.14), we have
From (3.12) and (3.15), we get
From (3.1), we have
where . This implies that
Hence, from (3.5), (3.9) and our assumption, we have
From (3.2), we have
where . This implies that
Hence, from (3.8) and (3.9), we have
By using (3.18), we have
Since \(\mathcal{S}\) and \(\mathcal{T}\) are nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mappings, we obtain
By using (3.21), (3.23), and (3.24), we have
From (3.19), (3.24), (3.25), and (3.26), we have
Using the uniform continuity of \(\mathcal{T}\) in (3.19) and the definition of nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mapping \(\mathcal{T}\) in (3.28), we have \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\mathcal{T}\chi _{n}, \mathcal{T}^{n+1} \chi _{n}) =0\) and \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\mathcal{T}^{n+1}\chi _{n}, \mathcal{T}^{n+1} \chi _{n+1}) =0\).
Using the uniform continuity of \(\mathcal{S}\) in (3.26) and the definition of nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mapping \(\mathcal{S}\) in (3.28), we have \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\mathcal{S}\chi _{n}, \mathcal{S}^{n+1} \chi _{n}) =0\) and \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\mathcal{S}^{n+1}\chi _{n}, \mathcal{S}^{n+1} \chi _{n+1}) =0\).
This completes the proof. □
Now, we are ready to prove the main result.
Theorem 3.1
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete CAT (0) space \((\mathcal{X},d)\). Let \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C } \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, and let \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be uniformly continuous mappings satisfying the following:
-
(a)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings with sequence \(\{(a_{n},\Upsilon _{n})\}\) such that \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty } a_{n}<\infty \) and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(\Upsilon _{n}-1)<\infty \);
-
(b)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mappings with sequence \(\{(q_{n}, \Gamma )\}\).
Let \(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) satisfy the demiclosedness principle and \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S})\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in \mathcal{C}} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in \mathcal{ C}} \tau (\varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in C\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in C defined by (1.1). Then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) Δ-converges to an element of P.
Proof
Since \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\), therefore from Lemma 2.7 and (3.12), (3.15), and (3.16), we have
Proceeding in the same manner as above and using (3.12), we have
Next we show that \(w_{\Delta }(\chi _{n})=\bigcup_{\{\eta _{n}\}\subset \{\chi _{n}\}}A( \{\eta _{n}\})\subset P\). Let \(\eta \in w_{\Delta }(\chi _{n}) \). Then there exists a subsequence \(\{\eta _{n}\}\) of \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) such that \(A(\eta _{n})=\{\eta \}\). Therefore, there exists a subsequence \(\{\vartheta _{n}\}\) of \(\{\eta _{n}\}\) such that \(\Delta -\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }\vartheta _{n} = \vartheta \) for some \(\vartheta \in P\). In view of Proposition 3.1, (3.30), and (3.31), we have \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\vartheta _{n}, \mathcal{T}\vartheta _{n})=0\), \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\vartheta _{n}, \mathcal{S}\vartheta _{n})=0\), \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\operatorname{prox}_{\nu \zeta } \vartheta _{n}, \vartheta _{n})=0\), \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\operatorname{prox}_{\delta \tau } \vartheta _{n}, \vartheta _{n})=0\). Since \(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) satisfy demiclosedness conditions, we have \(\vartheta \in P\). Hence, by Proposition 3.1(a), \(\lim_{n\rightarrow \infty }d(\chi _{n},\vartheta )\) exists, and by Lemma 2.2, we have \(\eta = \vartheta \). This shows that \(w_{\Delta }(\chi _{n})\subset P\). Finally, we show that the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) generated by (1.1) Δ-converges to a point in P. To this end, it suffices to show that \(w_{\Delta }(\chi _{n})\) consists of exactly one point. Let \(\{\eta _{n}\}\) be a subsequence of \(\{\chi _{n}\}\), and let \(A(\{\chi _{n}\}) =\{\chi \}\). Since \(\eta \in w_{\Delta }(\chi _{n})\subset P\) and \(d(\chi _{n}, \eta )\) converges, we have \(\chi =\eta \). Hence \(w_{\Delta }(\chi _{n}) =\{\chi \}\). □
Theorem 3.2
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete CAT (0) space \((\mathcal{X},d)\). Let \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, and let \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} : \mathcal{C }\rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be uniformly continuous nearly asymptotically nonexpansive mappings with sequence \(\{(a_{n},\Upsilon _{n})\}\) such that \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty } a_{n}<\infty \) and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(\Upsilon _{n}-1)<\infty \). Let \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S})\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in \mathcal{C}} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in \mathcal{C}} \tau (\varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in \mathcal{C}\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in \(\mathcal{C}\) defined by (1.1). Then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) Δ-converges to an element of P.
Proof
\(\mathcal{T}\), \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly asymptotically nonexpansive mappings with \(P\neq \emptyset \). This implies that \(\mathcal{T}\), \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings. Set . Then \(\mathcal{S}\) and \(\mathcal{T}\) are nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian. By Lemma 2.5, \(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) satisfy the demiclosedness principle. Therefore, the proof follows from Theorem 3.1. □
Theorem 3.3
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete CAT (0) space \((\mathcal{X},d)\). Let \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C } \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, and let \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be uniformly continuous mappings satisfying the following:
-
(a)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are quasi-nonexpansive mappings:
-
(b)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mappings with sequence \(\{(q_{n}, \Gamma )\}\).
Let the mappings \(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) satisfy the demiclosedness principle and \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S})\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in C} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in C} \tau ( \varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in C\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in \(\mathcal{C}\) defined by (1.1). Then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) Δ-converges to an element of P.
Remark 2
If we take \(\mathcal{T}^{n}=\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}^{n}=\mathcal{S}\), then (1.1) reduces to the following iterative process:
Theorem 3.4
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a complete CAT (0) space \((\mathcal{X},d)\). Let \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, and let \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} : \mathcal{C } \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be nonexpansive mappings with \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S}) \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in \mathcal{C}} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in \mathcal{C}} \tau (\varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in \mathcal{C}\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in \(\mathcal{C}\) defined by (1.1a). Then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) Δ- converges to an element of P.
Remark 3
If we take \(\tau =\zeta =0\) and \(\mathcal{T}=\mathcal{S}\), then (1.1a) reduces to the Thakur iteration process in a \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space studied by Garodia and Uddin [18] for generalized nonexpansive mappings.
Since every Hilbert space is a complete \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) space, we directly obtain the following result.
Corollary 3.1
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a Hilbert space \(\mathcal{X}\). Let \(\zeta , \tau : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions, and let \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} :\mathcal{ C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be uniformly continuous mappings satisfying the following:
-
(a)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings with sequence \(\{(a_{n},\Upsilon _{n})\}\) such that \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty } a_{n}<\infty \) and \(\sum_{n=1}^{\infty }(\Upsilon _{n}-1)<\infty \);
-
(b)
\(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) are nearly uniformly Γ-Lipschitzian mappings with sequence \(\{(q_{n}, \Gamma )\}\).
Let the mappings \(\mathcal{T}\) and \(\mathcal{S}\) satisfy the demiclosedness principle and \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S})\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in \mathcal{C}} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in \mathcal{C}} \tau (\varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in \mathcal{C}\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in \(\mathcal{C}\) defined by
Then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) weakly converges to an element of P.
4 Application
In this section, particularly using Theorem 3.4 in a Hilbert space, we obtain the following.
Theorem 4.1
Let \(\mathcal{C}\) be a nonempty closed convex subset of a Hilbert space, \(\mathcal{X}\). Let \(\zeta ,\tau : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow (-\infty , \infty ]\) be proper convex and lower semi-continuous functions and \(\mathcal{T}, \mathcal{S} : \mathcal{C} \rightarrow \mathcal{C}\) be two nonexpansive mappings with \(P= \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{T})\cap \mathcal{F}(\mathcal{S})\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{ \varphi \in \mathcal{C}} \zeta (\varphi )\cap \operatorname{argmin}_{\varrho \in \mathcal{C}} \tau (\varrho )\neq \emptyset \). Let \(\{\rho _{n}\}\), \(\{\sigma _{n}\}\), and \(\{\varsigma _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0, 1)\) such that \(0 <\rho \leq \rho _{n}\), \(\sigma _{n}, \varsigma _{n}\leq \sigma <1\) for all . Let \(\{\nu _{n}\}\) and \(\{\delta _{n}\}\) be sequences in \((0,\infty )\) such that \(0 <\nu \leq \nu _{n}\) and \(0 <\delta \leq \delta _{n}\) for all . For \(\chi _{1} \in \mathcal{C}\), let \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) be a sequence in \(\mathcal{C}\) defined as follows:
Then the sequence \(\{\chi _{n}\}\) converges to an element of P.
Example 4.1
Let with the Euclidean norm. Define nonexpansive mappings as follows:
and
We define by
where
The functions ζ and τ are proper convex and lower semi-continuous. Hence, from proximity operators in [14], it follows that, for \(\nu , \delta > 0\), we have
and
Note
Algorithm (1.1c) becomes
We choose the particular values of \(\rho _{n}=\sigma _{n}=\varsigma _{n} = 1/2\) and \(\nu _{n} = \delta _{n} = 1\) for all . It can be clearly seen that all the presumptions of Theorem 4.1 are fulfilled. Therefrom, algorithm (4.1) converges to an element of P.
Table 1 shows the computative result for the proposed iteration and Sahu’s iteration with starting point \((-3, 1, 2)\), and it can be seen directly from the table that both iteration processes converge to the point \((-3.5, 0.5, 0)\) of P.
Table 2 shows the computative result for the proposed iteration and Sahu’s iteration with starting point \((3, -1, 2)\), and it can be seen directly that both iteration processes converge to the point \((0.5, -3.5, 0)\) of P.
Table 3 shows the computative result for the proposed iteration and Sahu’s iteration with starting point \((3, 1, -2)\), and it can be seen directly that both iteration processes converge to the point \((-0.5, -2.5, 0)\) of P.
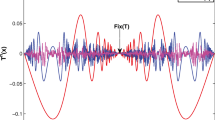
Figures 1, 2, 3 represent the behavior of errors \(E(n) = \|\chi _{n} - \chi _{n+1}\|\) for the proposed iteration and Sahu’s iteration with starting points \((-3, 1, 2)\), \((3, -1, 2)\), and \((3, 1, -2)\).
Remark 4
From data in Tables 1–3, we see that computative results of our proposed iteration process have the lower number of iterations than the modified PPA of Sahu et al. [34], 35% on average. This shows that our proposed iteration has better convergence rate than the modified PPA iteration.
5 Conclusion
The purpose of this paper was to propose a modified proximal point algorithm based on the Thakur iteration process to approximate the common element of the set of solutions of convex minimization problems and the fixed points of two nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings in the framework of \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. We proved the Δ-convergence of the proposed algorithm. We also provided an application and a numerical result based on our proposed algorithm as well as the computational result by comparing our modified iteration with previously known Sahu’s modified iteration.
Availability of data and materials
No data were used to support this study.
References
Abbas, M., Kadelburg, Z., Sahu, D.R.: Fixed point theorems for Lipschitzian type mappings in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. Math. Comput. Model. 55, 1418–1427 (2012)
Abbas, M., Nazir, T.: A new faster iteration process applied to constrained minimization and feasibility problems. Mat. Vesn. 66, 223–234 (2014)
Agarwal, R.P., O’Regan, D., Sahu, D.R.: Iterative construction of fixed points of nearly asymptotically nonexpansive mappings. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 8, 61–79 (2007)
Ambrosio, L., Gigli, N., Savare, G.: Gradient Flows in Metric Spaces and in the Space of Probability Measures, 2nd edn. Lectures in Mathematics ETH Zurich. Birkhäuser, Basel (2008)
Ariza-Ruiz, D., Leustean, L., Lopez, G.: Firmly nonexpansive mappings in classes of geodesic spaces. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 366, 4299–4322 (2014)
Bačák, M.: The proximal point algorithm in metric spaces. Isr. J. Math. 194, 689–701 (2013)
Bnouhachem, A., Qin, X.: An inertial proximal Peaceman–Rachford splitting method with SQP regularization for convex programming. J. Nonlinear Funct. Anal. 2020, Article ID 50 (2020)
Ceng, L.C., Petrusel, A., Yao, J.C., Yao, Y.: Hybrid viscosity extragradient method for systems of variational inequalities, fixed points of nonexpansive mappings, zero points of accretive operators in Banach spaces. Fixed Point Theory 19, 487–502 (2018)
Ceng, L.C., Petrusel, A., Yao, J.C., Yao, Y.: Systems of variational inequalities with hierarchical variational inequality constraints for Lipschitzian pseudocontractions. Fixed Point Theory 20, 113–133 (2019)
Cheng, S.S., Yao, J.C., Wang, L., Qin, L.J.: Some convergence theorems involving proximal point and common fixed points for asymptotically nonexpansive mappings in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2016, 68 (2016)
Cholamjiak, P.: The modified proximal point algorithm in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. Optim. Lett. 9, 1401–1410 (2015)
Cholamjiak, P., Abdou, A.A., Cho, Y.J.: Proximal point algorithms involving fixed points of nonexpansive mappings in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2015, 227 (2015)
Cohen, E., Sabach, S., Teboulle, M.: Non-Euclidean proximal methods for convex-concave saddle-point problems. J. Appl. Numer. Optim. 3, 43–60 (2021)
Combettes, P.L., Pesquet, J.C.: Proximal splitting methods in signal processing: fixed-point algorithms for inverse problems in science and engineering. Springer Optim. Appl. 49, 185–212 (2011)
Dadashi, V., Postolache, M.: Hybrid proximal point algorithm and applications to equilibrium problems and convex programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 174(2), 518–529 (2017)
Dhompongsa, S., Kirk, W.A., Panyanak, B.: Nonexpansive set-valued mappings in metric and Banach spaces. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 8, 35–45 (2007)
Dhompongsa, S., Panyanak, B.: On Δ-convergence theorems in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. Comput. Math. Appl. 56, 2572–2579 (2008)
Garodia, G., Uddin, I.: Some convergence results for generalized nonexpansive mappings in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces. Commun. Korean Math. Soc. 34(1), 253–265 (2019)
Goebel, K., Kirk, W.A.: A fixed point theorem for asymptotically nonexpansive mappings. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 35, 171–174 (1972)
Halpern, B.: Fixed points of nonexpanding maps. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 73, 957–961 (1967)
Ishikawa, S.: Fixed points by a new iteration method. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 44(1), 147–150 (1974)
Jost, J.: Convex functionals and generalized harmonic maps into spaces of nonpositive curvature. Comment. Math. Helv. 70, 659–673 (1995)
Kirk, W.A.: Geodesic Geometry and Fixed Point Theory, Seminar of Mathematical Analysis, Malaga, Seville, 2002–2003, Colec. Abierta, vol. 64, pp. 195–225. Univ. Sevilla Seer. Publ., Seville (2003)
Kirk, W.A., Panyanak, B.: A concept of convergence in geodesic spaces. Nonlinear Anal. 68, 3689–3696 (2008)
Lim, T.C.: Remarks on some fixed point theorems. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 60, 179–182 (1976)
Mann, W.R.: Mean value methods in iteration. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 4, 506–510 (1953)
Martinet, B.: Réularisation d’inéquations variationnelles par approximations successives (French). Rev. Fr. Inf. Rech. Opér. 4, 154–158 (1970)
Noor, M.A.: New approximation schemes for general variational inequalities. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 251, 217–229 (2000)
Osilike, M.O., Aniagbosor, S.C.: Weak and strong convergence theorems for fixed points of asymptotically nonexpansive mappings. Math. Comput. Model. 32, 1181–1191 (2000)
Pakkaranang, N., Kumam, P., Cho, Y.J.: Proximal point algorithms for solving convex minimization problem and common fixed points problem of asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings in \(\operatorname{CAT}(0)\) spaces with convergence analysis. Numer. Algorithms 78, 827–845 (2018)
Phuengrattana, W., Suantai, S.: On the rate of convergence of Mann, Ishikawa, Noor and SP-iterations for continuous functions on an arbitrary interval. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235(9), 3006–3014 (2011)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithm. SIAM J. Control Optim. 14, 877–898 (1976)
Sahu, D.R.: Fixed points of demicontinuous nearly Lipschitzian mappings in Banach spaces. Comment. Math. Univ. Carol. 46(4), 653–666 (2005)
Sahu, D.R., Kumar, A., Kang, S.M.: Proximal point algorithms based on S-iterative technique for nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings and applications. Numer. Algorithms (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11075-020-00945-2
Sahu, D.R., Pitea, A., Verma, M.: A new iteration technique for nonlinear operators as concerns convex programming and feasibility problems. Numer. Algorithms 83(2), 421–449 (2020)
Sahu, D.R., Yao, J.C.: A generalized hybrid steepest descent method and applications. J. Nonlinear Var. Anal. 1(1), 111–126 (2017)
Schu, J.: Weak and strong convergence to fixed points of asymptotically nonexpansive mappings. Bull. Aust. Math. Soc. 43(1), 153–159 (1991)
Shimizu, K., Hishinuma, K., Iiduka, H.: Parallel computing proximal method for nonsmooth convex optimization with fixed point constraints of quasi-nonexpansive mappings. Appl. Set-Valued Anal. Optim. 2, 1–17 (2020)
Thakur, B.S., Thakur, D., Postolache, M.: A new iteration scheme for approximating fixed points of nonexpansive mappings. Filomat 30(10), 2711–2720 (2016)
Thakur, B.S., Thakur, D., Postolache, M.: A new iterative scheme for numerical reckoning fixed points of Suzuki’s generalized nonexpansive mappings. Appl. Math. Comput. 275, 147–155 (2016)
Usurelu, G.I., Bejenaru, A., Postolache, M.: Operators with property (E) as concerns numerical analysis and visualization. Numer. Funct. Anal. Optim. 41(11), 1398–1411 (2020)
Usurelu, G.I., Postolache, M.: Convergence analysis for a three-step Thakur iteration for Suzuki-type nonexpansive mappings with visualization. Symmetry 11(12), 1441 (2019)
Wang, X., Ou, X., Zhang, T., Chen, J.: An alternate minimization method beyond positive definite proximal regularization: convergence and complexity. J. Nonlinear Var. Anal. 3, 333–355 (2019)
Yao, Y., Leng, L., Postolache, M., Zheng, X.: Mann-type iteration method for solving the split common fixed point problem. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 18, 875–882 (2017)
Yao, Y., Postolache, M., Yao, J.C.: Iterative algorithms for generalized variational inequalities. UPB Sci. Bull., Ser. A 81, 3–16 (2019)
Yao, Y., Postolache, M., Yao, J.C.: An iterative algorithm for solving the generalized variational inequalities and fixed points problems. Mathematics 7, Article ID 61 (2019)
Acknowledgements
Authors are very thankful to the learned referees for pointing out many omissions and for their valuable comments. The first author is grateful to University Grants Commission, India, for providing financial assistance in the form of Senior Research Fellowship.
Funding
No funding availability.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally and significantly in writing this paper. All authors have read and agreed to the revised version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Khatoon, S., Cholamjiak, W. & Uddin, I. A modified proximal point algorithm involving nearly asymptotically quasi-nonexpansive mappings. J Inequal Appl 2021, 83 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13660-021-02618-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13660-021-02618-7