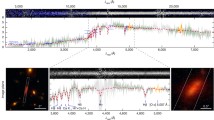
Abstract—Using the MaNGaL tunable-filter photometer at the 2.5-m telescope of the Caucasian Mountain Observatory of the Sternberg Astronomical Institute of Lomonosov Moscow State University, we studied star formation in an early-type gas-rich galaxy, which was until now considered to be elliptical,—NGC 5173. The gas has probably been accreted in the recent past by the galaxy from a direction inclined to its disk. Star formation that we observe now has led in the past 400 Myr to the formation of compact massive clusters with shock excitation of gas around them—a star formation behavior corresponding to what is usually observed in the interacting Antennae-like galaxies. In combination with the almost solar metallicity of the gas, this allows us to conclude that NGC 5173 has assimilate a very gas-rich companion with a mass of at least 10–20% of its own stellar mass.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Alatalo, T. A. Davis, M. Bureau, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 432 (3), 1796 (2013).
M. G. Allen, B. A. Groves, M. A. Dopita, et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 178 (1), 20 (2008).
P. Anders, N. Bissantz, L. Boysen, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 377 (1), 91 (2007).
J. A. Baldwin, M. M. Phillips, and R. Terlevich, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 93, 5 (1981).
L. Binette, C. G. Magris, G. Stasińska, and A. G. Bruzual, Astron. and Astrophys. 292, 13 (1994).
R. J. Buta,MonthlyNotices Royal Astron. Soc. 488 (1), 590 (2019).
D. Calzetti, Star Formation Rate Indicators, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2013).
M. Cappellari, E. Emsellem, D. Krajnović, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 413 (2), 813 (2011).
B. Catinella, A. Saintonge, S. Janowiecki, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 476 (1), 875 (2018).
R. Cid Fernandes, G. Stasińska, A. Mateus, and N. Vale Asari, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 413 (3), 1687 (2011).
T. A. Davis, K. Alatalo, M. Sarzi, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 417 (2), 882 (2011).
E. Emsellem, M. Cappellari, D. Krajnović, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 414 (2), 888 (2011).
G. Fasano, B. M. Poggianti, W. J. Couch, et al., Astrophys. J. 542 (2), 673 (2000).
K. C. Freeman, Astrophys. J. 160, 811 (1970).
E. P. Hubble, Realm of the Nebulae (Yale University Press, New Haven, 1936).
S. Janowiecki, B. Catinella, L. Cortese, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 493 (2), 1982 (2020).
S. J. Kannappan and D. G. Fabricant, Astron. J. 121 (1), 140 (2001).
G. Kauffmann, T. M. Heckman, C. Tremonti, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 346 (4), 1055 (2003).
R. C. Kennicutt, Jr., Annual Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 36, 189 (1998).
R. C. Kennicutt and N. J. Evans, Annual Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 50, 531 (2012).
L. J. Kewley, M. A. Dopita, R. S. Sutherland, et al., Astrophys. J. 556 (1), 121 (2001).
G. R. Knapp and E. Raimond, Astron. and Astrophys. 138, 77 (1984).
E. A. D. Lacerda, R. Cid Fernandes, G. S. Couto, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 474 (3), 3727 (2018).
S. S. Larsen, Astron. and Astrophys. 494 (2), 539 (2009).
J. C. Lee, A. Gil de Paz, C. Tremonti, et al., Astrophys. J. 706 (1), 599 (2009).
C. Leitherer, D. Schaerer, J. D. Goldader, et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 123 (1), 3 (1999).
R. A. Marino, F. F. Rosales-Ortega, S. F. Sánchez, et al., Astron. and Astrophys. 559, A114 (2013).
A. Moiseev, A. Perepelitsyn, and D. Oparin, Experimental Astronomy 50 (2–3), 199 (2020).
A. Naim, O. Lahav, R. J. Buta, et al.,Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 274 (4), 1107 (1995).
D. E. Osterbrock, Astrophysics of gaseous nebulae and active galactic nuclei (University Science Books, Herndon, 1989).
M. Pettini and B. E. J. Pagel, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 348 (3), L59 (2004).
A. Rest, F. C. van den Bosch, W. Jaffe, et al., Astron. J. 121 (5), 2431 (2001).
H. Salo, E. Laurikainen, J. Laine, et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. 219 (1), 4 (2015).
P. Serra, T. Oosterloo, R. Morganti, et al., Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 422 (3), 1835 (2012).
N. Shatsky, A. Belinski, A. Dodin, et al., in Proc. All-Russian Conf. on Ground-Based Astronomy in Russia. 21st Century, Nizhny Arkhyz, Russia, 2020 Ed. by I. I. Romanyuk, I. A. Yakunin, A. F. Valeev, and D. O. Kudryavtsev, (Spec. Astrophys. Obs. Russian Acad. Sci., Nizhnij Arkhyz, 2020), pp. 127–132 (2020).
K. Sheth, M. Regan, J. L. Hinz, et al., Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 122 (898), 1397 (2010).
O. K. Silchenko and V. L. Afanasiev, Astronomy Reports 52 (11), 875 (2008).
O. K. Sil’chenko, A. V. Moiseev, and O. V. Egorov, Astrophys. J. Suppl. 244 (1), 6 (2019).
J. W. Sulentic, L. Verdes-Montenegro, G. Bergond, et al., Astron. and Astrophys. 449 (3), 937 (2006).
L. J. Tacconi, R. Genzel, and A. Sternberg, Annual Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 58, 157 (2020).
J. P. Vader and L. Vigroux, Astron. and Astrophys. 246, 32 (1991).
V. V. Vlasyuk and O. K. Sil’chenko, Astron. and Astrophys. 354, 28 (2000).
T. Wiklind, F. Combes, and C. Henkel, Astron. and Astrophys. 297, 643 (1995).
T. Wiklind, F. Combes, C. Henkel, and F. Wyrowski Astron. and Astrophys. 323, 727 (1997).
M. K. Yıldız, P. Serra, R. F. Peletier, et al., Monthl Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 464 (1), 329 (2017).
L. M. Young, P. Serra, D. Krajnović, and P.-A. Duc, Monthly Notices Royal Astron. Soc. 477 (2), 2741 (2018).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We express our gratitude to the anonymous referee, whose attentive reading of the paper made it possible to significantly improve the presentation of our results. In our work we used the data of the NED Extragalactic Database (NASA/IPAC), which is operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory and California Institute of Technology under contract with NASA. Our results are based on the Hubble Space Telescope public data taken from the Hubble Legacy Archive (collaboration of the Telescope Science Institute, the Space Telescope European Coordinating Facility and Canadian Astronomy Data Centre), and data from the GALEX space telescope (NASA Galaxy Evolution Explorer), operated by the California Institute of Technology under contract with NASA number NAS5-98034. The GALEX data are taken from the MAST public archive (Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes) which is supported by the NASA Space Office under the grant NNX13AC07G and other grants. We also used the data from the SDSS-III survey. (http://www.sdss3.org/), which is supported by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation and the Association of Universities.
Funding
We are grateful to the Interdisciplinary Scientific and Educational School of the Moscow State University “Fundamental and Applied space exploration” for the support of our study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Translated by A. Potapova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sil’chenko, O.K., Proshina, I.S., Moiseev, A.V. et al. Star Formation in the Elliptical (?) Galaxy NGC 5173. Astrophys. Bull. 77, 40–50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341322010102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990341322010102