Abstract
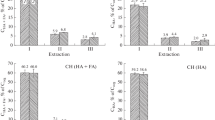
Chernozem humic acid (HA) fractions with nominal molecular sizes (MS) >100, 30–100, 5–30 and <5 kDa were obtained, using a combination of low-pressure preparative size exclusion chromatography with analytical polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis or multistep ultrafiltration. The initial HA and fractions were tested for the ability to destroy model aromatic compounds 2,4,6-trimethylphenol and furfurol in aqueous solution when illuminated with polychromatic light in the range 300–450 nm under laboratory conditions. It has been found that chernozem HA fractions with MS less than 5 kDa had the maximum ability to decompose the above-mentioned substances, while fractions with MS above 30 kDa practically did not perform this function. The data obtained allow us to explain partially the mechanisms of the photoinduced transformation of many organic pollutants by soil humic substances.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. N. Drozdova, S. V. Patsaeva, and D. A. Khundzhua, “Fluorescence of dissolved organic matter as a marker for distribution of desalinated waters in the Kara Sea and bays of Novaya Zemlya archipelago,” Oceanology (Engl. Transl.) 57, 41–47 (2017).
M. M. Kononova, Soil Organic Matter (Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Moscow, 1963) [in Russian].
I. V. Sokolova and O. N. Chaikovskaya, “Effect of humic acids on photoprocesses in aqueous media,” Vestn. Tomsk. Gos. Pedagog. Univ. 78, 42–46 (2008).
O. A. Trubetskoi, D. V. Demin, and O. E. Trubetskaya, “Fluorescent properties of low-molecular-weight fractions from chernozem humic acids,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 46, 1020–1025 (2013).
O. A. Trubetskoi and O. E. Trubetskaya, “Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography of the stable electrophoretic fractions of soil humic acids,” Eurasian Soil Sci. 48, 148–156 (2015).
J. J. Alberts and M. Takacs, “Total luminescence spectra of IHSS standard and reference fulvic acids, humic acids and natural organic matter: comparison of aquatic and terrestrial source terms,” Org. Geochem. 35, 243–256 (2004).
C. Belin, C. Quellec, M. Lamotte, M. Ewald, and Ph. Simon, “Characterization by fluorescence of the dissolved organic matter in natural water: application to fractions obtained by tangential ultrafiltration and XAD resin isolation,” Environ. Technol. 14, 1131–1144 (1993).
E. S. Boyle, N. Guerriero, A. Thiallet, R. D. Vecchio, and N. V. Blough, “Optical properties of humic substances and CDOM: relation to structure,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 2262–2268 (2009).
S. Canonica, B. Hellrung, and J. Wirz, “Oxidation of phenols by triplet aromatic ketones in aqueous solution,” J. Phys. Chem. A 104, 1226–1232 (2000).
S. Canonica, B. Hellrung, P. Müller, and J. Wirz, “Aqueous oxidation of phenylurea herbicides by triplet aromatic ketones,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 6636–6641 (2006).
J. Dahlén, S. Bertilsson, and C. Pettersson, “Effects of UV-A irradiation on dissolved organic matter in humic surface waters,” Environ. Int. 22, 501–506 (1996).
H. Gao and R. G. Zepp, “Factors influencing photoreactions of dissolved organic matter in a coastal river of the southeastern United States,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 2940–2946 (1998).
W. R. Haag and J. Hoigne, “Singlet oxygen in surface waters. 3. Photochemical formation and steady-state concentrations in various types of waters,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 341–348 (1986).
J. T. Jasper, M. T. Nguyen, Z. L. Jones, N. S. Ismail, D. L. Sedlak, J. O. Sharp, R. G. Luthy, A. J. Horne, and K. L. Nelson, “Unit process wetlands for removal of trace organic contaminants and pathogens from municipal wastewater effluents,” Environ. Eng. Sci. 30, 421–436 (2013).
K. Kadir and K. L. Nelson, “Sunlight mediated inactivation mechanisms of Enterococcus faecalis and Escherichia coli in clear water versus waste stabilization pond water,” Water Res. 50, 307–317 (2014).
G. McKay, K. D. Couch, S. P. Mezyk, and F. L. Rosario-Ortiz, “Investigation of the coupled effects of molecular weight and charge-transfer interactions on the optical and photochemical properties of dissolved organic matter,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 50, 8093–8102 (2016).
P. Schmitt-Kopplin, N. Hetkorn, H.-R. Shulten, and A. Kettrup, “Structural changes in dissolved soil humic acid during photochemical degradation processes under O2 and N2 atmosphere,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 2531–2541 (1998).
O. Trubetskaya, L. Shaloiko, D. Demin, V. Marchenkov, I. Proskuryakov, C. Coelho, and O. Trubetskoj, “Combining electrophoresis with detection under ultraviolet light and multiple ultrafiltration for isolation of humic fluorescence fractions,” Anal. Chim. Acta 690, 263–268 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.02.016
O. A. Trubetskoj, O. E. Trubetskaya, G. V. Afanas’eva, O. I. Reznikova, and C. Saiz-Jimenez, “Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of soil humic acid fractionated by size exclusion chromatography and ultrafiltration,” J. Chromatogr. A 767, 285–292 (1997).
O. A. Trubetskoj, C. Richard, G. Voyard, V. V. Marchenkov, and O. E. Trubetskaya, “Molecular size distribution of fluorophores in aquatic natural organic matter: application of HPSEC with multi-wavelength absorption and fluorescence detection following LPSEC-PAGE fractionation,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 52, 5287–5295 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03924
J. Wenk, M. Aeschbacher, M. Sander, U. von Gunten, and S. Canonica, “Photosensitizing and inhibitory effects of ozonated dissolved organic matter on triplet-induced contaminant transformation,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 8541–8549 (2015).
R. G. Zepp, P. F. Schlotzhauer, and R. M. Sink, “Photosensitized transformations involving electronic energy transfer in natural waters: role of humic substances,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 74–81 (1985).
Funding
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, project nos. 18-016-00078-a and 19-05-00056-a.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by T. Chicheva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trubetskoi, O.A., Patsaeva, S.V. & Trubetskaya, O.E. Photochemical Degradation of Organic Pollutants in Solutions of Soil Humic Acids. Eurasian Soil Sc. 52, 1075–1080 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229319090102
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064229319090102