Abstract
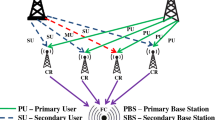
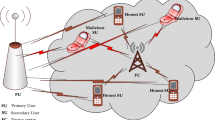
A two-level learned distributed networking (LDN) structure that uses existing machine learning (ML) algorithms and the novel Optimized Extreme Learning Machine (OELM) algorithm to perform intelligent spectrum sensing for 5G systems has been proposed and implemented. This novel technique uses input vectors like received signal strength indicator, the distance between Cognitive Radio users and gateways, and energy vectors to train the model. Extreme Learning Machine optimized by BAT algorithm outperforms the existing Machine Learning techniques in terms of detection accuracy, false alarm, detection probability and cross validation curves at different SNR scenarios.









Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. Haykin, IEEE J. Sel. Areas in Commun. 23, 2 (2005).
Y. Chen and H. Oh, IEEE Commun. Surv. & Tut. 18, 1 (2016).
J. Mitola and G. Q. Maguire, IEEE Pers. Commun. 6, 4 (1999)
M. Agiwal, A. Roy, and N. Saxena, IEEE Commun. Surv. & Tut. 18, 3 (2016).
C. Jiang, H. Zhang, Y. Ren, Z. Han, K. Chen, and L. Hanzo, IEEE Wireless Commun. 24, 2 (2017).
M. Shafi and A.F. Molisch, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 35, 6 (2017).
R. Li and Z. Zhao, IEEE Wireless Commun. 24, 5 (2017).
N. Abbas, Y. Nasser, and K. E. Ahmad, Eur. J. Wireless Commun. & Netw. 174, (2015).
W. Wang, A. Kwasinski, D. Niyato, and Z. Han, IEEE Commun. Sur. & Tut. 18, 3 (2016).
Y. Zhang, F. Tian, B. Song, and X. Du, IEEE Wireless Commun. 23, 4 (2016).
Y. Zhang, B. Song, S. Gao, X. Du, and M. Guizani, IEEE Access 6, (2018).
S. Lall, A. K. Sadhu, A. Konar, K. K. Mallik, and S. Ghosh, “Multi-agent reinfocement learning for stochastic power management in cognitive radio network,” in Proc. Int. Conf. on Microelectronics, Computing and Communications, (MicroCom), Durgapur, Jan. 23–25, 2016, (MicroCom), pp. 1–6.
S. Tubachi, M. Venkatesan, and A. V. Kulkarni, “Predictive learning model in cognitive radio using reinforcement learning,” in IEEE Int. Conf. Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering, Chennai, 2017 (IEEE, New York, 2017), pp. 564– 567.
M. H. Ling and K. A. Yau, IEEE Trans. Cog. Commun. Netw. 5, 1 (2019).
Z. Li, W. Wu, X. Liu, and P. Qi, IET Commun. 12, 19 (2018).
K. M. Thilina and K. W. Choi, IEEE J. on Sel. Areas Commun. 31, 11 (2013).
J. Tian, IEEE Trans. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 68, 11 (2019).
M. K. Giri and S. Majumder, “Extreme learning machine based cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks,” in Proc. 7th Int. Conf. on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 2020 (SPIN, 2020).
K. W. Choi, E. Hossain, and D. I. Kim, IEEE Trans. on Wireless Commun. 10, 6 (2011).
G.-B. Huang, Q.-Y. Zhu, and C.-K. Siew, NeuroComputing 70, 1 (2006).
G.-B. Huang, Z. Bai, L. L. C. Kasun, and C. M. Vong, IEEE Comp. Intel. Mag. 10, 2 (2015).
I. Chaturvedi and E. Ragusa, J. Frank. Inst. 355, 4 (2018).
A. M. A. Sattar, Ö. F. Ertugrul, and B. Gharabaghi, Neural Comp. App. 31, 1 (2019).
V. Christou, M. G. Tsipouras, and N. Giannakea, Neurocomputing 361, 10 (2019).
L. Y. Chong, T. S. Ong, and A. B. J. Teoh, Applied Soft Comp. 75, (2019).
B. Adarsh, T. Raghunathan, and T. Jayabarathi, Energy 96, 666 (2016).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the help given by the lab staff at the Department of ECE, Indira Gandhi Delhi Technical University for solving any software and system malfunctions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kansal, P., Kumar, A. & Gangadharappa, M. Optimized Extreme Learning Machine for Intelligent Spectrum Sensing in 5G systems. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 66, 322–332 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064226921040045
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1064226921040045