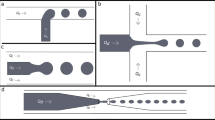
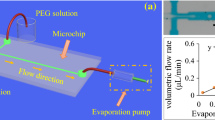
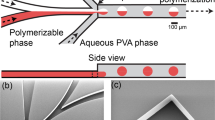
Abstract
Monodisperse polymeric particles have great potential in biomedical and physical applications. Modern high-throughput droplet microfluidic technologies make it possible to produce monodisperse water-in-oil macroemulsions with desired properties. Polymerization in a macroemulsion transforms it to a suspension of microparticles. These particles may be viewed as containers for targeted delivery of drugs and also as bioink for 3D printing of tissues and organs. Conditions for formation of PEGDA and polyacrylamide particles using a microfluidic flow-focusing emulsion generator have been studied. Manufactured microparticles have been characterized by their geometrical sizes and mechanical properties. In addition, the diffusion escape of small molecules from microparticles has been studied using Rhodamine B fluorescent dye.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Choi, K. D. Seo, D. W. Kim, B. C. Kim, and D. S. Kim, Lab Chip 17, 591 (2017). doi 10.1039/C6LC01023G
L. Mazutis, R. Vasiliauskas, and D. A. Weitz, Macromol. Biosci. 15, 1641 (2015). doi 10.1002/mabi.201570046
R. Zilionis, J. Nainys, A. Veres, V. Savova, D. Zemmour, A. M. Klein, and L. Mazutis, Nat. Protoc. 12, 44 (2017). doi 10.1038/nprot.2016.154
H. Hwang, S.-H. Kim, and S.-M. Yang, Lab. Chip 11, 87 (2011). doi 10.1039/C0LC00125B
R. K. Gao, Z. Y. Cheng, A. J. Demello, and J. Choo, Lab. Chip 16, 1022 (2016). doi 10.1039/C5LC01249J
Z. Zhu, W. Zhang, X. Leng, M. Zhang, Z. Guan, J. Lu, and C. J. Yang, Lab. Chip 12, 3907 (2012). doi 10.1039/C2LC40461C
W. Jiang, M. Li, Z. Chen, and K. W. Leong, Lab. Chip 16, 4482 (2016). doi 10.1039/c6lc01193d
N. Shembekar, C. Chaipan, R. Utharalaa, and C. A. Merten, Lab. Chip 16, 1314 (2016). doi 10.1039/C6LC00249H
J. F. Huggett, S. Cowen, and C. A. Foy, Clin. Chem. 61, 79 (2015). doi 10.1373/clinchem.2014.221366
J. H. Kim, T. Y. Jeon, T. M. Choi, T. S. Shim, S.-H. Kim, and S.-M. Yang, Langmuir 30, 1473 (2014). doi 10.1021/la403220p
S.-S. Liu, C.-F. Wang, X.-Q. Wang, J. Zhang, Y. Tian, S.-N. Yin, and S. Chen, J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 9431 (2014). doi 10.1039/C4TC01631A
T. Nisisako, H. Suzuki, and T. Hatsuzawa, Micromachines 6, 1435 (2015). doi 10.3390/mi6101428
Y. Geng, J. Noh, I. Drevensek-Olenik, R. Rupp, G. Lenzini, and J. P. F. Lagerwall, Sci. Rep. 6, 26840 (2016). doi 10.1038/srep26840
R. K. Vadivelu, H. Kamble, M. J. A. Shiddiky, and N.-T. Nguyen, Micromachines 8, 94 (2017). doi 10.3390/mi8040094
C. A. DeForest, B. D. Polizzotti, and K. S. Anseth, Nat. Mater. 8, 659 (2009). doi 10.1038/nmat2473
I. V. Kukhtevich, Ya. S. Posmitnaya, K. I. Belousov, A. S. Bukatin, and A. A. Evstrapov, Nauchn. Priborostr. 25 (3), 65 (2015).
T. Cubaud and T. G. Mason, Phys. Fluids 20, 053302 (2008). doi 10.1063/1.2911716
A. S. Bukatin, I. S. Mukhin, E. I. Malyshev, I. V. Kukhtevich, A. A. Evstrapov, M. V. Dubina, Tech. Phys. 61, 1566 (2016).
N. A. Filatov, D. V. Nozdriukhin, and A. S. Bukatin, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 917, 042024 (2017). doi 10.1088/1742-6596/917/4/042024
P. Gonzalez-Tello, F. Camacho, and G. Blazquez, J. Chem. Eng. Data 39, 611 (1994). doi 10.1021/je00015a050
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by grant no. MK-2131.2017.4 of the President of the Russian Federation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by V. Isaakyan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nozdriukhin, D.V., Filatov, N.A., Evstrapov, A.A. et al. Formation of Polyacrylamide and PEGDA Hydrogel Particles in a Microfluidic Flow Focusing Droplet Generator. Tech. Phys. 63, 1328–1333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784218090141
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784218090141