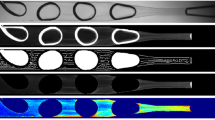
Abstract
Some hydromechanical aspects of the generation of a dispersed gas phase by the electrochemical method and with tubular microfiltration membranes under the action of liquid phase inertia and the hindered motion of gas particles in the gravity field are considered as they apply to microflotation. Experimentally verified equations for calculating the average diameter of spherical gas bubbles and the velocity of their hindered motion are proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elektroflotatsionnaya tekhnologiya ochistki stochnykh vod promyshlennykh predpriyatii (Electroflotation Technology of Industrial Wastewater Treatment), Kolesnikov, V.A., Ed., Moscow: Khimiya, 2007.
Rodrigues, R.T. and Rubio, J., New basis for measuring the size distribution of bubbles, Miner. Eng., 2003, vol. 16, pp. 757–765.
Yoon, R.-H., Microbubble flotation, Miner. Eng., 1993, vol. 6, pp. 619–630.
Kukizaki, M. and Goto, M., Spontaneous formation behavior of uniform-sized microbubbles from Shirasuporous-glass (SPG) membranes in the absence of water-phase flow, Colloids Surf., A, 2006, vol. 296, pp. 174–181.
Trushin, A.M., Dmitriev, E.A., and Akimov, V.V., Mechanics of the formation of microbubbles in gas dispersion through the pores of microfiltration membranes, Theor. Found. Chem. Eng., 2011, vol. 45, pp. 26–32.
Kukizaki, M. and Goto, M., Size control of nanobubbles generated from Shirasu-porous-glass (SPG) membranes, J. Membr. Sci., 2006, vol. 281, pp. 386–396.
Schröder, V., Behrend, O., and Schubert, H., Production of emulsions using microporous ceramic membranes, Colloids Surf., A, 1999, vol. 152, pp. 103–109.
Rulev, N.N., Collective velocity of bubbles floating up, Kolloidn. Zh., 1977, vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 80–86.
Deryagin, B.V., Dukhin, S.S., and Rulev, N.N., Mikroflotatsiya: Vodoochistka, obogashchenie (Microflotation: Water Purification and Enrichment Processes), Moscow: Khimiya, 1986.
Marrucci, G., Rising velocity of a swarm of spherical bubbles, Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam., 1965, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 224–225.
Coulson, J.M., Richardson, J.F., Backhurst, J.R., and Harker, J.H., Coulson and Richardson’s Chemical Engineering, vol. 2: Particle Technology and Separation Processes, Oxford: Butterworth–Heinemann, 1991.
Trushin, A.M., Dmitriev, E.A., Nosyrev, M.A., Tarasova, T.A., and Kuznetsova, I.K., Determining the velocity of the hindered motion of spherical gas particles through liquid in a gravity field, Theor. Found. Chem. Eng., 2013, vol. 47, pp. 368–374.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.A. Dmitriev, V.A. Kolesnikov, A.M. Trushin, V.A. Brodskii, R.B. Komlyashev, 2015, published in Teoreticheskie Osnovy Khimicheskoi Tekhnologii, 2015, Vol. 49, No. 5, pp. 489–495.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dmitriev, E.A., Kolesnikov, V.A., Trushin, A.M. et al. Some hydromechanical aspects of microflotation. Theor Found Chem Eng 49, 585–591 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579515050218
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0040579515050218