Abstract
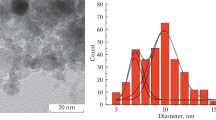
Nickel oxide nanoparticles are synthesized for the first time by spraying of high-purity nickel in the oxygen plasma of a low-pressure arc discharge. The structure, morphology, and optical and magnetic properties of the NiO nanoparticles are studied by various techniques. X-ray diffraction data and processing X-ray diffraction patterns by the Rietveld method show that the nanoparticles have a cubic lattice and are 13 nm in size. Transmission electron microscopy images show that the NiO nanoparticles are characterized by a narrow particle-size distribution, from 5 to 25 nm. The band gap of NiO determined from its optical absorption spectrum is 3.21 eV. Based on the experimental data and their analysis, possible scopes of application of the prepared material as magnetic recording devices are suggested.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
D. Lisjak and A. Mertelj, “Anisotropic magnetic nanoparticles: a review of their properties, syntheses and potential applications,” Progr. Mater. Sci. 95, 286–328 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.03.003
X. Fuku, N. Matinise, M. Masikini, K. Kasinathan, and M. Maaza, “An electrochemically active green synthesized polycrystalline NiO/MgO catalyst: use in photo-catalytic applications,” Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 457–465 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.09.022
A. Kumar Rai, Anh L. Tuan, C.-J. Park, and J. Kim, “Electrochemical study of NiO nanoparticles electrode for application in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries” Ceram. Intern. 39 (6), 6611–6618 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.01.097
R. M. Silva, R. A. Raimundo, W. V. Fernandes et al., “Proteic sol-gel synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Ni/NiO core–shell powders,” Ceram. Intern. 44, (6), 6152–6156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.248
Y. Bi, A. Nautiyal, H. Zhang, et al., “One-pot microwave synthesis of NiO/MnO2 composite as a high-performance electrode material for supercapacitors, “Electrochim. Acta 260, 952–958 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.12.074
S. Senobari and A. Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, “A comprehensive study on the enhanced photocatalytic activity of CuO–NiO nanoparticles: designing the experiments,” J. Mol. Liq. 261, 208–217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.04.028
S. Mørup, D. E. Madsen, C. Frandsen, et al., “Experimental and theoretical studies of nanoparticles of antiferromagnetic materials,” J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 19, 213202 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/19/21/213202
A. V. Ushakov, I. V. Karpov, and A. A. Lepeshev, “Peculiarities of magnetic behavior of CuO nanoparticles produced by plasma-arc synthesis in a wide temperature range,” J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 30 (12), 3351–3354 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4311-2
I. V. Karpov, A. V. Ushakov, V. G. Demin, et al., “Investigation of the residual stresses effect on the magnetic properties of CuO nanoparticles synthesized in a low-pressure arc discharge plasma,” J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 490, 165492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165492
E. Winkler, R. D. Zysler, M. Vasquez Mansilla, et al., “Surface anisotropy effects in NiO nanoparticles,” Phys. Rev. B 72, 132409 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.132409
M. Tadić, M. Panjan, D. Marković, et al., “Unusual magnetic properties of NiO nanoparticles embedded in a silica matrix,” J. Alloys Compd. 509 (25), 7134–7138 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2011.04.032
S. D. Tiwari and K. P. Rajeev, “Signatures of spin-glass freezing in NiO nanoparticles,” Phys. Rev. B 72, 104433 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.104433
M. Tadic, D. Nikolic, M. Panjan, et al., “Magnetic properties of NiO (nickel oxide) nanoparticles: Blocking temperature and Neel temperature,” J. Alloys Compd. 647, 1061–1068 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.06.027
I. V. Karpov, A. V. Ushakov, A. A. Lepeshev, et al., “Plasma-chemical reactor based on a low-pressure pulsed arc discharge for synthesis of nanopowders,” Techn. Phys. 62 (1), 168–173 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S106378421701011X
A. V. Ushakov, I. V. Karpov, and A. A. Lepeshev, “Influence of the oxygen concentration on the formation of crystalline phases of TiO2 during the low-pressure arc-discharge plasma synthesis,” Techn. Phys. 61 (2), 260–264 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063784216020262
A. A. Lepeshev, O. A. Bayukov, E. A. Rozhkova, et al., “Modification of the phase composition and structure of the quasicrystalline Al–Cu–Fe alloy prepared by plasma spraying,” Phys. Solid State. 57 (2), 255–259 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063783415020249
J. Tauc, Optical Properties of Solids (Academic Press Inc., New York, 1966).
M. Alagiri, S. Ponnusamy, and C. Muthamizhchelvan, “Synthesis and characterization of NiO nanoparticles by sol-gel method,” J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electronics 23 (3), 728–732 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-011-0479-6
X. G. Zheng, C. N. Xu, K. Nishikubo, et al., “Finite-size effect on Néel temperature in antiferromagnetic nanoparticles,” Phys. Rev. B 72, 014464 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.72.014464
M. Asharf Shah and M. S. Al-Ghamd, “Preparation of copper (Cu) and copper oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles under supercritical conditions,” Mater. Sci. Appl. 2, 977 (2011). https://doi.org/10.4236/msa.2011.28131
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, the Government of Krasnoyarsk Territory, the Territory Science Foundation, and OOO Seismiklab in terms of project no. 20-48-242904.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by N. Kolchugina
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ushakov, A.V., Karpov, I.V., Fedorov, L.Y. et al. Magnetic State of the Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles Formed in Low-Pressure Arc Discharge Plasma. Russ. Metall. 2021, 1656–1660 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029521130346
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029521130346