Abstract
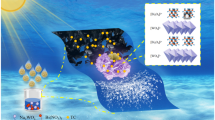
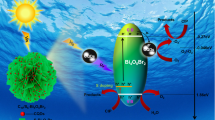
Magnetic BiOCl flowers were fabricated using a one-pot hydrothermal process by self-assemble of BiOCl nanosheets on magnetic carbon nanodots (MCDs) Bi25FeO40–g-C3N4. The photodegradation activities of the heterojunctions were detected for Tetracycline hydrochloride (TC) as antibiotic target pollutant. The degradation rate of ternary junction was detected to be 6.5 times faster than bare BiOCl. The attractive performance mainly attributed to synergistic effects resulting from the formation of n–p–n heterojunction, especially MCDs can not only provide the high specific surface area, but suppress the recombination of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. Trapping experiments approve that h+ and \( \bullet {\kern 1pt} {\text{OH}}\) radicals were the major reactive species, meanwhile \( \bullet {\kern 1pt} {\text{O}}_{2}^{ - }\) radicals also involved in the process of TC photodegradation on BiFeCN catalysts, therefore a possible z-scheme reaction mechanism was proposed correspondingly.











Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
J. Davies and D. Davies, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 74, 417 (2010).
G. L. French, Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 36, S3 (2010).
K. Kümmerer, Chemosphere 75, 417 (2009).
R. Hirsch et al., Sci. Total Environ. 225, 108 (1999).
Z. Wang, C. Li, and K. Domen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 219 (2019).
Z. Zhang, L. Bai, Z. Li, et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 1879 (2019).
Q. Zhang, G. Ying, C. Pan, et al., Environ. Sci. Technol. 49, 6772 (2015).
M. A. Oturan and J. Aaron, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44, 2577 (2014).
C. Xu, P. Ravi Anusuyadevi, C. Aymonier, et al., Chem. Soc. Rev. 48, 3392 (2019).
S. Sun, X. Yu, Q. Yang, et al., Nanoscale Adv. 1, 34 (2019).
R. He, Sh. Cao, P. Zhou, and J. Yu, Chin. J. Catal. 35, 989 (2014).
Ruiping Li et al., Catal. Commun. 106, 1 (2017).
T. L. Silva, J. Clean. Prod. 171, 482 (2017).
X. Wu, N. Liu, M. Wang, et al., ACS Nano 13, 13109 (2019).
J. Yang, T. Xie, Q. Zhu, et al., J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 2579 (2020).
L. Ye, Y. Su, X. Jin, et al., Environ. Sci.: Nano 1, 90 (2014).
J. Henle, P. Simon, A. Frenzel, et al., Chem. Mater. 19, 366 (2007).
H. Cheng, B. Huang, and Y. Dai, Nanoscale 6, 29 (2014).
X. Zhang, Z. Ai, F. Jia, and L. Zhang, J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 747 (2008).
An Huizhong et al., Rare Met. 3, 243 (2008).
X. Wu, N. Liu, M. Wang, et al., ACS Nano 13, 13109 (2019).
Q. Ji, Z. Xu, W. Xiang, et al., Chemosphere 253, 126751 (2020).
J. Huang, W. Chen, X. Yu, et al., Colloids Surf., A 597, 124758 (2020).
X. Tang, H. Liu, C. Yang, et al., Colloids Surf., A 599, 124880 (2020).
S. Bao, H. Liang, C. Li, and J. Bai, J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 397, 112590 (2020).
X. Qu, M. Liu, Z. Gao, et al., Appl. Surf. Sci. 506, 144688 (2020).
C. Tan, G. Zhu, M. Hojamberdiev, et al., J. Clust. Sci. 24, 1115 (2013).
Jingyi Bai et al., Curr. Nanosci. 11, 186 (2015).
T. Xie, L. Xu, C. Liu, et al., J. Dalton Trans. 43, 2211 (2014).
Shan Feng et al., J. Nanopart. Res. 19, 33 (2017).
W. Ma, L. Chen, Y. Zhu, et al., Colloids Surf., A 508, 135 (2016).
Y. Ni, D. Shi, B. Luo, et al., Inorg. Chem. 58, 6966 (2019).
M. A. Basith, R. Ahsan, I. Zarin, and M. A. Jalil, Sci. Rep. 8 (2018).
G. Tan, Y. Zheng, H. Miao, et al., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 280 (2012).
W. Ong, L. Tan, Y. H. Ng, et al., Chem. Rev. 116, 7159 (2016).
T. Wang, and A. T. An, J. Mater. Chem. A 8, 485 (2020).
W. Guo, K. Fan, J. Zhang, and C. Xu, Appl. Surf. Sci. 447, 125 (2018).
J. Di, J. Xia, S. Yin, et al., J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 5340 (2014).
J. Zhu, Y. Shen, X. Yu, et al., J. Alloys Compd. 771, 309 (2019).
L. Ren, S. Y. Lu, J. Z. Fang, et al., Catal. Today 281, 656 (2017).
A. Kumar, A. Kumar, G. Sharma, et al., Chem. Eng. J. 334, 462 (2018).
Liangliang Chu, F. Duo, M. Zhang, et al., Colloids Surf. 589, 124416 (2020).
S. Huang, J. Zhong, J. Li, et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 84, 65 (2016).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The work was financially supported by Shandong Natural Science Foundation of China (ZR2020MB032), Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students in Shandong Province (S202010449058) and Binzhou University (BZXYL1801, BZXYLG2019) research Funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zhang, H., Bian, H. et al. BiOCl Flower Photocatalyst Heterostructured with Magnetic Carbon Nanodots Bi25FeO40–g-C3N4 for Visible-Light-Driven Efficient Photodegradation of Tetracycline Hydrochloride. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 96, 1340–1347 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024422060061
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036024422060061