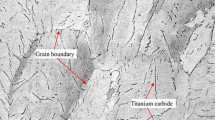
Abstract
In this paper, the commercial finite element code LS-DYNA is employed to simulate the process of a certain kind of a linear shaped charge jet penetrating into a TC4 (Ti–6Al–4V) titanium alloy plate of moderate thickness. The fracture profiles agree well with experimental observations, which confirms the validity of the code and the Johnson–Cook material model applied to describe the TC4 plate. The fracture pattern of the plate is drawn based on this comparison.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. L. Feng, M. B. Liu, H. Q. Li, and G. R. Liu, “Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Modeling of Linear Shaped Charge with Jet Formation and Penetration Effects,” Computers Fluids 86, 77–85 (2013).
C. Yu, Y. Tong, C. Yan, et al., “Applied Research of Shaped Charge Technology,” Int. J. Impact Eng. 23 (1), 981–988 (1999).
J. F. Molinari, “Finite Element Simulation of Shaped Charges,” Finite Elements in Analysis and Design. 38 (10), 921–936 (2002).
S. Lim, “Steady State Equation of Motion of a Linear Shaped Charges Liner,” Int. J. Impact Eng. 44, 10–16 (2012).
M. Johnston and S. Lim, “Numerical Observation of the Jet Flight Patterns of Linear Shaped Charges,” Appl. Sci. 2 (3), 629 (2012).
R. Cornish, J. T. Mills, J. P. Curtis, and D. Finch, “Degradation Mechanisms in Shaped Charge Jet Penetration,” Int. J. Impact Eng. 26, 105–114 (2001).
J. K. Yi, X. Q. Jiang, and H. Peng, “Effect of Initiation Ways on Jet Formation of Linear Shaped Charge,” Chin. J. Explos. Propel. 29 (3), 57–61 (2006).
O. Ayisit, “The Influence of Asymmetries in Shaped Charge Performance,” Int. J. Impact Eng. 35 (12), 1399–1404 (2008).
Q. Ning, X. Fang, and M. X.Wang, “Effect of Asymmetry on Linear Shaped Charge (in Chinese),” J. Ballistics 23 (2), 96–100 (2011).
Y. H. Cui, W. Q. Wan, Q. Tian, X. S. Tang, and Z. W. Deng, “Optimization Design of Linear Shaped Charge,” Initiators Pyrotech. 15 (4), 42–46 (2006).
W. A. Gooch, M. S. Burkins, W. P. Walters, A. A. Kozhushko, and A. B. Sinani, “Target Strength Effect on Penetration by Shaped Charge Jets,” Int. J. Impact Eng. 26, 243–248 (2001).
H. Y. Ma, Y. Long, and Y. Y. He, “Numerical Analysis on Effects of Burst Height on Penetration Depth of LSCC,” Initiators Pyrotech. 17 (4), 28–32 (2008).
G. Yang, X. Han, and D. Hu, “Computer Simulation of Two-Dimensional Linear-Shaped Charge Jet Using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics,” Eng. Comput. 28 (1), 58–75 (2011).
M. B. Liu, G. R. Liu, K. Y. Lam, and Z. Zong, “Meshfree Particle Simulation of the Detonation Process for High Explosives in Shaped Charge Unlined Cavity Configurations,” Shock Waves 12 (6), 509–520 (2003).
H. F. Qiang, K. P. Wang, and W. R. Gao, “Numerical Simulation of Shaped Charge Jet Using Multi-Phase SPH Method,” J. Tianjin Univ. 14 (1), 495–499 (2008).
S. Z. Zhang, Explosion and Impact Dynamics (The Publ. House of Ordnance Indust., Beijing, 1993) [in Chinese].
L. L. Wang, Foundations of Stress Waves (Elsevier, Oxford, 2007).
G. Kay, “Failure Modeling of Titanium-61–4V and 2024-T3 Aluminum with the Johnson–Cook Material Model,” Tech. Report (Lawrence Livermore Nat. Lab., Livermore, 2002).
J. O. Hallquist, LS-DYNA Keyword User’s Manual (Version 970) (Livermore Software Technol. Corp., California, 2003).
J. O. Hallquist, LS-DYNA Theoretical Manual (Livermore Software Technol. Corp., California, 1998).
M. J. Mullin and B. J. O’Toole, “Simulation of Energy Absorbing Materials in Blast Loaded Structures,” in 8th Int. LS-DYNA Users Conf. (Michigan, 2004).
D. R. Lesuer, “Experimental Investigations of Material Models for Ti–6Al–4V Titanium and 2024-T3 Aluminum,” Tech. Report (Lawrence Livermore Nat. Lab., 1999).
S. R. Yun, Explosion Mechanics (National Defend Industry Press, Beijing, 2005) [in Chinese].
Z. X. Huang, Theory and Practice of Shaped Charge, (Beijing Inst. Technol. Press, Beijing, 2014) [in Chinese].
P. A. Du Bois, S. Kolling, M. Feucht, A. Haufe, and A. G. DaimlerChrysler, “A Comparative Review of Damage and Failure Models and a Tabulated Generalization,” in 6th European LS-DYNA User’s Conf. (Gothenburg, Sweden, 2007).
M. Lobdell, B. Croop, and H. Lobo, “Comparison of Crash Models for Ductile Plastics,” in 10th European LS-DYNA User’s Conf. (Würzburg, Germany, 2015).
“Viscoplastic Strain Rate Formulation (VP),” in LSDYNA Support, http://www.dynasupport.com/howtos/ material/viscoplastic-strain-rate-formulation-vp.
M. Storheim and J. Amdahl, “On the Sensitivity to Work Hardening and Strain-Rate Effects in Nonlinear FEM Analysis of Ship Collisions,” Ships Offshore Structures (2015); DOI: 10.1080/17445302.2015.1115181.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © D.-Zh. Lyu, W.-R. Hong, M.-Ch. Yuan, H.-J. Xuan
Published in Fizika Goreniya i Vzryva, Vol. 53, No. 3, pp. 129–137, May–June, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyu, DZ., Hong, WR., Yuan, MC. et al. Spallation affected fracture pattern of a titanium alloy plate subjected to linear shaped charge jet penetration. Combust Explos Shock Waves 53, 362–369 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508217030169
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0010508217030169